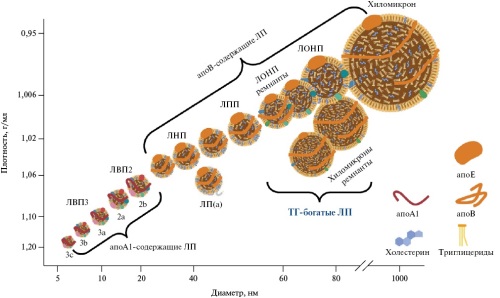
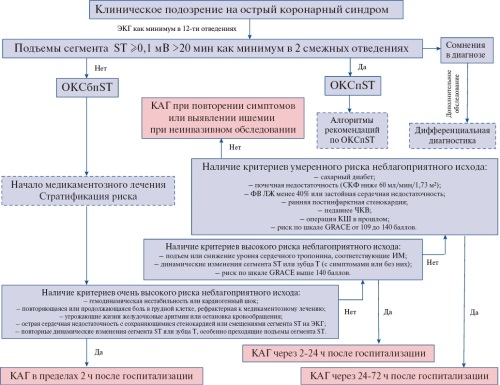
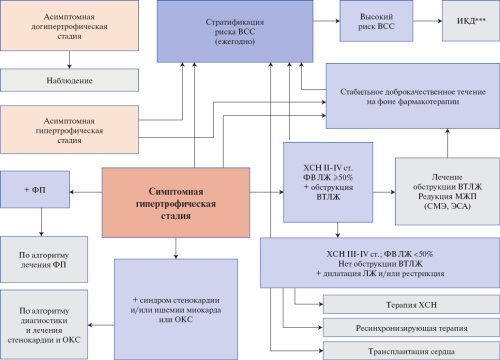
АКТУАЛЬНЫЕ ПРОБЛЕМЫ ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ
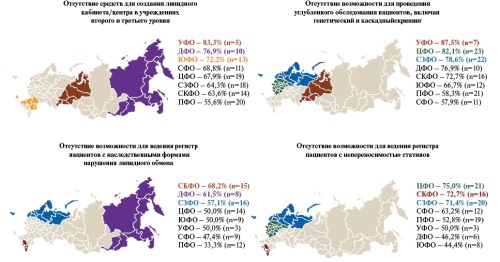
- Among the variety of barriers to the implementation of clinical guidelines for lipid metabolism disorders, there are both general and specific ones for each federal district of the Russian Federation, which can serve as a basis for the development of targeted strategies taking into account regional characteristics.
- The availability of diagnostics and therapy for dyslipidemia varies significantly between federal districts of the Russian Federation.
- Prescription of lipid-lowering therapy remains suboptimal, which prevents the achievement of target levels of atherogenic lipids.
- Insufficient patient awareness of dyslipidemia reduces adherence to therapy.
- Lipid service faces a shortage of resources and the lack of unified approaches, which limits the effective control of dyslipidemia.
Aim. To determine district-specific barriers to the implementation of key points of clinical guidelines on lipid metabolism disorders in practice, with a focus on identifying disagreements and inconsistencies in the perception of problems between health professionals in each district.
Material and methods. Based on the first phase of implementation study, which included survey data from 788 physicians, 124 heads of health facilities and 48 chief consultants from 8 federal districts of the Russian Federation, district-specific barriers were identified through comparative ranking of districts by key points. A discrepancy was revealed between respondents' positions regarding the reasons for insufficiently effective patient management.
Results. Regional differences in the availability of diagnostic and therapeutic options, as well as the management of the lipid service, were determined. The most frequent limitation of in-depth examination of patients with dyslipidemia was noted in the Siberian and Ural districts. Low screening rate for familial hypercholesterolemia is most typical for the Ural and North Caucasian districts. In a number of federal districts of the Russian Federation, the prescription of suboptimal lipid-lowering therapy remains a significant problem, leading to failure to achieve target levels of atherogenic lipids, which is especially pronounced in the Central, North Caucasian and Siberian districts. Insufficient awareness of the need to treat dyslipidemia in patients is especially relevant for the Siberian, North Caucasian and Southern federal districts. Limitation of resources for the lipid service is most often noted in the Ural, Far Eastern and Southern federal districts. Despite a number of common problems, each district faces a unique set of barriers, the causes of which are interpreted differently by medical specialists.
Conclusion. The analysis of district-specific barriers indicates problems both in the implementation of clinical guidelines and in the organization of a seamless service. Based on the first phase of the implementation study, a number of strategies were developed and implemented to eliminate the identified barriers, the effectiveness of which will be assessed as part of a repeat survey in 2025.
Aim. To evaluate the effectiveness of an analytical service with a clinical decision support system (CDSS) in increasing the frequency of monitoring low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in patients with acute cardiovascular events (CVE), coronary artery disease (CAD), or dyslipidemia in the Kemerovo Oblast.
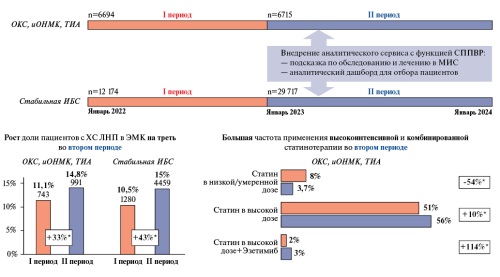
Material and methods. This non-interventional retrospective multicenter study was conducted in 16 health facilities of the Kemerovo Oblast from January 1, 2022 to March 31, 2024. There were main cohort (6694 patients with CVE) and an additional cohort (12174 patients with CAD or dyslipidemia). The study included two following follow-up periods: before (12 months) and after (15 months) the CDSS implementation. The CDSS was implemented through integration into the regional health information system (HIS). Physicians at the automated workplace in the single-window mode in the HIS received recommendations for the examination and treatment of patients according to clinical guidelines and Order 168n, as well as access to an analytical platform for monitoring patients with suboptimal indicators (including LDL-C ³1,4 mmol/L or no data on LDL-C at very high cardiovascular risk). The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients with a single determination of LDL-C levels within 6 and 12 months after the index event.
Results. In the main cohort, the proportion of patients with LDL-C assessment increased from 11,1% to 14,8% (relative change +33%, p<0,001). In the additional cohort, the same indicator increased from 10,5% to 15,0% (relative change +43%, p<0,001). A significant improvement in the completeness of electronic health records with clinical parameters was noted. The proportion of patients not covered by outpatient monitoring decreased in the main cohort from 62,2% to 40,2% (for patients with stroke/transient ischemic attack) and from 41,6% to 28,9% (for patients with myocardial infarction/unstable angina). In the additional cohort, the proportion of patients without outpatient monitoring decreased from 50,6% to 38,9%. Achievement of the target LDL-C level in the additional cohort increased from 10,8% to 14,4% (relative change +34%).
Conclusion. The implementation of the CDSS increases physicians' adherence to clinical guidelines and improves the quality of care for patients with cardiovascular diseases. An increase in the frequency of LDL-C monitoring, visits to specialists, and the intensity of lipid-lowering therapy was noted. The CDSS improves the continuity of care and the quality of outpatient monitoring, as well as identifies problem healthcare areas.
ОБЩЕСТВЕННОЕ ЗДОРОВЬЕ И ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ
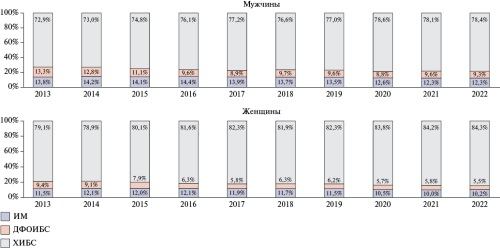
- Cardiovascular mortality has been decreasing over the past 10 years.
- Cardiovascular mortality is 2 times higher among men than among women.
- Myocardial infarction and cerebrovascular accident account for approximately 20% of all cardiovascular deaths.
Aim. To analyze the changes of standardized male and female cardiovascular mortality rates over 2013-2022.
Material and methods. Rosstat data on the mean annual population size and death rate according to C51 form "Deaths by sex and one-year age groups" based on the "Brief nomenclature of causes of death of Rosstat" in 2013-2022 were used. Standardized mortality rates (SMR) were calculated using software using the European population standard by the direct standardization.
Results. In the Russian Federation, a decrease in the SMR for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), coronary artery disease (CAD), alcoholic cardiomyopathy (ACM) and acute cerebrovascular accident (CVA) was registered among men and women with a slight increase in the SMR during the COVID-19 pandemic. The decrease in the SMR for myocardial infarction (MI) was 35%. Mortality from CVDs in men is 2 times higher than in women, from MI — 2,5 times, from other acute forms of CAD — 3 times, from ACM — 4 times. In addition, 40% of the SMR in men and women are chronic CAD forms. The total proportion of MI and CVA, which are the target of regional programs to reduce cardiovascular mortality, does not exceed 20%.
Conclusion. The revealed almost twofold excess of cardiovascular mortality in men compared to women indicates the need for more active preventive work among the male population of the country. When extending regional programs to combat cardiovascular diseases, it should be taken into account that 80% of cardiovascular mortality rate is due to causes other than MI and stroke.
- Demographic and social losses from cardiovascular diseases (CVD) in the Republic of Bashkortostan in 2002-2020 decreased, while economic losses increased.
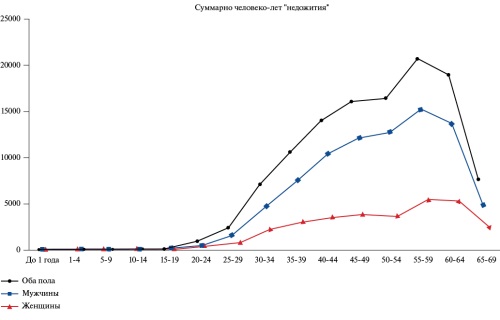
- The sex gap in years of potential life lost begins to form very early, starting from the age of 25.
- Human capital losses from coronary artery disease for the period 2002-2020 decreased by 37,25%, while losses from cerebrovascular disease also decreased, but the decline rate was moderate — 19,50% for the entire period.
Aim. To conduct a dynamic analysis of demographic, social and economic losses from premature cardiovascular mortality in the Republic of Bashkortostan (RB) based on the methodology for calculating the potential years of life lost (PYLL).
Material and methods. The work used official data from Bashkortostanstat for the period 2002-2020, including mortality rates, tables reflecting the distribution of the deceased by sex, age groups and causes of death, population data for the RB in five-year age groups, gross regional product, as well as consumer price indices. The study calculated the absolute PYLL, relative PYLL, and standardized PYLL.
Results. The changes of mortality rates in the Republic of Belarus in the period from 2002 to 2020 developed in line with the all-Russian trend towards a decrease in mortality rates in 2002-2019 from 791,7 to 571,0. In 2020, compared to 2019, an increase of 11,7% was observed. PYLL rates for both all diseases and cardiovascular diseases (CVD) also decreased during the period under review, while the decrease in PYLL rates from CVD occurred much more slowly than in general ones. As a result, the contribution of losses from CVD to the total volume of losses increased. An analysis of the distribution of PYLL from CVD by sex and age showed that a significant sex gap in losses begins to form from the age of 25. The study of PYLL structure showed that the life loss due to mortality from CAD in the period under review decreased by 37,25%, while from cerebrovascular diseases — by 19,5%.
Conclusion. Such an analysis is useful in assessing the effectiveness and planning programs aimed at preventing premature cardiovascular mortality.
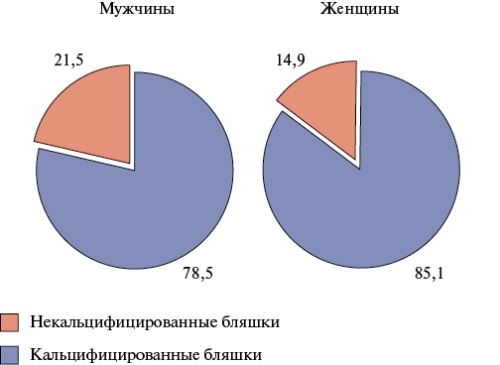
- In an epidemiological study, ultrasound was used to obtain data on the prevalence of carotid artery calcification in the general population aged 25-64 years in a large city of the Siberian Federal District.
- Carotid artery calcification was detected at the age of ≥45 years with a frequency of no more than 5% at the age of 45-54 years, and in 22% of men and 9% of women (in every third and fifth case of carotid atherosclerosis, respectively) among people aged 55-64 years.
- The detection rate of calcified plaques was associated with sex, and among people ≥55 years was higher in men than in women.
Aim. To study the detection rate of carotid calcified plaques in the general population of a large city of the Siberian Federal District.
Material and methods. The data of 1412 people from a representative population sample aged 25-64 years in Tomsk (n=1600) were studied, who underwent an examination according to the ESSE-RF study protocol and an assessment of plaque structure by ultrasound. All respondents signed informed consent to participate in the study. Measurements were carried out according to previously published methods. The presence of an acoustic shadow was considered the criterion for calcified plaques. The level of p<0,05 was considered statistically significant.
Results. The prevalence of calcified plaques in the examined population sample was 5,4% (7,8% in men and 3,7% in women (odds ratio =2,2; p=0,001)), and among people aged 50-64 years — 10,3% (16,7% in men and 6,4% in women (odds ratio =2,9; p<0,001)). Calcified plaques were observed only after 45 years, amounting to 4,9 and 2,1% (p=0,144) at the age of 45-54 years, 22,0 and 8,8% (p<0,001) at the age of 55-64 years, in men and women, respectively. Among individuals with plaques (n=415), calcified plaques were detected in 21,5% of men and 14,9% of women (p=0,08). After 55 years, the proportion of such cases increased from 9,6 to 32,5% in men (p<0,001) and from 8,6 to 18,5% in women (p=0,08). The detection rate of carotid calcified plaques was closely associated with sex, and after 55 years was higher in men than in women.
Conclusion. In the general population aged 25-64 in Tomsk, calcified plaques were detected at the age of ³45 years, and more often in men than in women. The proportion of calcified plaques significantly increased in men after 55 years. Promising areas include studying the prognostic significance of calcified plaques, as well as factors contributing to plaque calcification. The study results can be used in practical healthcare activities, in research planning, and in the development of preventive technologies.
STRESS IN THE POPULATION
- Among individuals of both sexes with high anxiety levels, leptin levels were one and a half times higher than in individuals with low anxiety levels.
- There is a positive correlation between blood leptin and high levels of trait anxiety (TA), a positive correlation between the L/A index and high levels of TA for individuals of both sexes, and a negative correlation between adiponectin and high levels of TA for both sexes and for women.
Aim. To determine the associations of serum adipokines (leptin, adiponectin, leptin/adiponectin index (L/A)) and trait anxiety (TA) in individuals aged 25-44.
Material and methods. This cross-sectional survey of a random representative sample of individuals aged 25-44 in the Oktyabrsky District of Novosibirsk was conducted at the Research Institute of Internal and Preventive Medicine, a branch of the Institute of Cytology and Genetics, during 2013-2016. A total of 933 persons (43,7% men) were examined (response rate 71% of 1314 respondents). General examination and medical history collection were conducted using standard methods included in the WHO MONICA-psychosocial program. TA was assessed using the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Biochemical research was performed in the Laboratory of Clinical Biochemical and Hormonal Studies of Internal Diseases.
Results. Among individuals with a high level of anxiety, there are the highest median levels of serum leptin (6573,7 pg/ml) than with a moderate (5017,7 pg/ml) and low
(4171 pg/ml) levels of anxiety. The median L/A index is higher with a high level of TA of 167,7 than with a moderate (74,5) and low (72,2) TA (p=0,002). Median serum adiponectin levels were lower among individuals with high anxiety (33,2 μg/ml) compared to those with moderate (38,9 μg/ml) and low (40,8 μg/ml) anxiety levels. A positive correlation was found between TA and leptin and L/A index, as well as a negative correlation between TA and adiponectin.
Conclusion. Associations were found between high TA and elevated leptin levels, the leptin/adiponectin ratio, and lower adiponectin levels in individuals aged 2544 years.
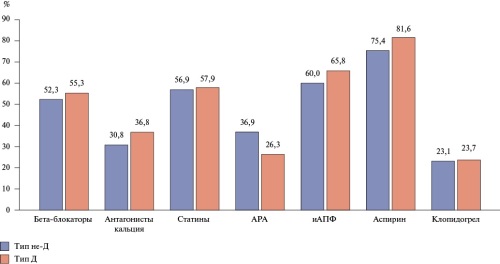
- Type D personality has prognostic value in long-term follow-up of patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
- Patients with CAD and type D personality are more likely to undergo repeat PCI and develop a combined endpoint in a three-year period than patients without type D personality.
- In patients with CAD, subjective improvement 3 years after PCI was noted more often in patients with non-type D than in type D personality.
Aim. To study the prognostic value of type D personality on the three-year prognosis in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Material and methods. The study included 112 patients hospitalized for preparation for elective PCI. All patients underwent a standard preoperative examination. Additionally, the psychological status of patients was assessed (determination of type D personality, assessment of the level of anxiety and depression). Remote results were assessed after 3-year follow-up. The incidence of a combined endpoint (death, nonfatal myocardial infarction and stroke, myocardial revascularization) was assessed in the group without (n=65) and with type D personality (n=38).
Results. Type D personality was detected in 37% of patients. Subjective improvement 3 years after PCI was noted in 86,2% of patients with non-type D and 68,4% with type D personality (p=0,032). Repeat PCI was performed more often in patients with type D (10,5%) than without type D personality (1,5%; p=0,041). The incidence of a combined endpoint was higher in type D than in non-type D patients (21,1% and 7,7%, p=0,04).
Conclusion. The study results highlight the need for individualized behavioral interventions in patients with coronary artery disease with manifestations of psychological distress.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY
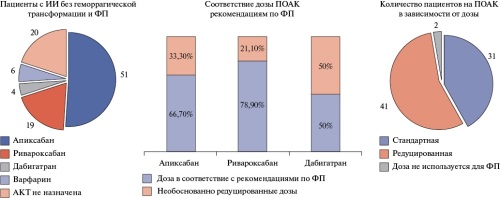
- 30,8% of patients with recurrent ischemic stroke (IS) were diagnosed with atrial fibrillation for the first time.
- No differences in the risk of bleeding were found between patients with and without hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic stroke (p=0,652).
- All patients participating had indications for anticoagulant therapy, however, in real-world practice, these drugs were prescribed in only 78% of cases.
Aim. To analyze anticoagulant therapy (ACT) in patients hospitalized with ischemic stroke (IS) and nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AF) in neurological departments, based on a subanalysis of the ACT registry of patients with AF treated in multidisciplinary hospitals of the North Caucasus Federal District.
Material and methods. Patients were recruited from January to December 2018. A total of 2667 clinical records were analyzed; 118 patients with IS and AF were included in the study. In all patients, the risks of thromboembolic and bleeding events were calculated using the CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores. In addition, examination data and prescribed therapy, including ACT, were studied.
Results. Of the 118 patients with IS included in the study, 106 (89,8%) had a recurrent event. In 30,8% of patients with recurrent ischemic stroke, AF was registered for the first time. The included patients were characterized by a high risk of ischemic (CHA2DS2-VASc 4,0 [4,0; 5,0] points) and moderate risk of bleeding (HAS-BLED 2,0 [1,0; 2,0] points) events. Also, 21,2% of patients received triple antiplatelet therapy for percutaneous coronary intervention preceding the index event. Hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic stroke occurred in 18 (15,3%) patients. ACT was prescribed to 80% (n=80) of patients with ischemic stroke without hemorrhagic transformation and 66,7% (n=12) of patients with hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic stroke. Direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC) were prescribed to 92,5% (n=74) of patients with ischemic stroke without hemorrhagic transformation and 91,7% (n=8) of patients with hemorrhagic transformation of ischemic stroke. Most often, factor Xa inhibitors were prescribed. In 51,2% (n=41) of cases, patients with ischemic stroke without hemorrhagic transformation were prescribed reduced anticoagulant doses, while the dose reduction was justified in half of the cases. Thus, among patients with ischemic stroke without hemorrhagic transformation and AF, ACT was prescribed in accordance with guidelines to 57% of patients.
Conclusion. According to the study, anticoagulants are under prescribed to patients with IS and AF. In real-world practice, physicians prefer DOAC in reduced doses. Despite the lack of guidelines on the timing of ACT initiation in patients with hemorrhagic transformation of IS, anticoagulants are prescribed to two thirds of such patients.
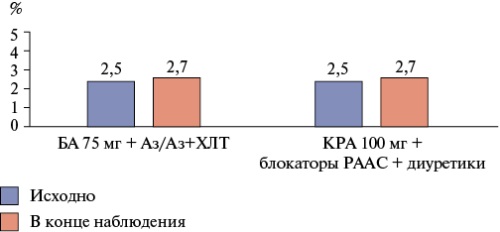
Aim. To compare clinical outcomes in patients with hypertension and atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) prescribed a combination of buffered acetylsalicylic acid (BA) (Cardiomagnyl®) + Azilsartan/Azilsartan+chlorthalidone (Edarbi/Edarbi Clo®) or enteric-coated acetylsalicylic acid (ECA) + reninangiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blockers without diuretics or the most common combinations with diuretics within a real-world practice.
Material and methods. Information accumulated in the predictive integrated analytics platform containing anonymized electronic medical records of 39935673 patients was used. According to the inclusion criteria, medical data from electronic medical records of 61696 patients were taken into the study. The data of 2120 patients with atherosclerotic CVDs were included and divided into 2 groups: BA (Cardiomagnyl® 75 mg) + Azilsartan or Azilsartan + chlorthalidone (main group) or ECA and other RAAS blockers and diuretics: ECA 100 mg + RAAS (angiotensin receptor blockers/angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors) ± hydrochlorothiazide/indapamide (comparison group). Propensity score matching was performed. Comparable groups were generated taking into account 11 parameters. The combined endpoint with 4-major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) (myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, hospitalization for CVD, all-cause death) was considered as the primary endpoint.
Results. Comparison of the groups by achieving primary endpoint showed a significantly lower number of 4-MACE in patients of the main group. The risk of PCT was 28% (p=0,006) lower in the main group. In the main group, there were significantly fewer myocardial infarctions, ischemic strokes, any-cause deaths, as well as the risks of its achievement by 83%, 56% and 69%, respectively. There was a tendency towards a lower number of hospitalizations for CVD in the main group (p=0,08). In both groups, there was a significant (p<0,001) and comparable blood pressure decrease. Decrease in total cholesterol (Δ -0,26±1,0 mmol/l compared to Δ -0,13±1,1 mmol/l, p<0,001) and increase in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (Δ 0,13±0,3 mmol/l compared to Δ 0,02±0,3 mmol/l, p<0,001) was significantly greater in the main group. Multidirectional changes of glucose levels were noted (p<0,001). In the main group, it decreases (Δ -0,14±2,2 mmol/l, p<0,001), while in the control group, on the contrary, it increases (Δ 0,08±2,2 mmol/l, p=0,001).
Conclusion. Therapy for asthma in combination with azilsartan medoxomil/ azilsartan medoxomil + chlorthalidone (Cardiomagnyl® 75 mg + Edarbi/Edarbi Clo®) has shown greater efficacy in preventing cardiovascular events compared to therapy with a combination of ECA with other RAAS blockers and diuretics in real-world practice.
PROGNOSIS AND DIAGNOSTICS
- The combination of atrial fibrillation and coronary artery disease significantly worsens the course of both diseases.
- Mathematical modeling methods allow for highly reliable and effective prediction of diseases with the identification of individual risks.
- This study presents one of the options for developing a method for assessing the probability of atrial fibrillation in patients with coronary artery disease, which can be used in practical healthcare.
Aim. To create a method for assessing the probability of atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
Material and methods. Our openlabel, continuous, retrospective, nonrandomized study included data from female and male patients (n=181) with a diagnosis of CAD who were treated at the City Clinical Hospital № 1 (cardiology department) in Novosibirsk for CAD from September 2022 to September 2023. Based on the data obtained, models for predicting the probability of AF detection were developed.
Results. Prognostic models of AF risk in patients with CAD were constructed. The model with explanatory variables (left ventricular ejection fraction, hypertension, highdensity lipoprotein level, GG variant of the interleukin6 gene) showed a sensitivity of 84% and a specificity of 92% in a leaveoneout cross validation.
Conclusion. The constructed prognostic method for assessing the risk of AF in patients with CAD has good prognostic value and is quite easy to use, including for practical healthcare physicians.
- The intensity of inflammatory response in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) with new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) after percutaneous coronary intervention is significantly higher than in STEMI without cardiac arrhythmia.
- The highest level of inflammatory response indicators was recorded in patients with postoperative AF and TIMI flow grade <3.
- Based on the ROC analysis, threshold values of inflammatory response indicators were identified, deviation from which allows them to be classified as potential predictors of postoperative AF.
- The prognostic resource of the novel inflammatory response indicators proposed by the authors (neutrophil/eosinophil ratio (NER) and neutrophil/basophil ratio (NBR)) was comparable with the classical ones (NLR, SII, SIRI, AISI). The prognostic value of PLR and MLR was significantly lower.
Aim. To assess the predictive potential of inflammatory response indicators for risk stratification of newonset atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with STelevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Material and methods. We analyzed data from 4152 electronic health records of patients with STEMI (2858 men and 1294 women). Two following groups were identified: the first group included 3781 (91,1%) patients without cardiac arrhythmia (CA), while the second group included 371 (8,9%) patients with newonset AF after PCI (POAF). The state of coronary flow after PCI was assessed using the thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) score. Previously developed (neutrophil/lymphocyte (NLR), platelet/lymphocyte (PLR), monocyte/lymphocyte (MLR), systemic immune inflammation index (SII), systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI) and systemic inflammation total index (AISI)) and novel inflammatory response indicators (neutrophil/eosinophil ratio (NER) and neutrophil/basophil ratio (NBR)) were calculated.
Results. In patients with STEMI with AF and without CAs after PCI with different TIMI levels indicated more pronounced inflammatory response changes with a combination of POAF and TIMI <3. The highest predictive potential for POAF was demonstrated by neutrophil rate >75% (odds ratio (OR)=2,57; AUC=0,779), NLR >6,29 (OR=2,61; AUC=0,757), eosinophil rate <0,21% (OR=2,74; AUC=0,739), AISI (OR=2,14; AUC=0,737), NBR (OR=2,29; AUC=0,727) and NER (OR=2,49; AUC=0,725). MLR and PLR had lower predictive power.
Conclusion. In patients with STEMI and POAF, the intensity of the systemic inflammatory response is significantly higher than in individuals without CAs. The prognostic potential of the novel inflammatory response indicators (NER and NBR) was comparable to the classical ones (NLR, SII, SIRI, AISI).
EXPERT CONSENSUS
CLINICAL GUIDELINES
Russian Society of Cardiology (RSC)
With the participation of: the Association of Cardiovascular Surgeons, the Russian Society of Emergency Medical Care, the Russian Association of Ultrasound Diagnostics Specialists in Medicine (RASUDM)
Approved by the Research and Practical Council of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
Russian Society of Cardiology (RSC)
With the participation of: the Association of Cardiovascular Surgeons, the Russian Society of medical geneticists Approved by the Research and Practical Council of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)