ИШЕМИЧЕСКАЯ БОЛЕЗНЬ СЕРДЦА
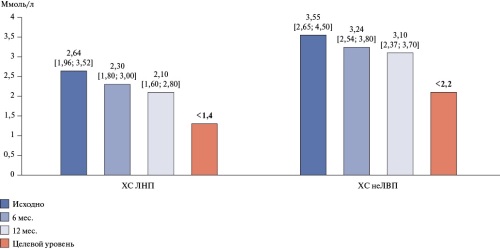
- During the 1-year follow-up, lipid-lowering therapy of patients with coronary artery disease and multifocal atherosclerosis was not properly strengthened, due to which the target levels of key lipid profile parameters were not achieved in the vast majority of patients (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in 78%, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in 81%).
- During the 1-year follow-up, antithrombotic therapy was not intensified' the low prescription rate of combination therapy with antiplatelet agents (15,7%) and low doses of rivaroxaban and acetylsalicylic acid (7,9%) remained.
- By the end of the 12-month follow-up period, a high rate of major adverse cardiovascular events (8,8%) was registered in patients included in the KAMMA registry.
Aim. To study real-world data on managing patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and multifocal atherosclerosis (MFA) for 12 months by outpatient cardiologists.
Material and methods. KAMMA is a real-world registry organized by the Eurasian Association of Therapists. The main branch included men and women over 18 years of age with confirmed atherosclerosis in two or more arterial systems and one or more risk factors for atherosclerosis. The start date for patient recruitment was February 1, 2022 and the end date was November 27, 2022. The design included 3 following visits: 1 — baseline, 2 — after 6 months, 3 — after 12 months. Twentyeight research centers were located in 7 federal districts of the Russian Federation, as well as in the Republics of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and Belarus.
Results. A patient population (n=2905) was formed, all of whom had verified CAD. The mean age was 66,0 [59,0; 72,0] years (men — 60,3%). Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol decreased by 20,4% over 12 months, while non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol — by 12,7%. Over 12 months, lipid-lowering therapy did not undergo significant changes. Statin monotherapy was maintained in 83%, of which only 53,7% of patients received high-dose therapy. Combined statin+ezetimibe therapy was used in 12,4%, while statin+ezetimibe+PCSK9 inhibitor — in 4,6%. During the 1-year follow-up, antithrombotic therapy was not enhanced. Low prescription rate of combination therapy with antiplatelet agents (15,7%) and low-dose rivaroxaban and acetylsalicylic acid (7,9%) remained. By the follow-up end, a high incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events (8,8%) was registered in patients included in the KAMMA registry.
Conclusion. Despite the fact that patients with MFA have a very high cardiovascular risk, routine management of these patients is characterized by high clinical inertia. During the 1-year follow-up, lipid-lowering and antithrombotic therapy was not properly strengthened, due to which the target levels of key lipid profile parameters were not achieved and a high rate of major adverse cardiovascular events was observed in patients included in the registry.
- Health information systems (HIS) have significant potential for accumulation and clinical analysis of data.
- For full use of HIS, expert approval of criteria for the application of ICD codes for various clinical types of coronary artery disease is required.
Aim. To assess the possibilities and problems of using health information systems (HIS) to record disease cases and causes of death using ICD-10 codes using coronary artery disease (CAD) forms as an example.
Material and methods. The study combined data from electronic databases of the Main Civil Registry Office and outpatient clinics of the Moscow Oblast. All cases with CAD codes registered as the underlying cause of death (UCD) in outpatient clinics and in medical certificates of cause of death (MCCD) one year before death were included. A total of 3476 deaths.
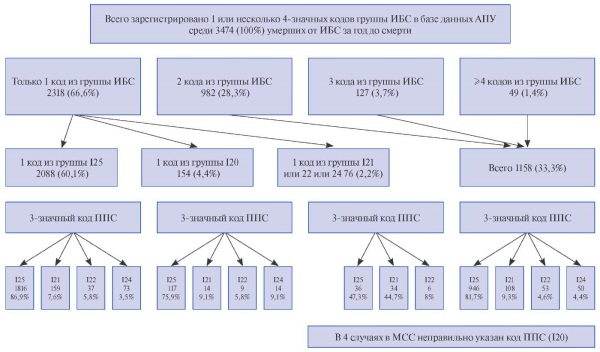
Results. On average, 1,4 four-digit ICD codes from the CAD group (I20-I25) per patient were registered in outpatient clinics per year. More than 1 code from the CAD group was registered in 33,3% of patients. For one conditional disease (CAD), 86 unique consecutive combinations of 4-digit CAD codes were identified, which indicates the changes of the patient's condition over time. Myocardial infarction (MI) as a UCD is indicated in 12,1% of the MCCD (9,1% — I21 and 3% — I22); in 83,9% — one of 7 codes of the chronic forms of CAD group (I25.0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9). Among those who had only codes of the chronic forms of CAD group (I25) indicated in outpatient clinics, 9,6% died of MI. The problems associated with the use of codes for creating registers and their subsequent clinical interpretation are described. In addition to CAD codes, other diseases represented by 4-digit codes (on average, 6,0±4,9 per patient) were registered in the outpatient clinics in 90,7% of patients. Causes of death (Part II of the MCCD) were indicated in 24,3%.
Conclusion. HIS have significant potential for accumulation and subsequent clinical analysis of data, but for full use, expert approval of the criteria for applying codes for various clinical forms of CAD is required.
- High lipoprotein(a) levels doubled the 5-year risk of major cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease, mainly in men — by 2,6 times, while in women the increase was non-significant.
- Quantitative real-time PCR assay of 2-∆∆Сt associated with the number of LPAKIV-2 repeats reliably reflected an increase in risk regardless of sex differences.
- Relative risk of major cardiovascular events in women with coronary artery disease was lower in the upper quartile of apoprotein A compared with the lower one.
Aim. To evaluate 5-year major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and high lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) levels in the Uzbek population.
Material and methods. The study included 216 patients (96 men and 120 women) hospitalized with a diagnosis of "CAD. Progressive angina", in whom MACE (cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction and stroke) was assessed during 5 years of follow-up. The 2-∆∆Сt value, correlating with the number of LPA KIV-2 repeats, was determined in genomic DNA using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).
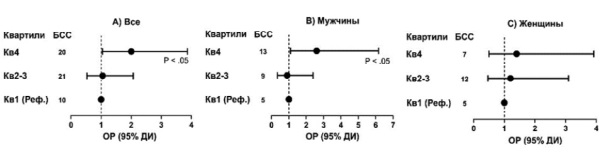
Results. In patients with CAD with elevated Lp(a) in the quartile 4 ≥48 mg/dL, the MACE risk was 2 times higher (relative risk 2,0; 95% confidence interval 1,04-3,87, P<0,05) than in quartile 1 ≤6 mg/dl. Moreover, among men it was 2,6 times higher (P<0,05), while in women — 1,4 times higher without significant difference. In contrast, in the study cohort, the MACE risk in quartile 1 <3,9 of 2-∆∆Сt was 3 times higher than in quartile 4 (>6) (P<0,01) in men, and 3,3 times higher among women (P<0,05). Lp(a) concentration in the examined subjects was inversely dependent on the 2-∆∆Сt value. We also observed a decreased MACE risk in women with high Apolipoprotein A-I (apoA) levels in quartile 4 (>175 mg/dL) versus quartile 1 (<140 mg/dL) with relative risk of 0,30 (95% confidence interval 0,10-0,98, P<0,05).
Conclusion. The 2-∆∆Сt value in the lower quartile associated with a low number of LPA KIV-2 repeats more accurately reflects the MACE risk in women with CAD. Also, the relative risk in women was lower in the upper quartile of apoA compared to the lower one.
ХРОНИЧЕСКАЯ СЕРДЕЧНАЯ НЕДОСТАТОЧНОСТЬ
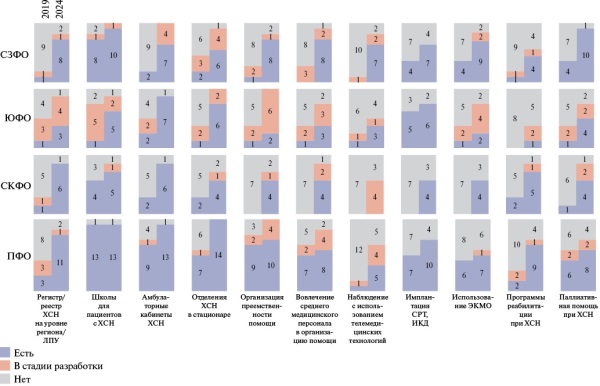
- Over the past 6 years, measures to improve cardiology services have been implemented in the regions of the Northwestern (NWFD), North Caucasian (NCFD), Volga (VFD) and Southern Federal Districts (SFD) under the leadership of the Ministry of Healthcare of the Russian Federation in cooperation with the National Medical Research Centers.
- In 2024, components of health care for patients with heart failure were implemented in 8 out of 11 regions in the NWFD, in all 7 and 14 regions in the NCFD and VFD, respectively, and in 7 out of 8 regions in the Southern Federal District.
- Further development of specialized health care programs for patients with heart failure is required in the regions of the NWFD, NCFD, VFD and SFD with the involvement of territorial multidisciplinary teams to overcome the existing barriers.
In connection with the increase in the prevalence and incidence of heart failure, the development of health care systems for patients with this disease in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation is relevant. Over the past 6 years, measures to improve the cardiology service have been implemented in the regions of the Northwestern, North Caucasian, Volga and Southern Federal Districts under the leadership of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation in cooperation with the National Medical Research Centers. Teams of chief non-staff cardiologists continue to actively participate in updating the regulatory framework, as well as expanding the programs of preferential medication provision as part of providing care to patients with heart failure. In some regions, organizational barriers remain, the elimination of which requires a comprehensive modernization of regional healthcare systems with the involvement of multidisciplinary teams.
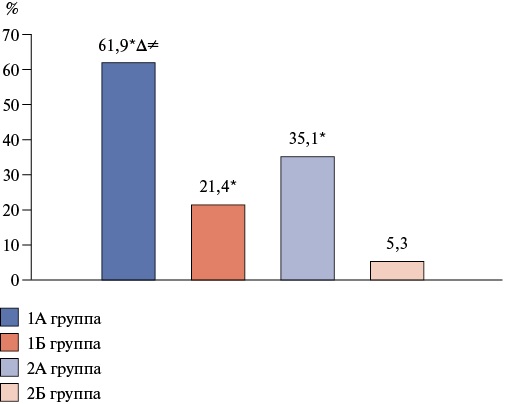
- The incidence of adverse outcomes during 12-month follow-up in patients with HTN aged 80 years and older with a combination of frailty syndrome and heart failure was accompanied by the highest cardiovascular mortality and heart failure-related hospitalization rates, as well as all-cause mortality, which apparently makes it possible to consider the potentiation of the effects of concomitant conditions.
Aim. To assess the frequency of adverse outcomes during 12-month follow-up in hypertensive (HTN) patients depending on heart failure (HF) and frailty syndrome (FS).
Material and methods. The study included 320 patients with HTN, who were divided by HF and FS into following groups: group 1A — patients with HTN, FS and HF (n=84), group 1B — patients with HTN, FS without HF (n=77), group 2A — patients with HTN, HF without FS (n=84), group 2B — patients with HTN and without HF and FS (n=75). The FS was identified using the "Age is not a hindrance" questionnaire, and the incidence of adverse outcomes (composite endpoint and all-cause mortality) was analyzed after 12 months. The composite endpoint was cardiovascular mortality and HF-related hospitalization rate.
Results. In HF, the risk of composite endpoint was 2,9 times higher in FS patients with hypertension (p=0,028), while there was no significant effect on all-cause mortality (p=0,526). In non-FS patients with HTN, HF was accompanied by a 6,6-fold increase in the risk of composite endpoint (p=0,015) and a tendency to an increase in all-cause mortality (p=0,079). FS contributed to an increase in the risk of composite endpoint and all-cause mortality in non-HF patients with HTN by 4 and 3 times, respectively (when comparing groups 1B and 2B), and in patients with HTN and HF — by 76,4% and 49,4%, respectively (when comparing groups 1A and 2A). With a combination of FS and HF, patients with HTN had the highest incidence of composite endpoint (11,7 times) and all-cause mortality (3,1 times) compared with patients with HTN without HF and FS.
Conclusion. HF contributes to a significant increase in the risk of cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization due to HF in hypertensive patients with and without FS. A tendency towards an increase in all-cause mortality was demonstrated in FS patients with HTN and HF. FS increases the incidence of composite endpoint and all-cause mortality in patients with HTN regardless of HF. The combination of FS and HF in patients with HTN increases the risk of composite endpoint and all-cause death to the greatest extent.
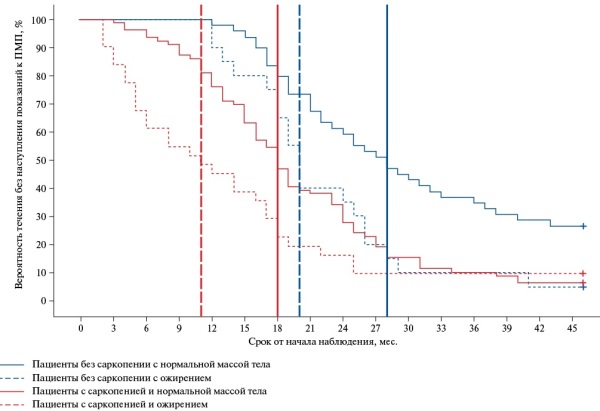
- Body composition disorders affect the need for palliative care in patients with heart failure; in patients without sarcopenia, it is 4 times less than in patients with sarcopenia.
- Muscle mass index to body mass index ratio, functional class, galectin level, Barthel index, and sarcopenia were included in the proportional hazards model for indications for palliative care.
Aim. To assess the need for palliative care (PC) in patients with heart failure (HF) depending on body composition.
Material and methods. The study involved 298 people (115 men and 183 women, mean age — 61 [53;69] years), who were divided into 5 groups depending on body composition — obesity and sarcopenia. Left ventricular ejection fraction, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and galectin-3 markers were determined. Kaplan-Meier analysis was performed to assess survival, while Cox regression — the influence of factors.
Results. The maximum values of the time of need for PC are characteristic of patients without body composition disorders, and the minimum ones are for patients with sarcopenic obesity. According to Cox regression, a significant increase in hazard ratio for PC indications occurrence was revealed as 22,9 times (p<0,001) with an increase in muscle mass index to body mass index ratio (MMI/BMI) by 1; 1,99 times (p<0,001) with an increase in functional class by 1; 1-1,02 times (p=0,002) with an increase in the galectin level by 1 ng/mL; 0,96 times (p<0,001) with a decrease in the Barthel index by 1; and 3,71 times (p<0,001) in the presence of sarcopenia.
Conclusion. The body composition of patients with HF affects the functional activity of the patient, and therefore the need for PC in patients.
COVID-19 И БОЛЕЗНИ СИСТЕМЫ КРОВООБРАЩЕНИЯ
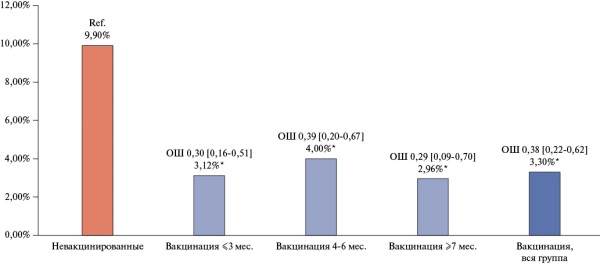
- The acute period of COVID-19 in vaccinated patients is milder than in unvaccinated patients with a smaller volume of lung parenchyma damage, and complications such as bacterial pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome develop less frequently.
- The positive effect of vaccination on the prognosis and patients persists 7 months after vaccination.
- In the population of unvaccinated patients, more often than among vaccinated patients, there are patients with a high risk of an unfavorable prognosis: older age, coronary artery disease, class 3-4 heart failure, atrial fibrillation, chronic kidney disease and anemia.
Aim. To assess the effectiveness of vaccination against Omicron and Delta variants according to the international registry "Dynamics Analysis of Comorbidities in SARS-CoV-2 Survivors" (AKTIV-4).
Material and methods. The AKTIV-4 registry included men and women over 18 years of age with a diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) (oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal swabs, SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers, typical computed tomography performance), undergoing hospital treatment. A total of 3543 patients from 25 medical centers in 7 countries (the Russian Federation, the Republic of Armenia, the Republic of Belarus, the Republic of Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, the Republic of Moldova, and the Republic of Uzbekistan) were included in the AKTIV-4 registry.
Results. The clinical status of patients from the AKTIV-4 registry was more severe than in the AKTIV-1 and AKTIV-2 registries. Patients in the AKTIV-4 registry were older than patients in the AKTIV-1 registry. The inhospital mortality rate in patients in the AKTIV-4 registry was higher (8,41%, p<0,001) than in the population of patients in the AKTIV-1 (7,60%) and AKTIV-2 (4,80%) registries. Of the 3543 patients included in AKTIV-4, 36% were vaccinated. Among the vaccines, Sputnik V (GamCOVID-Vac) was the leader in primary and repeated vaccination, used in 77,8% and 61,0%, respectively. In the population of unvaccinated patients, there were more patients with a high risk of an unfavorable prognosis than in the vaccinated as follows: older age, coronary artery disease, class 3-4 heart failure, atrial fibrillation, chronic kidney disease, and anemia. Unvaccinated patients had a higher volume of lung damage compared to vaccinated patients, and bacterial pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome developed more often. Among those who died in hospital, unvaccinated patients predominated (89,14%). Inhospital mortality for unvaccinated patients was 9,9%, while for vaccinated ones — 3,3% (odds ratio (OR) 0,31 [0,20;0,45], p<0,001). In patients within 3, 4-6, and ≥7 months after vaccination, the mortality rate was 3,12% (OR 0,30 [0,16;0,51], p<0,001), 4,00% (OR 0,39 [0,20;0,67], p<0,001), and 2,96% (OR 0,29 [0,09;0,70], p<0,001). Inhospital mortality of vaccinated patients did not differ significantly depending on the type of vaccine.
Conclusion. Vaccination, primarily with Sputnik V, is an independent predictor of survival in hospitalized COVID-19 patients and reduces the risk of death by 62% according to multivariate analysis.
What is already known about the subject?
- Hypertension (HTN) is associated with a higher susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, a more severe course, which is due to key pathophysiological mechanisms of HTN, such as activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
- At the same time, the direct role of HTN, regardless of age, comorbidities as a risk factor for SARS-COV-2 infection and COVID-19 outcomes, has not been definitively established.
What might this study add?
- It is known that the sympathetic autonomic nervous system is a regulator of immune function; in addition, there is a bidirectional relationship between the immune system and the circadian system of physiological activity of the body, including BP circadian rhythm. We hypothesized that there may be a cause-and-effect relationship between impaired circadian rhythm and chrono-structure of blood pressure and susceptibility to COVID-19.
Aim. To study the effect of hypertension (HTN) on the course of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and to evaluate the impairment of the chrono-structure of 24-hour blood pressure (BP) rhythm as a risk factor of infection in men working in the Arctic on a rotating basis.
Material and methods. In the village of Yamburg (Nadymsky district), 517 medical records of inpatients treated at the medical unit of OOO GAZPROM DOBYCHA YAMBURG in 2020-2021 were retrospectively analyzed by random sampling. Of these, 233 patients with HTN and normal BP had a verified diagnosis of COVID-19. The diagnosis of COVID-19 was based on the detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by polymerase chain reaction. After matching the groups by age, 2 following groups were selected: group 1 — 88 patients with HTN; group 2 — 108 patients with normal blood pressure who had COVID-19, matched by shift work experience. All patients underwent general clinical examinations in the hospital, determination of blood oxygen saturation, chest computed tomography, and electrocardiography. In the group of patients with further COVID-19, before the disease, standard 24-hour BP monitoring and a chronobiological study using computer software to determine BP chronobiological types according to Cugini P. classification (1992).
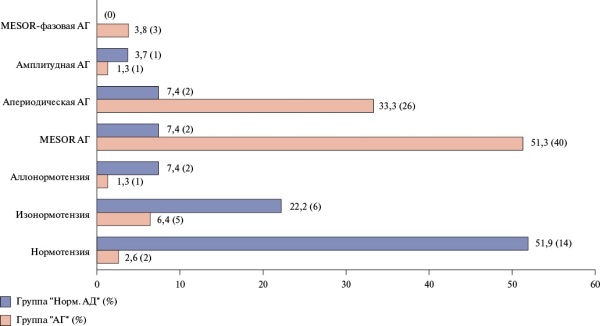
Results. Patients with HTN were significantly more likely to be diagnosed with severe COVID-19 due to the high frequency of hypoxemia, dyspnea at rest upon admission to hospital, prolonged hyperthermia, and lower blood oxygen saturation levels than those with normal BP. Patients with HTN and COVID-19 were more likely to have grade 2 respiratory failure, more often needed prone position, resuscitation, and more often had cardiac arrhythmias. Patients with HTN had significantly higher blood glucose and creatinine levels. Complaints of cough, headache, heart palpitations, heavy feeling in the chest also prevailed in patients with HTN. In patients, regardless of the BP level, normal 24-hour profile for systolic and diastolic BP was observed only in a third of those examined. In 64% of hypertensive patients and 60% of normotensive individuals who subsequently recovered from COVID-19, there was an impaired 24-hour BP profile of the non dipper and night peaker types. In 39,7% of men with HTN and 37,0% of normotensive individuals, there was no 24-hour BP periodicity with a predominance of the high-frequency component (3,4-8,0-hour oscillations) in 24-hour BP rhythm. The conducted correlation analysis revealed a fairly clear inverse correlation between COVID-19 and MESOR (r=-0,339, p=0,0001) and a direct relationship between COVID-19 and the aperiodic chronotype of HTN (r=0,244, p=0,002). In individuals with normal BP, correlation relationships between COVID-19 and the iso-normotension chronotype were revealed (r=0,240, p=0,052).
Conclusion. Working in the Arctic conditions, patients with HTN had more severe clinical manifestations of COVID-19. At the same time, regardless of BP level, the risk of COVID-19 infection in men may increase with an impaired chrono-structure of BP 24-hour rhythm with a predominance of the high-frequency component.
GENETICS IN CARDIOLOGY
What is already known about the subject?
- Ectopic fat depots are not always associated with obesity in general; this dissociation makes studying the distribution of adipose tissue interesting, as well as the influence of genetic/epigenetic factors on this process.
- Many genes and polymorphisms have been identified that are of interest in relation to obesity phenotypes and the distribution of adipose tissue, among them there are genes such as PPARG, VEGF-Aand AGTR1.
What might this study add?
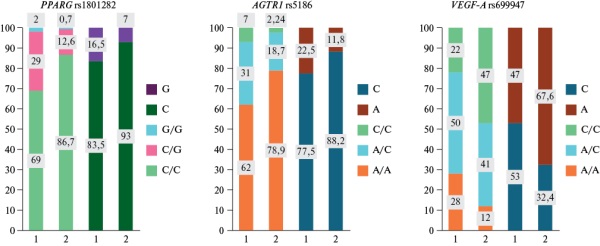
- A following significant difference in the genotype distribution of AGTR1rs5186 polymorphism was found in individuals with any type of obesity compared to patients without obesity: individuals with any type of obesity had a higher frequency of the mutant allele C.
- The distribution of genotypes and the increase in the frequency of the mutant allele C of AGTR1rs5186 polymorphism in groups with isolated EO and mixed obesity (EO+AO), as well as the distribution of alleles and the increase in the frequency of the mutant allele C of VEGF-Ars699947 polymorphism in the group with isolated EO differ from the general population, which is manifested by a deviation from the HWE; this suggests that these single nucleotide polymorphisms can be markers of obesity.
Aim. To assess the association of the allele and genotype frequencies of following single nucleotide polymorphisms: rs1801282 of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG) gene, rs5186 of the angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AGTR1) gene, rs699947 of the vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) gene in patients with various phenotypes of abdominal (AO) and ectopic (EO) obesity.
Material and methods. The cross-sectional study included 100 Caucasian patients (47 men, 53 women, median age 58,5 [50;69] years). All patients underwent chest and retroperitoneal computed tomography with calculation of the volumes of perivascular (PVAT) and pericardial (PAT) adipose tissue, and perirenal fat thickness (PFT). PAT volume ≥3,2 cm3, PVAT volume ≥0,4 cm3, PFT thickness ≥1,91 cm were considered criteria for pericardial (PCO), perivascular (PVO) and perirenal (PRO) obesity. Alleles and genotypes of polymorphic markers of candidate genes were identified in all patients.
Results. In the distribution of genotypes of the polymorphic marker AGTR1 rs5186, statistical significance (p=0,014) was found between the group with any type of obesity and patients without obesity; the distribution of genotypes differed from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) in the EO (p=0,0009) and mixed obesity (p=0,05) groups. With regard to the marker VEGF-A rs699947, a significant increase in the frequency of the mutant allele C (62,5%, 50%, 46,3%, 47,75%, respectively) was found in the EO, AO, and EO+AO groups with any type of obesity compared to the non-obese group (40%) (χ2=10,806; p=0,013). A deviation of the frequency of VEGF-A rs699947 genotypes from HWE was found in the EO group (p=0).
Conclusion. Our data suggest that single nucleotide polymorphisms PPARG rs1801282, AGTR1 rs5186, VEGF-A rs699947 may be associated with fat distribution in the body and be markers of various EO and AO phenotypes. Verification of our hypothesis requires additional studies with the inclusion of larger samples and comparison groups.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY
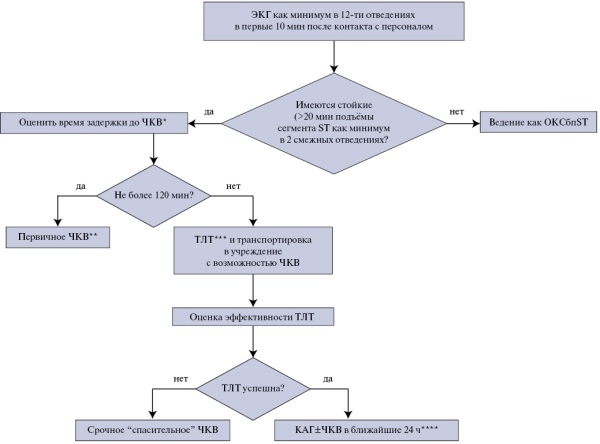
In patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction, primary percutaneous coronary intervention should be performed within 120 minutes after diagnosis if possible. Timely revascularization helps to preserve left ventricular function, minimizing myocardial damage, which subsequently reduces disability and mortality. There are patients for whom this approach cannot be implemented within the specified time frame for a number of reasons. In such a situation, a pharmacoinvasive strategy is recommended, which involves thrombolytic therapy as the first stage. Current treatment strategies for myocardial infarction have been compared many times. An undoubted advantage in Russia is the availability of domestic staphylokinase agent, which has a good efficacy and safety profile, meeting the requirements for fibrin specificity. Thus, research determining the current place of pharmacoinvasive strategy should be continued to optimize thrombolysis and improve the prognosis in patients with myocardial infarction.
- Normotensive patients with intermediate-to-high risk pulmonary embolism (PE) and 30-day mortality have a high risk of hemodynamic instability in the first 72 hours of hospital stay.
- The use of systemic thrombolysis in this group of patients is limited by the high incidence of hemorrhagic complications.
- The study will assess the impact of selective transcatheter thrombolysis on the short-term and long-term prognosis of patients with PE with intermediate-high mortality risk.
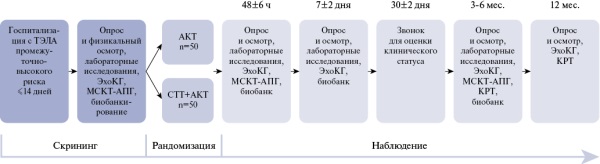
Aim. Comparison of conservative and invasive treatment strategies in patients with intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism (PE) based on a multimodal assessment of efficacy and safety.
Material and methods. This single-center, open-label, randomized, comparative trial will include 100 patients with a verified diagnosis of PE with intermediate-high risk of 30-day mortality. Patients will be randomized 1:1 to standard anticoagulant therapy or selective low-dose alteplase transcatheter thrombolysis. Patients will be followed for 12 months. The primary endpoint is a decrease in the right ventricle to left ventricle ratio by 20% or more from baseline at 48±6 hours after initiation of therapy. There are secondary endpoints: patient hemodynamic instability; ISTH major bleeding; Qanadli index decrease at 48 hours; degree of residual thrombosis with reduced perfusion at 3-6 months; incidence of post-thromboembolic syndrome at 3-6 months; 30-day, 90-day, and 1-year mortality.
Conclusion. The study will provide important clinical data on the short- and long-term efficacy and safety of different treatment approaches in patients with intermediate-to-high-risk acute pulmonary embolism.
- The improvement of 24-hour blood pressure monitoring characteristics is shown with the use of two variants of combined antihypertensive therapy in combination with psychocorrective therapy in hypertensive (HTN) men with anxiety and depressive disorders (ADD) in the andropause period.
- More pronounced improvement of key 24-hour blood pressure parameters, arterial stiffness, central aortic pressure in men with HTN and ADD during andropause were determined with the use of a combination of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor + calcium channel blocker + antidepressant compared to an alternative combination therapy with angiotensin II receptor blocker + calcium channel blocker + antidepressant.
Aim. To evaluate the effectiveness of two variants of combined antihypertensive therapy in combination with psychopharmacotherapy in hypertensive (HTN) men with anxiety and depressive disorders (ADD) in the andropause period.
Material and methods. The study involved 67 men with uncontrolled HTN and ADD in the andropause period, of whom 35 with a median age of 57 [56; 63] years took a combination of "angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor perindopril + calcium channel blocker (CCB) amlodipine + antidepressant (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor) trazodone", and 32 patients with a median age of 58,5 [57; 61] years received "angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) candesartan + amlodipine + trazodone". All subjects underwent 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) at inclusion and after 6 months of therapy, and the most significant prognostic parameters of vascular stiffness and central aortic pressure (CAP) were assessed using the BPLabVasotens hardware complex (OOO Petr Telegin, Russia).
Results. High antihypertensive and vasoprotective efficacy of both variants of combined pharmacotherapy in men with HTN and ADD in andropause was established. However, with the use of the combination of ACE inhibitor + CCB + antidepressant, more pronounced improvement of 24-hour BP profile, arterial stiffness and CAP were observed compared to patients receiving ARBs + CCB + antidepressant.
Conclusion. When comparing the antihypertensive and vasoprotective efficacy of two variants of combined pharmacotherapy in men with HTN and ADD in the andropause period, certain advantages of the combination of ACE inhibitors + CCB + antidepressant were revealed. This was manifested in a more pronounced improvement in ABPM parameters, a decrease in arterial stiffness and CAP, than in patients receiving ARB + CCB + antidepressant.
- PCSK9 inhibitors and inclisiran effectively reduce low-density lipoprotein levels in patients with high, very high, and extreme cardiovascular risk, with the effect noticeable from the first months of treatment.
- Therapy with a PCSK9 inhibitor and inclisiran is well tolerated.
- The single-center, non-randomized study had no endpoints, but the small sample size and short follow-up period do not allow its reliable assessment.
Aim. To compare efficacy and safety of inclisiran, evolocumab and alirocumab in patients with high, very high and extreme cardiovascular risk (according to data from the Federal Research Center for Cardiology and Microbiology, Novosibirsk).
Material and methods. This prospective two-year observational comparative included 53 patients (43 men and 10 women) with an average age of 61,2±4,7 years. They were treated with alirocumab at a dose of 75 mg (n=9) and 150 mg (n=25), evolocumab 140 mg (n=10), and inclisiran (n=9). Two patients were diagnosed with definite familial hypercholesterolemia according to DLCN criteria, while five patients had a myocardial infarction. Lipid profile, transaminase, creatinine, and glucose levels were assessed after 3, 6, 12, and 24 months. The primary efficacy endpoint was achievement of target low-density lipoprotein (LDL) values. The secondary efficacy endpoint was recurrent cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction, stroke, urgent coronary and non-coronary artery revascularization, critical ischemia and lower extremity amputation). New cases of diabetes and atrial fibrillation were also monitored. Safety was assessed based on clinical data and laboratory parameters, such as transaminase, total bilirubin, creatinine and blood glucose levels. The follow-up period ranged from 6 months to 2 years.
Results. Target LDL cholesterol levels for extreme cardiovascular risk were achieved in 21 of 32 patients, and for very high and high risk levels — in 16 of 21 patients. The average LDL level decreased from 3,71 to 1,47 mmol/L during the period of lipid-lowering therapy, while no differences were found between the treatment subgroups. During the two-year follow-up, no endpoints were observed in the study patients. High compliance and good tolerability of all types of treatment with no adverse reactions, including local ones, were noted. None of the patients discontinued therapy.
Conclusion. This single-center study showed that therapy with a PCSK9 inhibitor and inclisiran was well tolerated, and LDL-C reduction was similar to that observed in randomized, placebo-controlled trials.
ANNIVERSARY
CLINICAL GUIDELINES
Russian Society of Cardiology (RSC)
With the participation of: the Association of Cardiovascular Surgeons, the Russian Society of Emergency Medical Care, the Russian Association of Ultrasound Diagnostics Specialists in Medicine (RASUDM)
Approved by the Research and Practical Council of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)