Scientific and practical per-reviewed journal
Russian Journal of Cardiology is currently issued since 1996. It is official journal of the Russian Society of Cardiology (RSC).
Editor-in-Chief: Prof. Eugene V.Shlyakhto, Academician of Russian Academy of Sciences, President of RSC. FSBI «Almazov North-Western Federal Medical Research Center» of the Healthcare Ministry. Saint-Petersburg, Russia
The target audience of this peer-reviewed journal is cardiologists and internal disease specialists. The journal is primarily focused on original studies, cardiac surgery, and cardiac pharmacotherapy. It also publishes lectures and literature reviews on various problems of modern cardiology, reports on new diagnostic methods, and other information which is important for the practitioners. The aim of the journal is both scientific and practical, also with referring to organizing matters of the RSC. The best of all cardiological research in Russia is submitted to Journal.
The language of publication is Russian, with contents and abstracts of all the articles presented in English. The Journal also accepts manuscripts from foreign authors and publishers them in English with abstracts in Russian.
Science Index (2024) 9,997 (5th procentile, 9 in "Medicine and healthcare")
Impact-factor 2024) 2,116
Current issue
GENETICS IN CARDIOLOGY. ORIGINAL ARTICLES
- The association between Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) and molecular genetic polymorphisms of various genes (in particular, VDR, ADRB1, SP4, MMP3, and MMP9)was studied.
- The search for molecular genetic prognostic markers for clinical manifestations and the anatomical substrate of WPW syndrome is an important part of personalized medicine and enables early diagnosis of the syndrome to predict the disease course.
- The study revealed that the 5A/5A genotype of the MMP3gene reduces the probability of WPW syndrome by almost 2-fold, while the AA genotype of the MMP9 gene also increases the risk of cardiovascular events by 2-fold.
Aim. To analyze the association of VDR (rs1544410), ADRB1 (rs1801252), SP4 (rs1011168), MMP3 (rs35068180), and MMP9 (rs11697325) gene polymorphisms with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW).
Material and methods. A total of 169 patients with WPW syndrome and 158 controls were included in the study. DNA was isolated from whole blood leukocytes using the phenol-chloroform extraction. Commercial kits from OOO NPF Litekh (Moscow) were used for genotyping the rs1544410 and rs11697325 polymorphisms in the VDR and MMP9 genes. Analysis of rs1011168, rs1801252, and rs35068180 was performed using the "PCR-Komplekt" amplification reagent kit ("Sintol", Moscow).
Results. When comparing the frequency of the studied polymorphisms between patients with WPW syndrome and the control group, significant differences were found for MMP3 rs35068180 and MMP9 rs11697325. No differences were found for the VDR (rs1544410), ADRB1 (rs1801252), and SP4 (rs1011168) polymorphisms. When comparing the genotype frequencies for the five studied polymorphisms between groups of patients with different clinical variants of WPW syndrome, significant differences were found for SP4 rs1011168 and MMP3 rs35068180.
Conclusion. The 5A/5A genotype of the MMP3 gene was shown to reduce the probability of WPW syndrome by almost twofold, while the AA genotype of the MMP9 gene also increased the risk of cardiovascular events by twofold.
What is already known about the subject?
- In addition to genetic predisposition to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW), phenotypic characteristics can be determined. Their combination will provide more accurate data for preventing WPW syndrome and related arrhythmias.
What might this study add?
- Multivariate regression analysis identified the most significant statistical predictors that could potentially influence the prognosis of this condition and be risk factors for WPW syndrome.
How might this impacton clinical practice?
- Somatometry and molecular genetic testing may prove valuable tools for the prevention and systematic monitoring of high-risk individuals and close relatives of patients with WPW syndrome and phenomenon. This could potentially facilitate the development of a tool for arrhythmia risk assessment in this syndrome, based on personalized medicine.
Aim. To study the phenotypic and molecular genetic characteristics of patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome.
Material and methods. The study group consisted of 200 patients with WPW syndrome, including 97 men (n=48,5%) and 103 women (n=51,5%). All patients underwent clinical and paraclinical examinations, including electrocardiography (ECG), Holter monitoring, echocardiography, somatometry according to the standard V. V. Bunak method, and molecular genetic testing. DNA was extracted using the phenol-chloroform method, and genotyping was performed using the polymerase chain reaction.
Results. Multivariate regression analysis revealed significant associations between some factors and WPW syndrome. The strongest predictor was a delta wave on the ECG (odds ratio (OR) =21,3; p<0,0001). Genetic variants PRKAG3="CC" (OR =16,7; p=0,0009), PRKAG2="GA" (OR =6,3; p=0,0023) and TBX3="GG" (OR =6,1; p=0,0078) also demonstrated a significant association with an increased probability of WPW syndrome. An increase in the QRS duration (OR =1,1 per unit; p<0,0001) and heart rate (OR =1,1; p=0,0008) on the ECG were associated with a non-significant odds increase. In contrast, QT interval increase (OR =0,97; p<0,0001) and higher height (OR =0,96; p=0,0073) were associated with a low risk of WPW syndrome. Rees-Eysenck normosthenic body type significantly reduced the odds (OR =0,47; p=0,0367).
Conclusion. Heredity is a key factor in the development of WPW syndrome, as confirmed by data from numerous studies. Phenotypic characteristics, in addition to genetic markers, can serve as a valuable tool for risk stratification and the development of preventive strategies aimed at preventing the manifestation of WPW syndrome.
- The CG genotype of ANRILrs1333049 was detected in 71,4% of patients with hyperlipoproteinemia(a) (hyperLP(a)) and in 63,9% of patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. The AG genotype of LPArs10455872, which also increases the cardiovascular risk, was detected predominantly in patients with hyperLP(a) (in 34,3% of cases).
- Familial hypercholesterolemia associated with the CG/CC genotype of ANRIL rs1333049 is characterized by an aggressive course with the development of cardiovascular events in 36,7% of patients under 44 years of age, predominantly in men.
- HyperLP(a) is characterized by a smaller increase in low-density lipoprotein levels compared to the group of patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. The CG/CC genotype in this group of patients determines the risk of cardiovascular events before age 40 in 15% of cases.
Aim. To study the impact of ANRIL rs1333049 and LPA rs10455872 polymorphisms on the clinical status of patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) and hyperlipoproteinemia(a) (hyperLP(a)).
Material and methods. A total of 171 patients aged 3 to 44 years were examined. Lipid profile, apolipoprotein B (apoB), and lipoprotein(a) (LP(a)) were determined using chemiluminescence immunoassay on the Roche Cobas 8000 automated modular analyzer. Single-nucleotide variant (SNV) carriage was determined using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on a Rotor-Gene 6000 system with TaqMan allelic discrimination technology and Applied Biosystems fluorescent probes for LPA rs10455872 (A/G) and ANRIL rs1333049 (C/G). Genotype frequency distributions corresponded to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Extracranial vessel ultrasound was assessed taking into account age-specific references.
Results. A study of relationship between the ANRIL rs1333049 and LPA rs10455872 in patients with FH and hyperLA revealed that the CG genotype of ANRIL rs1333049 directly correlates with apoB levels and intima-media thickness (IMT) in both target groups. An influence of the AG genotype of LPA rs10455872 on apoB, LP(a), and IMT levels was revealed in patients with FH and hyperLA(a). The mean age at onset of coronary events was 35 years. The incidence of myocardial infarction was 2,5 times higher in the FH group than in the LP(a) group.
Conclusion. In patients with FH and hyperLA(a), a predominance of the ANRIL CG genotype is associated with high apoB, IMT, and the incidence of coronary events. The AG genotype of LPA rs10455872 is associated with high LP(a) levels, increased IMT, and the risk of early myocardial infarction.
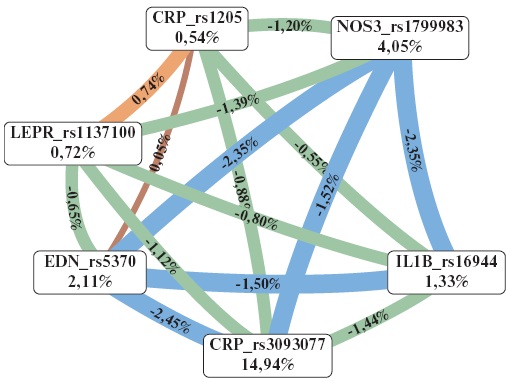
- The risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) is associated with CRPrs3093077, NOS3 rs1799983, EDNrs5370, LEPR rs1137100, and IL1B rs16944 polymorphic variants.
- Two haplotypes have been identified that are significantly associated with a predisposition to CAD.
- The CRPrs3093077 polymorphism is associated with higher serum C-reactive protein levels in patients with CAD.
Aim. To evaluate the involvement of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of genes related to the inflammatory response, endothelial dysfunction, lipid metabolism, and oxidative stress in the development of coronary artery disease (CAD).
Material and methods. The study included 560 patients, including 260 with a confirmed diagnosis of stable CAD and 300 healthy donors. DNA was isolated from peripheral blood according to a standard protocol. Genotyping of 42 polymorphic variants was performed using real-time polymerase chain reaction. Serum levels of the studied proteins were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using commercial kits.
Results. The development of CAD is associated with CRP rs3093077, NOS3 rs1799983, EDN rs5370, CRP rs1205, LEPR rs1137100, and IL1B rs16944 polymorphic variants. Two haplotypes, rs16944A-rs1205T-rs3093077C-rs5370Grs1799983G-rs1137100A (p=0,04) and rs16944A-rs1205T-rs3093077C-rs5370G-rs1799983T-rs1137100A (p=0,032), were found to be significantly associated with a predisposition to CAD. Carriers of the A allele of CRP rs3093077 variant were characterized by higher serum C-reactive protein concentrations.
Conclusion. Thus, this study demonstrates a significant contribution of polymorphic variants of inflammatory response (IL1B rs16944, CRP rs1205, and CRP rs3093077), endothelial dysfunction (EDN rs5370 and NOS3 rs1799983), and lipid metabolism (LEPR rs1137100) genes to CAD predisposition.
- Studying the relationship between gene polymorphisms and the degree of arterial stiffness in hypertensive patients can help assessing their impact on the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- The AGTC521T polymorphism can serve as a marker of early vascular damage in patients with a confirmed diagnosis of hypertension.
- Studying genetic polymorphisms pushes the boundaries for a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying the onset and development of hypertension and cardiovascular disease, which, in turn, will reduce their risk and improve patients’ quality of life.
Aim. To study the relationship between specific gene polymorphisms and arterial stiffness to assess the impact of these gene polymorphisms on the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
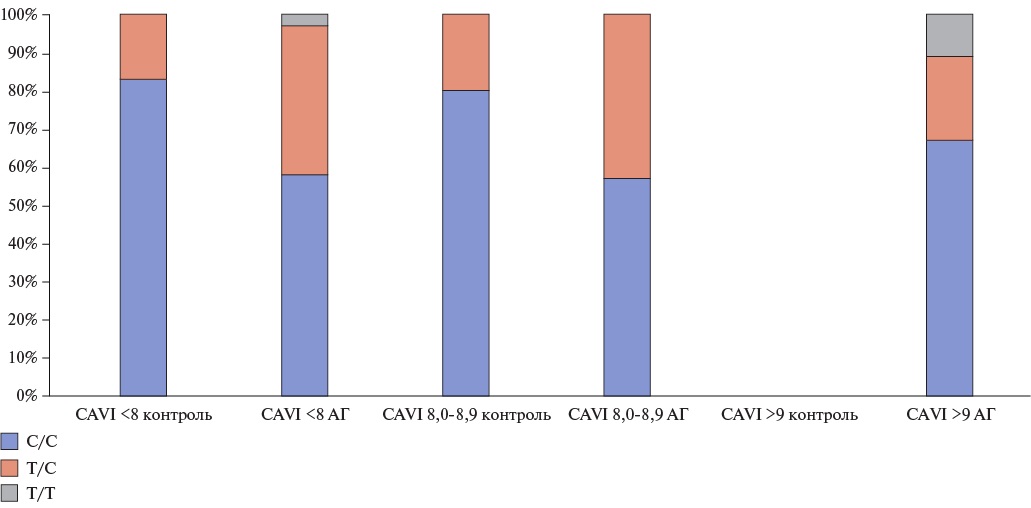
Material and methods. Seventy-seven patients, with an average age of 52,9±11,3 years, were examined. Patients underwent clinical and paraclinical examinations, including volume sphygmoplethysmography to assess the cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI), biochemical blood tests, and gene polymorphism determination. Patients were divided into two groups based on hypertension (HTN) presence. Each group was then divided into three subgroups based on CAVI level as follows: CAVI <8, CAVI 8,0-8,9, and CAVI >9.
Results. In the HTN group, the frequency of T/C and T/T genotypes of the AGT C521T polymorphism was higher in all three subgroups compared to the control one. The T/C genotype of the GNB3 C825T polymorphism was more common in the HTN group in the subgroups with CAVI <8 and CAVI >9, while the T/T genotype was more common in the control group with CAVI of 8,0-8,9. In the subgroup with CAVI of 8,0-8,9, the C/C allele of the NOS3 T786C polymorphism was significantly more common in the control group, while the T/C allele was predominant in the control group with CAVI <8. In the control group with a CAVI <8 and a CAVI of 8,0-8,9, the T/T genotype of the NOS3 G894T polymorphism was more common, while the T/G allele was more common in the hypertensive group with a CAVI of 8,0-8,9.
Conclusion. The AGT C521T polymorphism can serve as a marker of early vascular damage in patients with confirmed HTN. The homozygous C/C genotype of the AGT T704C polymorphism more likely leads to HTN. The study of genetic polymorphisms pushes the boundaries for rethinking the onset and development of HTN and cardiovascular diseases.
- In patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), an association was found between carriage of the GG genotype of SCN5Ars1805126 and impaired recovery of myocardial contractility after outpatient rehabilitation course.
- In patients with AMI, no association was found between carriage of the CC, CG, and GG genotypes of LRRC31rs16847897 and impaired myocardial contractility recovery after outpatient rehabilitation course.
- Elastic mapping made it possible to clearly differentiate patients with the GG, AA, and AG genotypes of SCN5Ars1805126, as well as to identify areas for further research with the AGTR1rs5186 and ADRB2 rs1042714 genotypes.
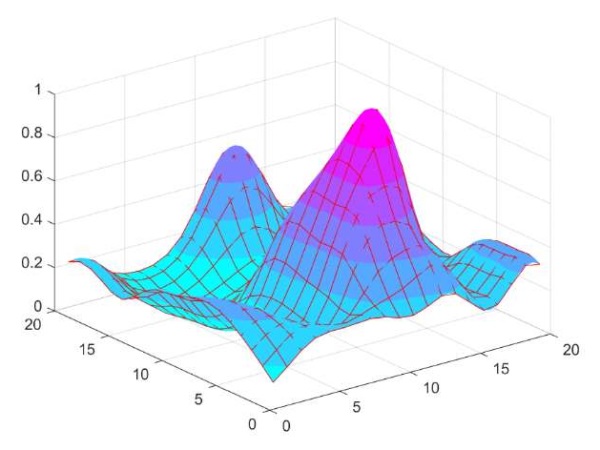
Aim. To study the impact of patients’ genetic characteristics on myocardial contractility recovery after acute myocardial infarction (AMI) during the outpatient rehabilitation using the elastic mapping.
Material and methods. The study included 127 patients (98 men and 29 women), aged 36 to 65 years, with a mean age of 59,0±8,7 years, who had an AMI. Three to six weeks after AMI, all patients underwent the third (outpatient) 14-day stage of rehabilitation. All patients also completed a course of cycling training. Before and after cycling, patients underwent cycle ergometry, a six-minute walk test, and a Borg Scale assessment. Recovery of myocardial contractility was assessed based on changes in these test parameters. All patients underwent genomic DNA extraction, and the following nucleotide sequence variants were analyzed: SCN5A rs1805126, LRRC31 rs16847897, AGTR1 rs5186, and ADRB2 rs1042714. Elastic maps were created using the ElMap software.
Results. An association was established between carriage of the GG genotype of SCN5A rs1805126 and impaired recovery of cardiac contractility. No association was found between carriage of the CC, CG, and GG genotypes of LRRC31 rs16847897 and impaired myocardial contractility recovery. Elastic map visualization made it possible to clearly differentiate patients with the GG, AA, and AG genotypes of SCN5A rs1805126 and to identify areas for further research on AGTR1 rs5186 and ADRB2 rs1042714. No significant differences were found between men and women.
Conclusion. Information on the association between carriage of these genotypes can be used for an individualized approach to exercise level selection during cycling training at the third (outpatient) rehabilitation stage in patients after AMI.
- The reference rs5370 GG and rs1126643 CC genotypes may be part of a genetic predisposition to left ventricular remodeling in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction with successful reperfusion.
- The identified polymorphisms may indicate new molecular mechanisms underlying post-infarction left ventricular remodeling and may identify potential therapeutic targets.
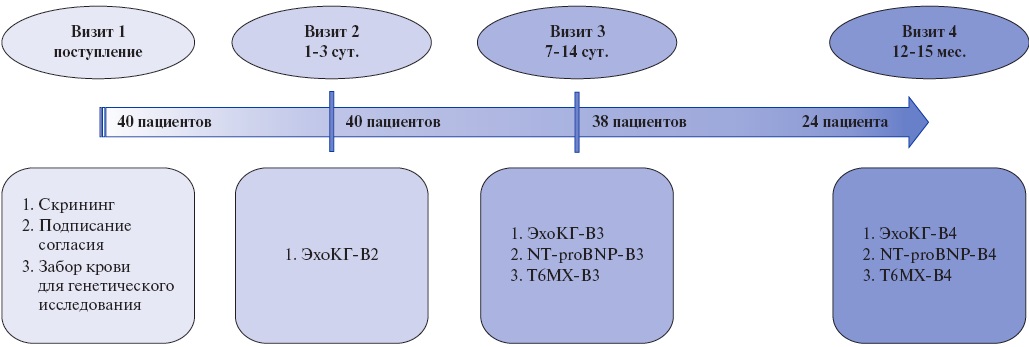
Aim. To identify genetic characteristics of patients with left ventricular remodeling (LVR) after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with reliable reperfusion.
Material and methods. This single-center observational study included 40 patients with STEMI who successfully underwent PCI. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes involved in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, coagulation cascade, platelet function, endothelial function, and folate metabolism were determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with commercial kits. During follow-up, patients underwent echocardiography on days 1-3 and 7-14, as well as after 12-15 months. LVR was established according to following criteria: 1) combined echocardiographic criterion: a decrease in the left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction <50%, an increase in LV end-diastolic volume ≥20% or end-systolic volume ≥15% based on a comparison of the last and first echocardiography or 2) a clinical criterion: hospitalization for decompensated heart failure. Twentyfour patients attended the final visit, forming comparison and control groups of 12 each. The median follow-up was 392 [383; 406] days.
Results. Significant intergroup differences were identified for two following polymorphisms: rs5370 and rs1126643. In the group of patients with LVR, the frequency of rs5370 GG genotype was 91% (n=10) versus 40% (n=4) in the control group (p=0,024); the frequency of rs1126643 CC genotype was 67% (n=8) versus 8% (n=1), respectively (p=0,009). Multivariate regression analysis revealed that the reference rs5370 GG and rs1126643 CC genotypes may be associated with an increased risk of LVR in STEMI patients with achieved reperfusion, while carriage of an alternative allele (both homozygous and heterozygous) in at least one of these loci was protective.
Conclusion. The reference rs5370 GG and rs1126643 CC genotypes may be part of a genetic predisposition to LVR in STEMI patients with successful reperfusion. These data are not exhaustive and require verification in larger studies.
- Patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) were most likely to have Omicron (2022) coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), while severe COVID-19 was more often observed in Delta variant.
- The ACErs1799752 nucleotide sequence variant is associated with the risk of ACS in patients depending on the severity of their COVID-19.
- Genetic markers may be predictors of ACS in patients depending on COVID-19 severity.
Aim. To assess the detection rate of genotypes of ACE rs1799752 nucleotide sequence variants in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) depending on the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Material and methods. A total of 100 patients (50 men and 50 women) hospitalized with a diagnosis of ACS and prior COVID-19 were included in the study. COVID-19 severity and variant (Alpha, Delta, or Omicron) were assessed for all patients. Upon admission, all patients underwent diagnostic testing according to the ACS examination protocol, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty with stenting, and genetic testing of the ACE rs1799752 using polymerase chain reaction.
Results. In our study, patients with the Omicron variant were more frequently encountered (n=87, 73,7%). Severe COVID-19 was more often recorded with the Delta variant — 7 patients (5,93%). When comparing the carrier frequencies of the ACE rs1799752 genotype in patients with ACS depending on COVID-19 severity, significant differences were found (p=0,043). Carriage of the heterozygous ID genotype was recorded most frequently among both outand inpatients. When separated by sex, the heterozygous ID variant was again more common among outpatients, both men and women, as well as among women hospitalized with COVID-19.
Conclusion. The ACE rs1799752 (I/D) nucleotide sequence variant is associated with ACS in patients depending on COVID-19 severity.
- When calculating the HTN risk using univariate analysis, the most significant non-genetic risk factors were high body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio >0,88, positive family history for cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, elevated total cholesterol, male sez, and positive family history for metabolic syndrome.
- However, in multivariate analysis, a combination of genetic factors demonstrated the highest sensitivity and specificity.
- Mathematical modeling of multivariate logistic regression allowed us to rank the contribution of various genotypes to HTN development, with some genotypes having a protective effect.
Aim. To identify independent genetic and non-genetic predictors of hypertension (HTN) and rank their contribution to disease progression, as well as to identify potential new mechanisms that may influence the hypertension development.
Material and methods. This cross-sectional observational study included 610 patients, including 142 with HTN. All participants completed a questionnaire, blood pressure (BP) measurements, biometric measurements, and molecular genetic testing. HTN predictors were identified using logistic regression models. Using singlefactor models, individual HTN predictors were determined. A multivariate logistic regression model was created using covariates with a significance level of p<0,3 in univariate models to rank the contribution of each trait to HTN development.
Results. A mathematical model was constructed using non-genetic and genetic markers to assess the risk of HTN, better classifying individuals with a low genetic risk for HTN. Genetic predictors were more significant for optimal calculations of HTN probability in the logistic regression model, while non-genetic traits were not included in the final model. Possible mechanisms that may lead to HTN, based on the identified genetic predictors, are considered. In addition, the concept of the contribution of a protective combination of genetic variants is also explored.
Conclusion. A logistic regression model based on molecular genetic testing results is optimal for identifying individuals with a low HTN risk. Thus, for patients with a low genetic risk, lifestyle factors are more significant, and lifestyle modification is especially important for them to prevent HTN.
- Advances in specific treatments for orphan diseases imitating hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), particularly cardiac amyloidosis and Fabry disease, highlight the importance of their diagnosis.
- Improvements in myocardial imaging and the availability of genetic testing make it possible to detect phenocopies in an average of every 20 adult patients with the HCM phenotype.
- Molecular diagnosis is important not only for the patient but also for their family, allowing for the early identification of mutation carriers.
Aim. To assess the incidence of cardiac amyloidosis and Fabry disease among adult patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) phenotype in a Russian observational study and compare the results with international data based on a meta-analysis.
Material and methods. This prospective study conducted at City Clinical Hospital № 17 (Moscow) from 2009 to 2024 included 223 patients with the HCM phenotype (mean age 54±14,9 years, 55% men). All patients underwent clinical, paraclinical and genetic examinations. Phenocopy diagnoses were verified according to guidelines. Their proportion in general cohort was then compared with data from a metaanalysis of publications identified through a systematic search of PubMed for the prevalence of cardiac AL and ATTRv amyloidosis and Fabry disease among adult patients with HCM.
Results. In our cohort, the diagnosis was revised to AL amyloidosis in six (2,7%), to ATTRv amyloidosis in three (1,4%), and to Fabry disease in one (0,5%) patient. The meta-analysis included 16 studies (n=8243). No differences were found between Russian data and data from other populations. There was following overall prevalence of phenocopies, based on the meta-analysis results and taking into account the Russian cohort: AL amyloidosis — 1,8%, ATTRv amyloidosis — 1,2%, and Fabry disease — 1,2%.
Conclusion. Phenocopies account for a significant proportion of HCM phenotype causes in adults, and their prevalence in Russia is comparable to other populations. Apprehensive attitude and mandatory genetic testing can improve the detection of rare diseases imitating HCM.
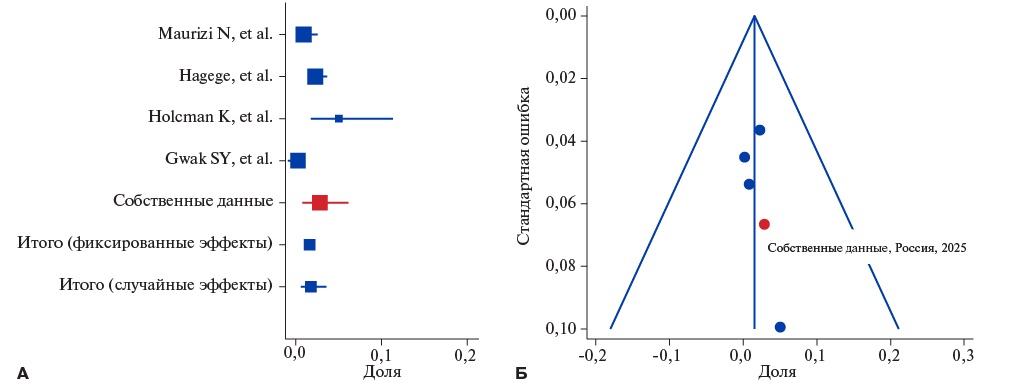
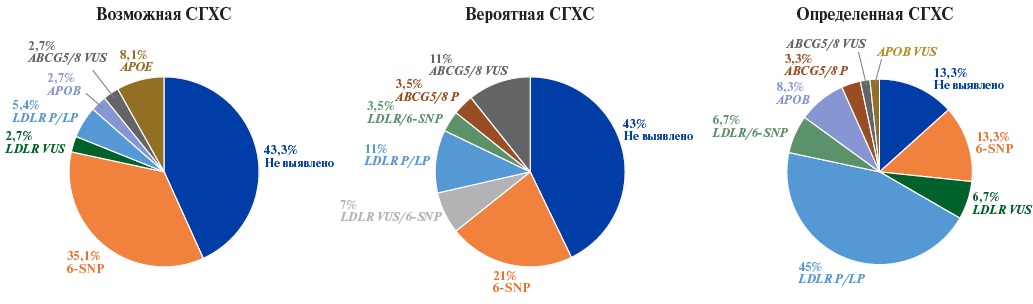
- In patients with possible and probable familial hypercholesterolemia, polygenic hypercholesterolemia makes a significant contribution (up to 35,1% for the applied genetic risk score (GRS)).
- The expanded NGS panel, which includes the genes of hereditary dyslipidemia, as well as loci for calculating GRS, can be effectively used for differential diagnosis, determining the etiology of hypercholesterolemia, and for personalizing treatment approaches.
Aim. To determine the frequency of pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants associated with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) with assessment of the proportion of polygenic FH according to the 6-SNP genetic risk score (GRS) among patients diagnosed with possible/probable/definite FH in St. Petersburg.
Material and methods. This study tested a hybrid targeted panel for gene diagnostics of hereditary dyslipidemias, including an expanded list of genes associated with monogenic dyslipidemias and a number of single-nucleotide variants associated with polygenic hypercholesterolemia and cardiovascular risk. Genetic testing was performed on 125 patients.
Results. A total of 26 pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in the LDLR gene were identified in 38 patients, while 6 variants of uncertain clinical significance in the LDLR gene — in 7 patients, and a pathogenic variant 10580G>A (p.Arg3527G) in the APOB gene — in 6 patients. The highest detection rate of causal genetic variants (66,7%) was observed, as expected, in the subgroup of patients with definite FH. Patients with a high polygenic risk of hypercholesterolemia predominated in the subgroups diagnosed with possible and probable FH.
Conclusion. The use of an expanded next-generation sequencing (NGS) panel, including genes for hereditary dyslipidemias, as well as loci for calculating the GRS, may be critical for differential diagnosis, determining the etiology of hypercholesterolemia, and personalizing treatment approaches.
- The distribution of high-sensitivity troponin I (hsTnI) concentrations in the analyzed representative sample (n=1162) was asymmetric, with a shift toward lower values.
- The median hsTnI concentration and interquartile range in the Slavic group was 1,4 (0,8; 2,2) pg/ml, which was significantly higher than among the Kyrgyz ethnic group (1,0 (0,45; 1,85) pg/ml, p=0,003). This was true for both men (p=0,003) and women (p=0,001).
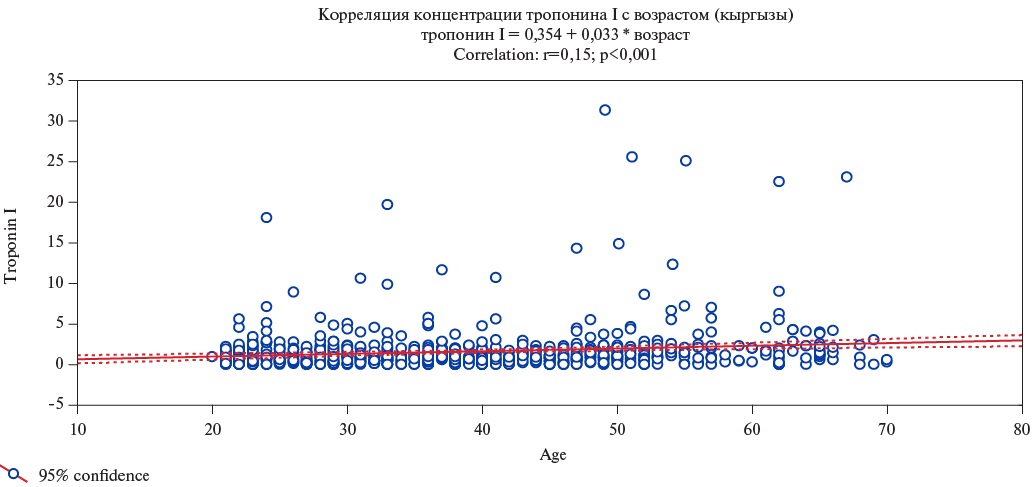
- A correlation was found between the concentration of hsTnI and the age of respondents in both ethnic groups, more pronounced among women and in the Kyrgyz group.
Aim. To identify ethnic characteristics in the distribution of high-sensitivity troponin I (hsTnI) concentrations in a representative sample of residents of the Chui Region of the Kyrgyz Republic, taking into account age.
Material and methods. The study included a representative sample of Kyrgyz Republic population aged 18-65 years (n=1162). An analysis of hsTnI distribution in the population was conducted, taking into account ethnicity (Kyrgyz, Slavs). HsTnI levels in serum samples were measured using a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay (CMIA) using Architect Stat High Sensitive Troponin I reagents (Abbott, USA) on an Architect i2000SR analyzer (Abbott, USA) in the morning hours. The statistical significance level was set at 0,05.
Results. The median hsTnI concentration in the Kyrgyz group was 1,0 (0,45; 1,85) pg/mL. The 99th percentile (Q99) value was 14,9 pg/mL, which was significantly lower compared to the Slavic group (Me – 1,4 (0,8; 2,2) pg/mL, p=0,003; Q9923,1 pg/mL). In the Slavic ethnic group, the hsTnI concentration was higher than among the Kyrgyz when analyzed separately for men and women (p<0,001). HsTnI levels were significantly higher in men than in women in both the Kyrgyz (p<0,001) and Slavic (p=0,003) groups. A significant correlation was found between the hsTnI concentration and the age of respondents in both ethnic groups. The correlation level in the Kyrgyz ethnic group was r=0,15 (p<0,001), while in the Slavic group it was less pronounced and amounted to r=0,096 (p=0,046). Despite lower baseline hsTnI concentrations, the rate of its increase with age was higher in Kyrgyz ethnic group.
Conclusion. The following ethnic differences in hsTnI concentrations were revealed: higher values in the Slavic group compared to the native Kyrgyz. Moreover, in both ethnic groups, hsTnI levels were higher in men and increased with age.
ОБЩЕСТВЕННОЕ ЗДОРОВЬЕ И ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ
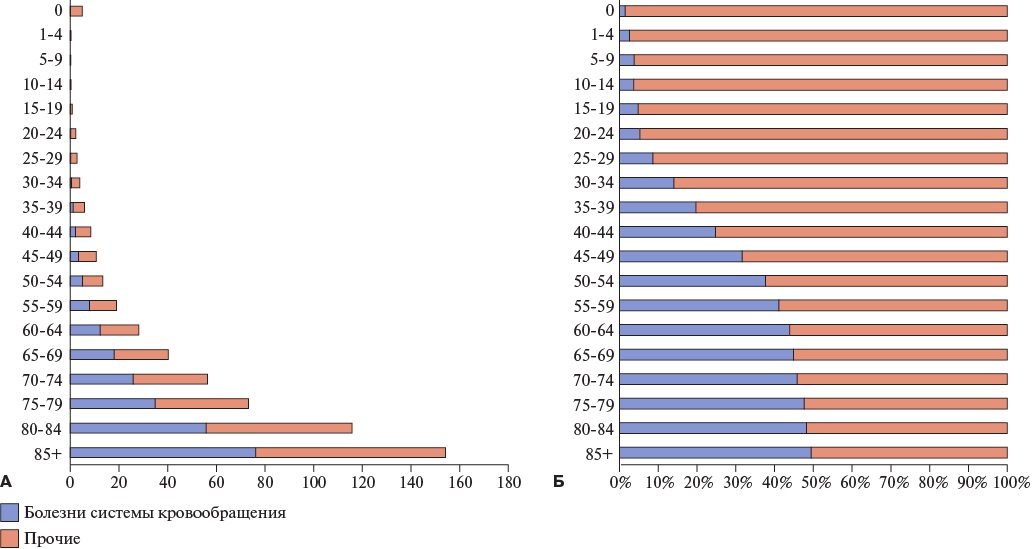
- The concept of preventable mortality makes it possible to identify the causes of death that the healthcare system can address most effectively with minimal effort.
- Donabedian model allows us to structure mortality reduction measures into the following blocks: structure, process, and outcome.
- A set of measures for cardiovascular preventable mortality reduction is presented, relevant for application in Russian regions.
- The proposed approach can serve as a basis for developing regional programs and evaluating their effectiveness.
- Regular updating of the list of measures is necessary due to advances in medical technology and changes in healthcare system resources.
This article demonstrates how the concept of preventable mortality can be used to develop mortality reduction measures using cardiovascular disease (CVD) as an example. The measures are structured according to Donabedian model. A Russian methodology for determining preventable mortality, based on international approaches and adapted to Russian healthcare system, was used. In collaboration with federal experts, a list of measures to reduce preventable cardiovascular mortality was developed. To systematize these measures, Donabedian’s triad was used, identifying resources, processes, and performance indicators for each measure. Following activity examples are presented: "health schools" using telemedicine technologies, individual patient information, and stress echocardiography. Their structuring according to the Donabedian model makes it possible to identify the causes of potentially unsatisfactory results and improve their implementation. Integrating the concept of preventable mortality with the Donabedian model ensures a rational selection and evaluation of measures to reduce cardiovascular mortality, as well as the effective allocation of resources. The list of activities requires regular updating, taking into account changes in medical technologies and healthcare system capabilities.
EXPERT CONSENSUS
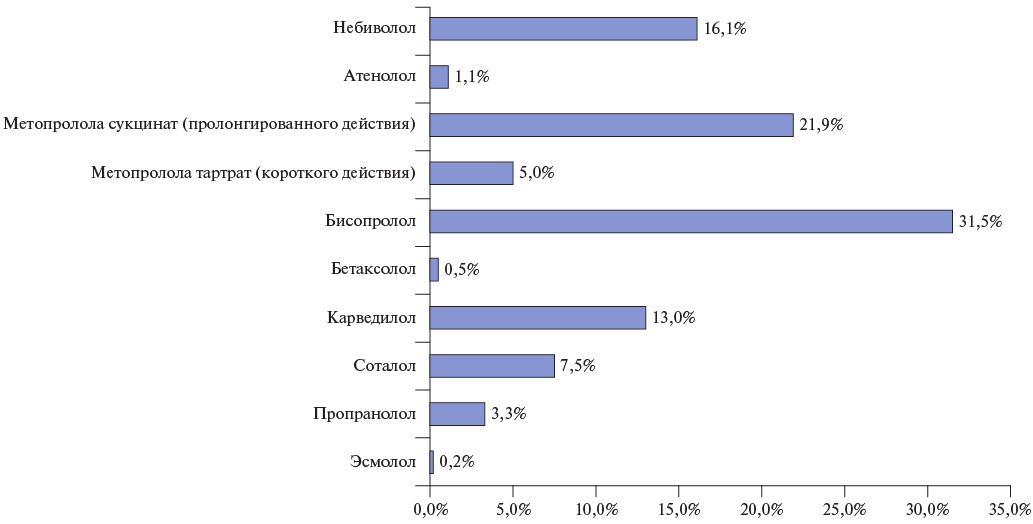
- National and international data confirm discrepancies between actual beta-blocker (BB) prescription practice and current guidelines.
- Key issues include low BB prescription rates when indicated, the use of suboptimal doses, an overestimation of obstructive lung diseases as contraindications for BB prescription, and low patient adherence.
- A significant limitation is physicians’ lack of awareness of dose titration, which leads to a false opinion on low BB efficacy.
- Positive aspects include physicians’ correct understanding of the target heart rate (HR) when prescribing BB and its achievement in most cases.
- To optimize BB therapy, it is necessary to implement educational programs emphasizing the proven benefits of dose titration, as well as the development of clinical algorithms that simplify achieving target HR parameters.
The use of beta-blockers (BB) plays a crucial role in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. However, there are significant discrepancies with current guidelines in real-world practice. The main issues related to suboptimal dosing regimens and poor medication adherence reduce the effectiveness of therapy and worsen the prognosis of patients. Under the auspices of the Eurasian Association of Internal Medicine (EUIMA), a working group was convened on BB use in real-world practice. The working group aim was to draw attention to the issue of the correctness and specific features of BB prescription by practitioners. The initiative analyzed physician survey data encompassing BB prescription trends, drug selection criteria, class perception, and implementation barriers. The EUIMA working group discussed the survey results and proposed approaches to optimizing BB prescriptions in realworld practice.
Announcements
2025-12-27
Последние номера 2025 года
Уважаемые читатели,
перед новогодними праздниками последние номера выкладываются в архив с большими временными задержками. Поэтому все опубликованные выпуски выложены постатейно в разделе "Принято в печать".
2025-12-26
Благодарность рецензентам
Редакция "Российского кардиологического журнала" выражает огромную благодарность экспертам, которые рецензировали статьи на протяжении 2025 года и помогали принимать редакционные решения.
2025-09-29
Политика использования инструментов ИИ в научных статьях (утверждение)
26 сентября 2025 г. на объединенном заседании редакционной коллегии и редакционного совета была утверждена политика по использованию инструментов искусственного интеллекта в научных статьях.
2025-09-16
Единый государственный перечень научных изданий (ЕГПНИ) – «Белый список»
«Российский кардиологический журнал» вошел в Единый государственный перечень научных изданий (ЕГПНИ) – «Белый список». Ему присвоен 1-й уровень. Это важное достижение, которое подтверждает качество и значимость издания в научном сообществе.
2025-08-29
Обработка персональных данных
С 1 сентября 2025 года вступают в силу поправки в ч. 1 ст. 9 Закона № 152-ФЗ, которыми вводится новое требование к согласию на обработку персональных данных. Согласие должно быть оформлено отдельно от информационных и (или) иных документов, которые подписывает субъект персональных данных (Федеральный закон от 24 июня 2025 года №156-ФЗ).
2025-06-01
Уточнения в «Правила для авторов» в отношении рисунков
Уважаемые авторы!
Журнал вносит уточнения в «Правила для авторов» в отношение рисунков, которые предоставляются при подаче статьи для рассмотрения к публикации.
| More Announcements... |
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)