ОБЩЕСТВЕННОЕ ЗДОРОВЬЕ И ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ
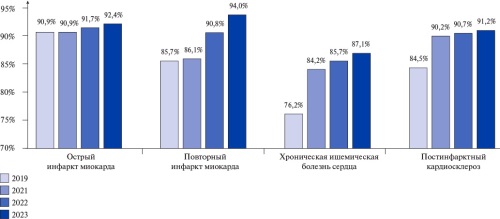
A serious barrier to the widespread practical implementation of evidence therapy for cardiovascular diseases is financial constraints, which exacerbate low patient complience and affect inequality in cardiovascular health indicators population, increasing morbidity and mortality. At the level of healthcare systems in different countries, drug provision is recognized as an effective tool for increasing patient adherence to treatment and improving clinical outcomes. The problematic article discusses the preferential drug program within the federal project for control of cardiovascular diseases. The key principles for forming priority groups, mechanisms and stages of program implementation are outlined. Monitoring the program’s effectiveness made it possible to identify reserves and prospects for its further strategic development.
ОЦЕНКА РИСКА
- Coronary artery tortuosity may indicate concomitant vasculopathy and microvascular ischemia.
- Coronary artery tortuosity correlated with the time of hypertension manifestation.
- The risk factors for coronary artery tortuosity were age, body mass index, diabetes/impaired glucose tolerance, and prior myocardial infarction.
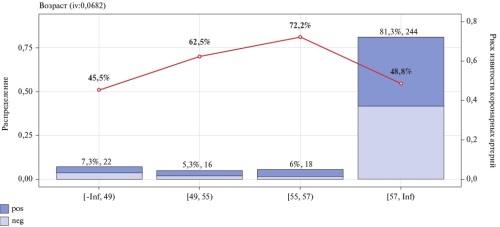
Aim. To study the relationship between hypertension (HTN) and coronary artery tortuosity (CAT), as well as to determine the predictors of coronary artery tortuosity (CAT).
Material and methods. In this retrospective, non-randomized, uncontrolled study, 296 patients with coronary artery disease were examined, including 148 with and 148 without CAT according to coronary angiography.
Results. CAT in patients correlated with the age of manifestation — 0,154 (p=0,008) and the duration of HTN — 0,148 (p=0,011). Logistic regression revealed the following factors influencing CAT: age of HTN manifestation (odds ratio (OR) 4,9, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1,4-20,3), body mass index (OR 4,3, 95% CI: 1,8-11,4), HTN duration (OR 4,4, 95% CI: 2,0-9,9), diabetes/impaired glucose tolerance (OR 4,6, 95% CI: 1,1-19,5) and a prior myocardial infarction (OR 3,1, 95% CI: 1,3-8,7).
Conclusion. The duration and age of HTN manifestation correlated with CAT presence, while age, body mass index, diabetes, and myocardial infarction were risk factors for tortuosity development.
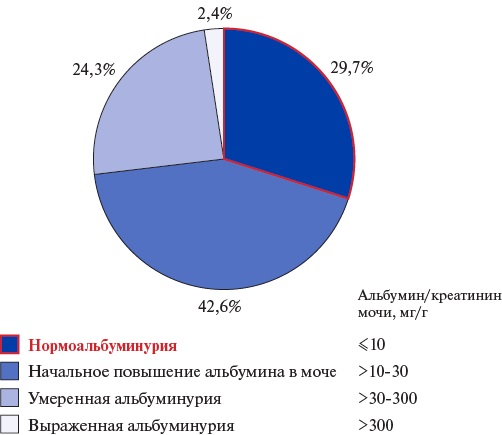
- Increased albuminuria (usually mild or moderate) is detected in 3/4 of patients with multifocal atherosclerosis.
- Even a single assessment of albuminuria can make a significant contribution to the risk stratification of cardiovascular events and bleeding in patients with coronary and peripheral artery disease.
- A predictor of the listed complications is albuminuria >10,6 mg/g (regardless of the glomerular filtration rate); in real-world practice, a formal cutoff value >10 mg/g can be used.
- The most unfavorable prognosis is characterized by patients with a simultaneous increase in albuminuria and von Willebrand factor activity (which probably reflects severe endothelial dysfunction).
Aim. To assess the significance of albuminuria in predicting prognosis-determining events (cardiovascular (CVEs) and hemorrhagic events) in patients with multifocal atherosclerosis, including in comparison with the generally accepted endothelial dysfunction laboratory marker — von Willebrand factor (VWF).
Material and methods. The study included participants of the single-center prospective registry REGATA-1 with coronary and peripheral artery disease. The albumin-to-creatinine ratio in a single morning urine sample and plasma VWF activity were determined. The primary endpoint was the sum of following prognosis-determining events: myocardial infarction, unstable angina, stroke, transient ischemic attack, peripheral artery disease, amputation, major/clinically significant bleeding (BARC 2-5).
Results. A total of 148 patients were included (median age 66 [65; 67] years, 79,1% men). An increase in the urine albumin level (at least mild, >10 mg/g) was detected in 71,3% of patients.
Median follow-up duration was 17 [15; 20] months; 7 CVEs and 18 BARC 2-3 bleedings were registered. ROC analysis revealed the albuminuria cutoff point of 10,6 mg/g, values above which are associated with an increase in the rate of prognosis-determining events. These events were registered in 4,5% of patients with albuminuria <10,6 mg/g and in 21,9% of patients with higher values (plog-rank=0,007).
According to multivariate analysis, the odds ratio (OR) was 5,5 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1,23-24,72), p=0,026. When analyzing secondary endpoints, a trend towards an increase in the risk of CVEs (p=0,065) and hemorrhagic events (p=0,05) was noted. In this cohort, no association was demonstrated between the glomerular filtration rate and the risk of prognosis-determining events.
The cutoff point for VWF was 157%. The incidence of prognosis-determining events was significantly higher in individuals with elevated VWF (23,0% vs 10,8%, p=0,048). In multivariate analysis, VWF lost its significance (OR 2,18; 95% CI 0,84-5,65; p=0,11). In 31,2% of patients, there was a simultaneous increase in albuminuria and VWF, and in this subgroup every third person had prognosis-determining events; in multivariate analysis, the OR was 3,53 (95% CI 1,31-9,49), p=0,012. The combined marker is associated with an increased risk of hemorrhagic events (p=0,006) and CVEs (p=0,027).
Conclusion. In patients with multifocal atherosclerosis, albuminuria >10,6 mg/g is an independent (including from the estimated glomerular filtration rate) predictor of CVEs and hemorrhagic events. The most unfavorable prognosis is in patients with a combination of albuminuria >10,6 mg/g and EF >157%.
What is already known about the subject?
- The use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICD) is contraindicated in cases of high one-year death risk.
- There are no generally accepted tools for stratifying such risk in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
What might this study?
- For the first time in Russia, an algorithm for assessing the risk of death from cardiovascular events in patients with HFrEF in the first year after ICD implantation has been proposed.
How might this impact on clinical practice?
- The developed prognostic index can be used to develop a personalized strategy for interventional primary prevention of sudden cardiac death.
Aim. To develop criteria for predicting one-year mortality in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) after cardioverter defibrillator implantation for sudden cardiac death primary prevention.
Material and methods. The full study protocol was completed by 451 patients with HFrEF referred for cardioverter defibrillator implantation for primary prevention of sudden cardiac death. The study participants underwent preimplantation clinical and paraclinical screening, as well as 12-month prospective follow-up to assess one-year mortality due to cardiovascular events. To solve the problem, training and test samples were formed.
Results. One-year mortality due to cardiovascular events in the training group were registered in 35 patients (11%). Univariate analysis identified 6 factors with the highest prognostic potential (p<0,1) associated with the studied endpoint. These included clinical data (history of hypertension and/or obesity), echocardiographic (left ventricular ejection fraction <25%, eccentric left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy) and laboratory parameters (glomerular filtration rate <60 ml/min/1,73 m2, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide >2000 pg/ml). Based on the regression coefficients, each factor was assigned points, the sum of which determined the original lethal risk index (LRI) value. LRI >3 allow predicting the one-year cardiovascular death probability in patients with heart failure with a sensitivity of 85,7% and a specificity of 76,8%. LRI in patients of the test sample demonstrated very good quality of the model in predicting the risk of one-year cardiovascular mortality (AUC 0,852±0,069 with 95% confidence interval: 0,716-0,988; p=0,0001).
Conclusion. Based on the obtained data, a LRI was developed, the practical application of which is aimed at improving the provision of health care and developing a risk-oriented strategy for managing patients with HFrEF.
- Patients with coronary artery disease living in the Far North are characterized by more frequent and complex coronary involvement.
- The detection rate of coronary chronic total occlusion in the Far North reached 50,3%, which corresponds to the upper range limit described in the literature, despite the younger age of patients.
- Living in extreme natural and climatic conditions was an independent predictor of coronary chronic total occlusion during coronary angiography.
Aim. To study the relationship between coronary chronic total occlusion (CTO) and living in extreme natural and climatic conditions of the Far North in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
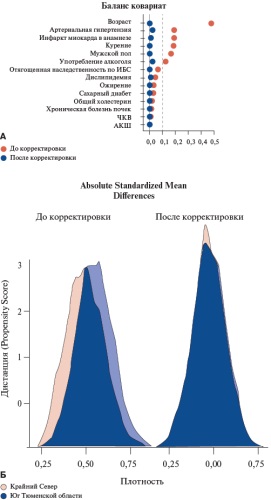
Material and methods. A total of 5679 patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) were selected from the "Registry of Coronary Angiography Operations". The main group consisted of 2588 non-native residents of the Far North, while the comparison group — 3091 patients living in the south of the Tyumen Oblast. CTO was defined as the absence of antegrade coronary flow for more than 3 months according to the medical history or previous coronary angiography. In order to eliminate the initial imbalance between the study groups, the propensity score matching method was used.
Results. Patients living in the Far North were younger (53,2±7,49 years vs 56,8±8,34 years, p<0,001), and were more often men. After propensity score matching, in groups balanced by the main risk factors for CAD, Far North patients were more likely to have significant coronary atherosclerosis. At the same time, CTO was significantly more often determined in patients permanently residing in the Far North (50,3% vs 41,7%, p<0,001). In patients of the main group, CTO was more often located in the proximal (35,0% vs 29,0%, p<0,001) and middle coronary segments (39,0% vs 33,0%, p<0,001) in comparison with the group of the South of the Tyumen Region. The most frequent occlusion location was determined in the anterior descending artery (22,0% vs 17,0%, p<0,001) and the right coronary artery (28,0% vs 24,0%, p=0,001). According to multivariate analysis, residence in the Far North was associated with an increase in detection rate of CTO during coronary angiography by 39% (odds ratio 1,39; 95% confidence interval: 1,25-1,54; p<0,001).
Conclusion. CTO is more common in patients with CAD living in the Far North compared to patients living in the South of the Tyumen Region. According to multivariate analysis, living in extreme natural and climatic conditions was an independent predictor of CTO according to coronary angiography.
PROGNOSIS AND DIAGNOSTICS
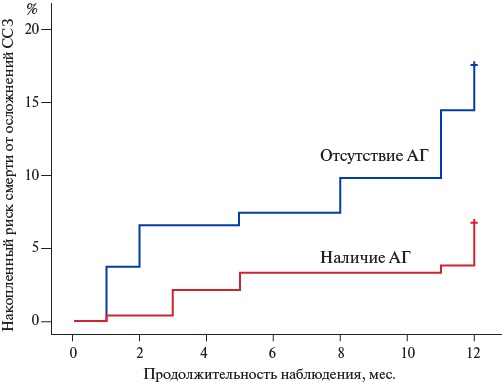
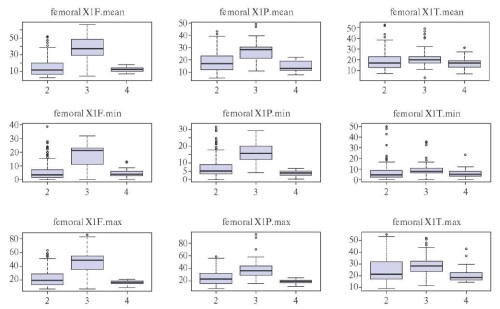
- The prognostic model of post-hospital outcome of lower limb deep vein thrombosis should take into account the stiffness of thrombus proximal part according to shear wave elastography.
- The probability of post-hospital death from deep vein thrombosis increases with coronary artery disease, cancer and stroke, femoral vein rethrombosis — against the background of injuries, surgery and prior venous thromboembolism.
Aim. To assess the prognostic value of shear wave elastography parameters in lower limb deep vein thrombosis for remote outcomes, taking into account comorbidities, and to propose a program for individual assessment of the probability of post-hospital one-year outcomes.
Material and methods. Duplex scanning of lower limb veins supplemented by two-dimensional shear wave elastography was performed in 153 patients with iliac and femoral vein thrombosis using an Aixplorer ultrasound system (Supersonic Imagine, France) on the first, third, and sixth days of hospitalization. Post-hospital outcomes were recorded for 6-12 months after discharge. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify the most significant variables for adverse outcomes (recanalization, rethrombosis, and death). Using these variables, we developed a program for assessing the probability of post-hospital one-year outcomes of lower limb deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Results. Multifold cross-validation showed that 13 following variables were significant for predicting post-hospital outcomes of iliac vein thrombosis: average, maximum, and minimum Young’s moduli of iliac and femoral vein thrombi on the first day of hospitalization; period from the symptoms’ onset to hospitalization; length of thrombus floating apex; concomitant diseases (stroke, coronary artery disease (CAD), cancer, previous venous thromboembolic events, recent injuries or surgery before DVT). In femoral vein thrombosis, 14 following variables were significant: on the first day of hospitalization, the average Young’s moduli of thrombi in the femoral, popliteal, and posterior tibial veins; the maximum Young’s moduli of thrombus in the femoral and popliteal veins; the presence and severity of pulmonary embolism; surgical treatment of DVT; period from the symptoms’ onset of to hospitalization; concomitant diseases (stroke, coronary artery disease, cancer, prior venous thromboembolic events, recent injuries or surgery before DVT).
Conclusion. The death probability within a year after discharge from the hospital in patients with proximal lower limb DVT increases with stroke, coronary artery disease, and cancer, while the probability of rethrombosis — with injuries, surgery, and prior venous thromboembolism. The ultrasound marker of rethrombosis was determined by the increased average Young’s modulus of the proximal venous thrombus part, while recanalization — by the maximum Young’s modulus of the femoral vein thrombus on the first day of hospitalization.
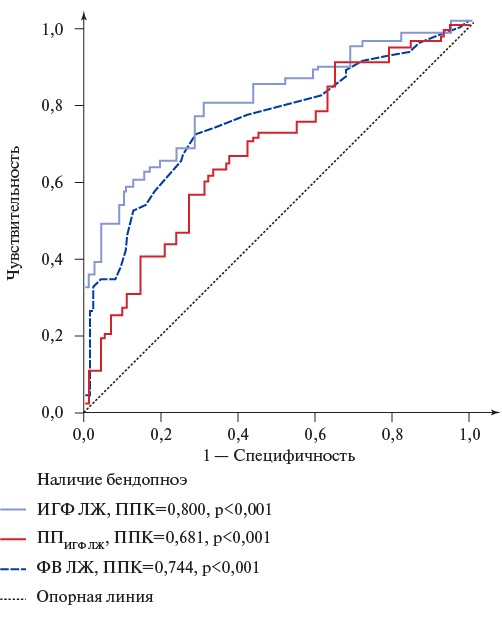
- Left ventricular (LV) global function index (LVGFI), LVGFI companion (LVGFIС) and bendopnea reflect the severity of clinical condition and LV myocardial remodeling in outpatients with heart failure (HF).
- The presence of bendopnea with low LVGFI and high LVGFIС values indicates a high death risk in the group of elderly outpatients with HF.
- Evaluation of LVGFI, LVGFIС and bendopnea in routine clinical practice allows identifying outpatients with HF and an unfavorable prognosis.
Aim. To assess the relationship and prognostic potential of left ventricular (LV) global function index (LVGFI) companion (LVGFIC) and bendopnea in outpatients aged 60 years and older with heart failure (HF).
Material and methods. The study included 134 outpatients (men, 46%) aged 74 (68-79) years with HF class II-IV. Depending on bendopnea, two following groups were identified: the main group — 62 patients with bendopnea; the comparison group — 72 patients without bendopnea. The follow-up period was 27 (22-36) months.
Results. The median LVGFI and LVGFIC were 21,4 (18,1-24,1)% and 297,8 (252,5-362,2) ml, respectively. The threshold value of LVGFI and LVGFIC for predicting bendopnea were ≤21,4% and ≥298,8 ml, respectively. The threshold value of LVGFI and LVGFIC for predicting death were ≤19,6% and ≥334,7 ml, respectively. Survival in the main group was lower (79,0%) than in the control one (93,1%) (Log-rank, p=0,005). Based on the LVGFI, LVGFIC, bendopnea and mortality analysis, two following risk groups for fatal outcome in patients with HF were identified: final group (FG) 1 and FG2. The probability of fatal outcome in FG1is more than 5 times higher than in FG2 (odds ratio 5,83, p<0,05).
Conclusion. Bendopnea was detected in 46,3% of patients and is most likely with LVGFI ≤21,4% and LVGFIС ≥298,8 ml. The presence of bendopnea with LVGFI ≤19,6% and LVGFIС ≥334,7 ml can predict fatal outcome with high probability in the group of elderly patients with HF. The obtained data indicate the role of LVGFI, LVGFIC and bendopnea as markers of the clinical condition severity, pronounced LV myocardial remodeling and an unfavorable prognosis in outpatients aged 60 years and older with HF.
- Cardiac involvement with wall thickening, atrial fibrillation, atrial tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, atrioventricular conduction abnormalities, and small vessel involvement are common in patients with Fabry disease, which can lead to dangerous complications such as heart failure, sudden death.
- Cardiac involvement in patients with Fabry disease can easily lead to confusion with patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and other infiltrative cardiac diseases.
- Patients with cardiovascular disease of unknown cause, such as left ventricular wall thickening and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction, especially with renal and/or neurological damage before age 50, should be screened for Fabry disease.
- Patients with proven Fabry disease require a thorough cardiovascular evaluation for timely diagnosis and prevention of complications.
Aim. Retrospective analysis of cardiovascular involvement in a patient with Fabry disease.
Material and methods. This retrospective assessment included 34 cases of Fabry disease (men, 64,7%). The median age of Fabry patients was 43,5 (32,8; 57) years.
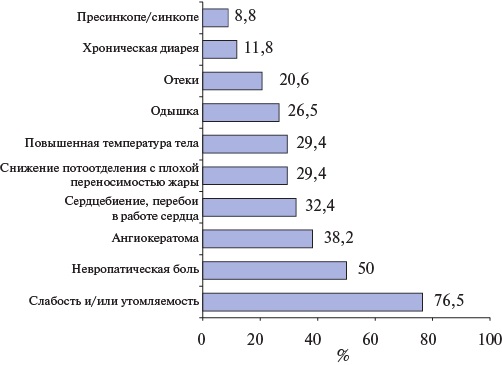
Results. Cardiac involvement was detected in 70,6% of patients. Acute cerebro-vascular events were noted in 23,5% of patients aged 32,5 (25,3; 51,5) years. Kidney damage was detected in 82,4% of patients, while hemodialysis was performed in 14,7% of patients. Among 24 patients with Fabry disease with cardiac damage, heart failure was diagnosed in 37,5% of patients. Simpson’s left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) was 60 (52,6; 66,7)%. LVEF >50% was detected in 83,3% of patients, LVEF of 40-50% — in 16,7% of patients. LV wall thickening was noted in 83,3% of patients, of which 58,3% had LV wall thickness ≥1,5 cm. Small pericardial effusion was detected in 12,5% of patients. LV diastolic dysfunction was detected in 45,8% of patients. Sinus bradycardia was detected in 41,7% of patients. Short PQ interval was detected in 25% of patients, while Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome was detected in 8,3%.
Conclusion. Cardiac involvement with wall thickening, sinus bradycardia and atrioventricular conduction disorders are frequent manifestations in patients with Fabry disease. Early detection of cardiac involvement and prevention of cardiac events are important to ensure the effectiveness of treatment and improve the quality of life of patients.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY
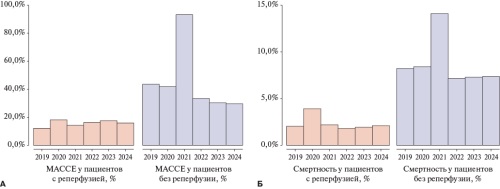
- Non-immunogenic staphylokinase is a fibrin-selective thrombolytic agent used to treat STEMI since 2012. Monitoring the safety and efficacy of non-immunogenic staphylokinase covered more than 51 thousand patients.
- The number of patients with reperfusion, as well as all-
cause mortality (4,2%) and major bleeding (1,1%) rates when using non-immunogenic staphylokinase in the FRIDOM-registry are comparable with data from previous clinical and observational studies. - A significant increase in mortality and major bleeding rates in 2021 was revealed in patients without reperfusion during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Aim. To evaluate real-world data on the safety of reperfusion therapy using non-immunogenic staphylokinase in a wide range of patients with STEMI at the prehospital stage.
Material and methods. FRIDOM-registry is a multicenter prospective non-interventional observational study. The registry included patients with an established diagnosis of STEMI who received reperfusion therapy with non-immunogenic staphylokinase (Fortelyzin®, OOO SupraGene, Russia) at a dose of 15 mg bolus or bolus-infusion. The safety criteria were all-cause inhospital mortality, major bleeding rate, and a combination of major adverse cardiac and cerebral events (MACCE) — all-cause death, cardiogenic shock, recurrent myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, heart failure deterioration, ischemic stroke, and intracranial hemorrhage during hospitalization. The rate and severity of bleedings were determined according to the BARC classification. The criterion for the effectiveness of reperfusion therapy was the coronary flow restoration according to electrocardiographic (ECG) data after 90 minutes. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and Good Clinical Practice.
Results. Monitoring the use of non-immunogenic staphylokinase in STEMI from June 1, 2013 to January 14, 2025 covered 51021 patients. The mean age of patients included in the registry was 64,5±12,1 years; 17% of patients aged over 75 years; 70% of patients were male. A total of 96% of patients received thrombolysis at the prehospital stage. According to ECG, reperfusion within 90 minutes after thrombolysis was achieved in 74% of patients. All-cause mortality was 4,2%, of which 1,2% at the prehospital and 3,0% in the hospital stage. The major bleeding rate was 1,1%, intracranial hemorrhages — 1,1%; the minor bleeding rate was 3,2%. A subanalysis of patients included in the period 2019-2025 using the online platform FRIDOM-registry showed that in 2021 the MACCE rate in the group of patients without reperfusion significantly exceeded the values of other years (93% vs 36%, p<0,001), which could probably be due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. In turn, the MACCE rate in the group of patients with reperfusion did not have significant fluctuations over the years and averaged 16±2% per year.
Conclusion. The real-world data obtained confirmed the high safety of non-immunogenic staphylokinase in 51021 patients, established earlier in clinical trials.
What is already known about the subject?
- Anticoagulant therapy for atrial fibrillation and high risk of thromboembolic events largely determines the prognosis of patients.
- In 2016-2019, according to a retrospective analysis, anticoagulation prescription rate in certain Russian regions in atrial fibrillation and high risk of thromboembolic events was 34,8%.
What might this study add?
- As of the end of 2023, anticoagulation prescription rate for atrial fibrillation and high risk of thromboembolic events in certain Russian regions increased to 53,7%, and the share of direct oral anticoagulants in its structure increased to 87,0%.
Aim. To conduct a retrospective analysis of anticoagulation prescription rate, including direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC), to patients with atrial fibrillation and high risk of thromboembolic events (TEEs) in certain Russian regions as of December 31, 2023.
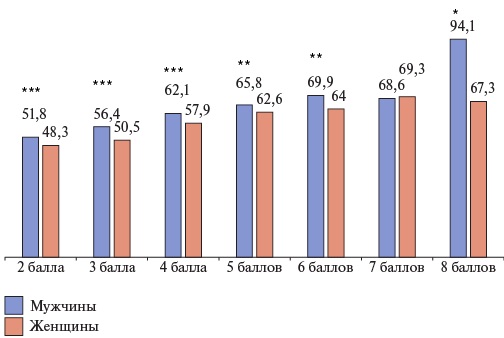
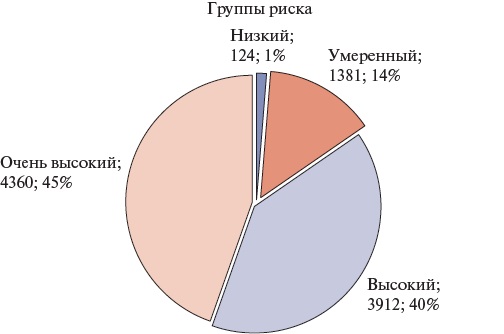
Material and methods. The analyzed group of patients was formed based on the information contained in the Webiomed predictive analytics platform (OOO K-Sky, Petrozavodsk, Russia). The information was presented as the extracted depersonalized anonymized data from the electronic health records of patients aged ≥18 years, attached to medical facilities of 17 Russian subjects (n=107561, men 37,8%, mean age 74,5±8,5 years, mean CHA2DS2-VASc score of 3,6±1,2) extracted by the continuous sampling method.
Results. Anticoagulation prescription rate in the group as a whole was 53,7%, while the DOAC share in its structure was 87,0%. Acetylsalicylic acid for TEE prevention was prescribed in 10,6% of cases. With an increase of non-gender-specific CHA2DS2-VASc score, the percentage of people receiving anticoagulation increased — from 49,7% with 2 points to 73,9% with 8 points. Anticoagulation was prescribed to patients aged ≥75 years significantly less often (49,1%, p<0,001). Regardless of age and type of arrhythmia, anticoagulants were prescribed to men significantly more often than to women.
Conclusion. The results of retrospective analysis indicate improvement in anticoagulation prescription rate for atrial fibrillation and a high risk of TEEs in certain Russian regions. Compared to a similar study for 2016-2019, in 2023 this indicator increased from 34,8% to 53,7%. The share of DOACs in anticoagulant therapy structure also increased significantly — from 52,0% to 87,0%. At the same time, oral anticoagulation rate in this cohort of patients still does not meet the requirements of current clinical guidelines.
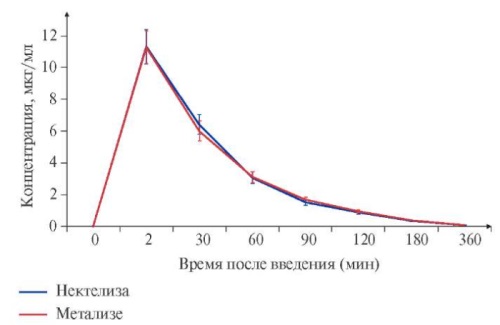
Aim. To present the results of a comparative study of the efficacy and safety of the Russian biosimilar Nektelisa (AO GENERIUM, Russia) and the reference biological drug Metalyse (Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, GmbH & Co. KG, Germany) when used in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
Material and methods. The study included 244 male (n=204) and female (n=41) patients aged 36 to 75 years with STEMI. The study was conducted in 14 clinical centers of the Russian Federation and 2 centers in Belarus. Patients were randomized into two groups 1:1 as follows: 122 patients received the domestic biosimilar Nektelisa, and 122 patients received the reference drug Metalyse. The main criterion of efficacy is the myocardial reperfusion rate (TIMI grade 3 coronary flow). Safety assessment included analysis of adverse reactions, hemorrhagic complications of thrombolytic therapy, and immunogenicity.
Results. The incidence of myocardial reperfusion (TIMI grade 3) was 53,7% in the Nektelisa group and 57,1% in the Metalyse group, confirming therapeutic equivalence of the drugs (difference -3,4%, 95% confidence interval: -16,0% to 9,1%). The safety profile of Nektelisa was comparable to that of Metalyse, with fewer adverse events recorded in the Nektelisa group (7,4% in Nektelisa group vs 15,7% in the Metalyse group). Most of the recorded adverse reactions were hemorrhagic complications of thrombolytic therapy (bleeding of varying severity and locations). During the study, 13 bleeding episodes were noted in 8 patients in the Nektelisa group and 30 bleeding episodes in 16 patients in the Metalyse group. The incidence of major bleeding in the Nektelisa and Metalyse groups according to TIMI classification was 0,8% and 2,5%, while according to the ISTH classification — 0,8% and 3,3%, respectively. In addition, BARC type 5b bleeding was revealed in 0% and 10%, respectively. The incidence of hemorrhagic strokes was 1,2%, all of which were registered in the Metalyse group.
Conclusion. The clinical trial proved that Nektelisa (AO GENERIUM, Russia) is a biological analogue of Metalyse (Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma, GmbH & Co. KG, Germany).
- Current approaches to diagnosing resistance to P2Y12 receptor blockers in patients with coronary artery disease have a number of limitations that reduce the effectiveness of their practical use.
- Immune activation can lead to a decrease in the effectiveness of antiplatelet therapy.
- Randomized studies are needed to assess the level of inflammation as a criterion for resistance to P2Y12 receptor blockers.
The review is devoted to current methods for evaluating the efficacy of P2Y12 receptor blockers in patients with coronary artery disease. Literature and original data are presented. Currently existing genetic and functional tests are insufficient for reliable diagnosis of resistance to P2Y12 receptor blockers, which may be due to a number of concomitant factors, including inflammatory process. Proinflammatory markers can be studied to develop novel approaches to assessing the risk of thrombotic events during P2Y12 receptor blocker therapy.
The use of fixed-dose combinations for hypertension (HTN) has long been a routine clinical practice. Recently, special attention has been paid to multi-target fixed-dose combinations with the ability to reduce not only blood pressure (BP), but also low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels. At the same time, there is not much evidence for this approach.
Aim. To evaluate the antihypertensive and lipid-lowering effect of fixed-dose combinations based on perindopril.
Material and methods. The INTEGRATION II study included 9777 patients (mean age 61,8±9,8 years) with HTN and dyslipidemia (DLP), who were prescribed a fixeddose antihypertensive combination of perindopril+amlodipine+indapamide (Co-Dalneva®) in combination with rosuvastatin (Roxera®) (n=5128) or a multi-target fixed-dose combination of perindopril+indapamide+rosuvastatin (Roxatenz-inda) (n=4649).
Results. In the Co-Dalneva® + Roxera® group, a decrease in systolic BP from 164,9±13,8 mm Hg to 127,2±8,8 mm Hg was noted over 12‑week treatment, diastolic BP — from 94,2±10,0 mm Hg to 77,6±6,3 mm Hg; total cholesterol level decreased from 6,2±1,1 mmol/l to 4,3±0,8 mmol/l, and LDL level — from 3,6±1,0 mmol/l to 2,1±0,7 mmol/l. In the Roxatenz-inda group, over the same period, systolic BP decreased from 161,9±12,7 mm Hg to 126,2±8,3 mm Hg, while diastolic BP — from 94,5±9,5 mm Hg to 76,9±6,8 mm Hg. The total cholesterol level decreased from 6,3±1,1 mmol/l to 4,4±0,8 mmol/l; the LDL level — from 3,5±1,0 mmol/l to 2,1±0,6 mmol/l. Both physicians and patients rated Likert scale satisfaction with therapy as very good (4,75-4,8 out of 5), while the compliance according to the patient corresponds to high and highest.
Conclusion. The results of the INTEGRATION II study demonstrated the efficacy and convenience of fixed-dose combinations of antihypertensive and lipid-lowering agents based on perindopril and rosuvastatin in practice. There are good tolerability and a high level of satisfaction with the treatment from both the patient’s and the phusician’s perspective.
EXPERT CONSENSUS
- Pharmacoinvasive approach with prehospital bolus administration of thrombolytic agents should currently be considered as a priority strategy in ST-elevation myocardial infarction if primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is not possible within 120 minutes after diagnosis.
- A pharmacoinvasive approach with prehospital bolus administration of thrombolytic agents should be considered as an alternative to primary PCI in the first 3 hours from the onset of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in cases where primary PCI cannot be performed within 1 hour after diagnosis.
The article presents an overview of the largest randomized and observational studies on the efficacy and safety of primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and pharmacoinvasive strategy for ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
The management of STEMI patients is one of the most discussed and pressing issues in modern cardiology, since timely myocardial revascularization significantly affects both patient mortality and long-term prognosis. It has been established that the key factor in choosing reperfusion therapy for STEMI should be the time from the onset of symptoms. Due to the fact that it is not possible to ensure the time before opening the infarct-related artery up to 120 minutes in all patients referred for primary PCI in real-world practice, prehospital thrombolysis can significantly improve their prognosis. Pharmacoinvasive approach with prehospital bolus administration of thrombolytic agents should currently be considered as a priority strategy in STEMI if primary PCI within 120 min after diagnosis is not possible. A pharmacoinvasive approach with prehospital bolus administration of thrombolytic agents should be considered as an alternative to primary PCI in the first 3 hours from the STEMI onset in cases where primary PCI cannot be performed within 1 hour after diagnosis.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)