ANNIVERSARY
ORIGINAL STUDIES
- In patients with initial and moderate coronary atherosclerotic changes and normal BDNF concentrations, elevated levels of TrkB receptors are detected, which have a protective role in vascular endothelium.
- In patients with severe coronary atherosclerosis, two variants of the BDNF/TrkB axis have been identified:
- Decreased BDNF and increased TrkB levels were associated with low VEGF and increased IL-6, indicating activation of systemic inflammation.
- Elevated levels of BDNF-TrkB are associated with high expression of VEGF, indicating activation of angiogenesis and/or vulnerable plaque, and may be a predictor of cardiovascular events.
Aim. To study the serum content of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and tyrosine kinase receptor B (TrkB) in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and evaluate the relationship of BDNF/TrkB signaling with the severity of coronary atherosclerosis, systemic inflammation (IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α) and angiogenesis (VEGF).
Material and methods. The study included 99 patients with stable CAD who underwent coronary angiography and 30 healthy volunteers. Coronary atherosclerosis was assessed using the Gensini score (GS). In blood serum, the concentrations of BDNF, TrkB, VEGF, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α were determined using the enzyme immunoassay. Cluster, correlation, and regression analyzes were used.
Results. In patients with CAD, a wide range of variations in BDNF concentrations was observed. To determine homogeneous groups using the k-means clustering, three clusters with different BDNF/TrkB axis vectors were identified. Patients differed in the severity of coronary atherosclerosis, the manifestation of the inflammatory reaction, and the intensity of angiogenesis. In patients with initial and moderate atherosclerotic changes in the coronary arteries, a normal concentration of BDNF and an increased level of TrkB (22,35/1,18 ng/ml) were noted. In patients with severe coronary atherosclerosis, two different BDNF/TrkB variants have been identified. Decreased BDNF and increased TrkB (6,0/1,52 ng/ml) were associated with low VEGF and increased IL-6. Elevated BDNF and normal TrkB values (26,95/0,96 ng/ml) were characteristic of patients with high VEGF expression, indicating angiogenesis activation and/or vulnerable plaques. A direct relationship between BDNF and VEGF (r=0,536, p<0,001) and an inverse relationship with TrkB (r=-0,301, p=0,019), IL-6 (r=-0,306, p=0,002) was revealed. TrkB levels were correlated with TNF-α (r=0,403, p=0,001). Regression analysis showed that BDNF expression is influenced by TrkB (β=-0,237, p=0,009), VEGF (β=0,490, p<0,001), IL-6 (β=-0,339, p<0,001).
Conclusion. In patients with stable CAD, different levels of BDNF/TrkB expression were found, which were associated with coronary atherosclerosis severity. BDNF/TrkB signaling is involved in the regulation of inflammation and angiogenesis in stable CAD.
- Patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in combination with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease are characterized by a predominance of a high thrombotic load, a higher level of transaminase and liver dysfunction markers.
- The main condition for these differences is steatohepatitis, which determines high troponin level and is a predictor of a high thrombotic load.
Aim. To assess the characteristics of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in patients with metabolic syndrome (MS) in the presence and absence of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD).
Material and methods. A total of 144 patients with STEMI and MS, admitted for primary coronary angiography and percutaneous intervention (PCI): 71 patients with MAFLD (group 1, age 62,9 (59,9;66,0) years, 17 women); 73 patients without MAFLD (control group, age 63,2 (59,1;66,8) years, 17 women). The examination program included transient hepatic elastography, determination of cardiac troponin I (cTnI) upon admission (cTnI-1) and after 24 hours (cTnI-24), mean platelet volume (MPV), transaminases, gamma-glutamyl transferase, concentration of cytokeratin-18 (CK-18) fragments.
Results. Patients with STEMI in combination with MAFLD are characterized by the predominance of a high thrombotic load (TIMI thrombus grade 5, p=0,048), requiring two-stage PCI (p=0,018), an increase in the platelet count and MPV, a decrease in the resolution of ST elevation after primary PCI, a higher transaminase and liver dysfunction markers’ level. The main condition for these differences is steatohepatitis, which determines significant troponin elevation (p<0,01) and is a predictor of high thrombus load (p=0,016), increased MPV (p=0,044) and a factor of adverse events during 18 months after acute coronary syndrome (p=0,00035). The inclusion of the CK-18 criterion in the multivariate model makes it possible to improve the quality of the initial clinical model for predicting subsequent coronary events in the case of STEMI-MAFLD combination with an increase in the area under the ROC curve from 0,788 (95% confidence interval (CI), 0,69-0,89) to 0,648 (95% CI, 0,52-0,78) (DeLong test, p=0,044).
Conclusion. MAFLD in patients with STEMI is combined with an increase in the severity of coronary thrombosis and difficulties in primary PCI, the main condition of which, as well as adverse events after acute coronary syndrome, is steatohepatitis.
- Postoperative atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common complication after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery.
- The pathogenetic mechanisms of the occurrence and development of postoperative AF are complex and are still not fully understood.
- Studying the extracellular matrix (ECM) components will help expand understanding of the nature and severity of myocardial remodeling in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease and evaluate the relationship between ECM proteins and AF after CABG.
Aim. To evaluate the serum fibronectin level in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease, and to identify the relationship of fibronectin level with atrial fibrillation (AF) developed in the hospital after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and types of left ventricular (LV) structural remodeling.
Material and methods. This prospective observational study of 80 patients after elective CABG at the Cardiac Surgery Department № 1 of the N. V. Sklifosovsky Research Institute for Emergency Medicine from October 2020 to May 2022. The groups were divided depending on the development of AF after CABG surgery (19 patients with AF developed in the hospital after CABG (up to 10 days), 61 patients — control group). All patients underwent a general clinical examination and transthoracic echocardiography, with estimation of left ventricular remodeling type. Serum fibronectin level was determined by enzyme immunoassay using the Fibronectin agent (Technozym, Austria).
Results. The median fibronectin values in the group with AF was 110,10 [86,86; 134,00] mcg/ml versus 120,90 [92,01; 161,50] µg/ml of the comparison group (p=0,19). The following LV patterns were observed: normal LV geometry (NLVG) — in 1 patient (5,26%), concentric LV remodeling (CLVR) — in 3 patients (15,79%), concentric LV hypertrophy (CLVH) — in 10 patients (52,63%), eccentric LV hypertrophy (ELVH) — in 5 patients (26,32%). In the group without AF, 25 patients (40,98%) were diagnosed with NLVG, 26 patients (42,62%) — CLVR, 6,56% (n=4) — CLVR, while ELVH was diagnosed in 6 patients (9,84%). Differences in geometry types between groups were significant (p<0,0001). Multivariate analysis adjusted for gender, age, cardiopulmonary bypass time, the predictive value remained for CLVH — odds ratio 15,83 (95% confidence interval, 4,0821,442,00; p=0,0001) and ELVH — odds ratio 5,17 (95% confidence interval, 1,36519,573; p=0,015). A further study showed that fibronectin <116,496 µg/ml with a sensitivity of 78% and specificity of 53% is associated with CLVH (p=0,006) in patients of both groups.
Conclusion. Fibronectin <116,496 µg/ml is associated with CLVH in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease (sensitivity 78%, specificity 53%; p=0,006).
- Arrhythmia against the background of undifferentiated connective tissue dysplasia (UCTD) is characterized by a predominance of premature supraventricular and ventricular contractions.
- In young patients with arrhythmia due to UCTD, speckle-tracking echocardiography revealed a local decrease in left ventricle longitudinal strain, confirming structural myocardial changes with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction.
- The relationship of systolic longitudinal strain with premature ventricular contractions and mitral valve prolapse requires further in-depth study in a cohort of patients with UCTD to optimize treatment and preventive measures.
Aim. To evaluate the left ventricular longitudinal strain in patients with arrhythmia and undifferentiated connective tissue disease (UCTD).
Material and methods. This cross-sectional comparative study included young patients with arrhythmia and UCTD (43 men and 84 women; mean age, 30,82±8,17 years (group 1, n=127)). The control group included volunteers with single phenotypic characteristics of UCTD, comparable in age and sex (9 men and 21 women, mean age, 34,13±6,87 years (group 2, n=30)). A standard clinical examination, 72-hour electrocardiographic monitoring, and speckle-tracking echocardiography were performed.
Results. Patients of group 1 were characterized by lower global systolic longitudinal myocardial strain compared to the control group: -22,96% [-24,56%;-21,50%] in group 1 vs -24,73% [-25,25%; -23,84%] in group 2 (p=0,016). A local decrease in longitudinal myocardial strain (in two or more segments) was noted in 62,2% of patients in group 1 and 13,3% of patients in group 2 (p=0,025). In group 1, a relationship was revealed between class I premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) and a longitudinal strain decrease in the medial anterior (r1=0,253, p=0,004) and apical anterior (r1=0,253, p=0,004) segments, as well as between class V PVCs and strain decrease in the basal lower (r1=0,215, p=0,021) and middle anterior (r1=0,211, p=0,023) segments. In addition, there was a moderate correlation between mitral valve prolapse (MVP) and a decrease in longitudinal systolic strain in the basal inferolateral (r1=0,405, p=0,041) and basal anterior (r1=0,519, p=0,003) segments.
Conclusion. Local decrease in left ventricular longitudinal systolic strain in association with arrhythmia and MVP in patients with UCTD makes it possible to recommend speckle-tracking echocardiography for early non-invasive assessment of myocardial remodeling in this cohort of patients.
НАБЛЮДАТЕЛЬНЫЕ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ
Aim. To evaluate the effectiveness of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) drugs for secondary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) in clinical practice and compare the effectiveness of the Cardiomagnyl with other ASA drugs.
Material and methods. This observational, non-interventional, retrospective study included data from electronic medical records (>18 million) of 18199 patients with ASCVD who were divided into 2 following groups: patients who received ASA 75100 mg (n=9784) and patients who did not receive ASA (n=8325). The prescription rate of ASA, the choice of the first drug, the duration of ASA therapy, the frequency of switching ASA during treatment, and the choice of the second ASA drug when changing therapy were assessed. Due to the heterogeneity of patients in the above groups, to assess the clinical outcomes, propensity score matching was performed and comparable groups were selected to evaluate the effectiveness of ASA drugs 75-100 mg in patients with ASCVD (n= 427) in comparison with patients not receiving ASA (n=427) and to assess the effectiveness of Cardiomagnyl 75 mg (n=1308) in comparison with enterosoluble ASA 100 mg (CRA) (n=1308) taking into account 24 parameters.
Results. The average proportion of patients with ASCVD taking ASA drugs was 58%. During treatment, 54% of patients underwent a change in drug therapy from one ASA drug to another. The prescription rate of Cardiomagnyl as a first-choice drug was 33%, and as a second drug when changing therapy — 21%. The duration of Cardiomagnyl therapy was the longest compared to other ASA drugs and amounted to 16,3 months. The incidence of ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction and major adverse cardiovascular events in the group of patients who received ACS 75-100 mg was significantly lower than in patients who did not take ASA drugs and amounted to 4,7% vs 8,7%, 0,9% vs 3,3%, 5,6% vs 11,9%, respectively. Significantly lower incidence of unstable angina (0,8% vs 2,0%), myocardial infarction (1,5% vs 3,9%) and major adverse cardiovascular events (5,4% vs 7,8%) in group of patients who received Cardiomagnyl 75 mg as opposed to enterosoluble ASA.
Conclusion. Significant advantages of buffered ASA (Cardiomagnyl) were revealed in comparison with enterosoluble ASA in clinical practice.
Published studies demonstrate insufficient implementation of clinical guidelines into actual clinical practice. Successful implementation of diagnostic and treatment guidelines for patients with lipid metabolism disorders directly depends on the identification of barriers and timely application of strategies to overcome them. A three-level remote structural questionary of healthcare quality for patients with dyslipidemia involved practitioner, heads of outpatient medical organizations and chief outpatient specialists to identify key barriers to implementation and compliance with clinical guidelines in real world setting. The obtained data in combination with implementation science approaches will facilitate development of strategies aimed to improvement of compliance with the guidelines for the management of patients with lipid metabolism disorders in practice.
Aim. To evaluate the effectiveness of PCSK9 inhibitors (alirocumab, inclisiran and evolocumab) in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and failure to achieve the target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level for the period from November 21, 2022 to December 31, 2023.
Material and methods. For the observational study, 50 patients were included in the inclisiran therapy group and 30 patients in the control group (patients with ASCVD receiving PCSK9 inhibitors (alirocumab, n=1; evolocumab, n=29)). All study participants had their anamnestic data analyzed, and initially underwent electrocardiography, echocardiography, extracranial and lower limb Doppler ultrasound, and laboratory tests (complete blood count, biochemical blood tests, lipid profile). Three medical organizations of the Moscow State Healthcare System participate in the study.
Results. Interim data are presented to evaluate the effectiveness of PCSK9 targeted therapy in patients with ASCVD, obtained 3 months from the study start. The comparison groups were comparable in main clinical characteristics. When analyzing the lipid-lowering effect of inclisiran in the examined patients with ASCVD, LDL-C level significantly decreased from 2,53±0,10 mmol/l to 110±0,08 mmol/l (by 56,5%), p<0,0001, while the target LDL-C level <1,4 mmol/l was achieved by 77,5% of the subjects. Analysis of the lipid-lowering effect of alirocumab/evolocumab showed a significant LDL-C decrease from 2,48±0,16 mmol/l to 1,07±0,11 mmol/l (by 56,8%), p<0,0001.
Conclusion. The use of PCSK9 targeted therapy (alirocumab or inclisiran or evolocumab) in patients with ASCVD in Moscow make it possible to achieve target LDL-C levels, which are indicated in clinical guidelines, by 3 months.
- With different COVID-19 variants, there were differences in clinical and demographic parameters and comorbidities of patients.
- With different COVID-19 variants, different mortality rates were observed in the long-term (18 months) after hospitalization.
The viral infection and pandemic of coronavirus infection 2019 (COVID-19) was characterized not only by high morbidity and in-hospital mortality, but also by an increase in the mortality of patients after hospital discharge. At the same time, differences were noted in hospitalization rate, the number of complications and mortality of patients, and mortality rate between different pandemic waves from 2020 to 2023.
Aim. To compare the 18-month post-hospital mortality rate of patients between three COVID-19 variants (Alpha, Delta and Omicron).
Material and methods. In this prospective, single-center, non-randomized continuous study, 2400 medical records of patients with the Alpha variant (2020), 1826 with the Delta variant (2021) and 997 with the Omicron variant (2022) were analyzed. The end point was all-cause mortality during the follow-up period.
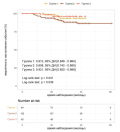
Results. There were following differences in clinical and demographic characteristics in the context of COVID-19 strains: more women were hospitalized in the Delta and Omicron waves; in the Omicron wave, patients were older. Also, comorbid patients were more common with the Delta and Omicron variants than with the Alpha (in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypertension and heart failure), but chronic kidney disease was more common with the Alpha and Omicron variants. The groups differed significantly in mortality, with the maximum being with Delta and the minimum with Omicron, and the maximum mortality with Delta was observed in the first 90 days after discharge. Between 12 and 18 months, survival estimates decreased most for patients hospitalized in the Delta wave, which is determined by the risk of long-term cardiovascular consequences.
Conclusion. Clinical and demographic differences between patients with different COVID-19 variants, as well as a significant difference in the mortality rate of patients of different waves, emphasize the importance of a personalized approach to treatment and long-term post-hospital monitoring.
- Patients over 70 years of age with myocardial infarction (MI) in hospital are recommended to be diagnosed with frailty syndrome using screening questionnaires.
- Predictors of poor prognosis within 12 months after MI in people over 70 years of age were identified.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention during the current hospitalization reduced the risk of adverse outcomes within 12 months after MI in patients over 70 years of age.
Aim. To develop a predictive model of the risk of adverse outcomes within 12 months after myocardial infarction (MI) in patients over 70 years of age with frailty syndrome.
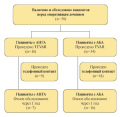
Material and methods. This prospective observational study included 92 patients over 70 years of age with MI who were treated in the cardiology departments of Samara State Medical University Clinics from 2020 to 2021. Levels of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and growth stimulation expressed gene 2 (ST2) were determined in serum by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay on day 5 of hospitalization. Frailty syndrome was identified 5th day of hospitalization using "Age is not a hindrance" questionnaire. The observation period was 12 months. The end point was the adverse event occurrence (all-cause death, cardiovascular death, recurrent MI, cerebrovascular accident). Statistical nonparametric methods, correlation analysis, ROC analysis, and logistic regression were used.
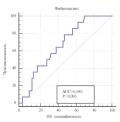
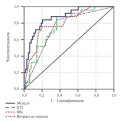
Results. There are following significant predictors of unfavorable outcome within 12 months after MI in patients over 70 years: age over 80 years (odds ratio (OR) 5,57, 95% confidence interval (CI) 2,07-14,96, with p=0,001), history of MI (OR 3,96, 95% CI 1,36-10,26, at p<0,05), CKD-EPI glomerular filtration rate <55 ml min/1,73 m2 (OR 4,05, 95% CI 1,55-10,57, with p=0,004), pulmonary artery systolic pressure above 38 mm Hg (OR 4,5, 95% CI 1,69-11,96, with p=0,003), Simpson's left ventricular ejection fraction <45% (OR 12,21, 95% CI 4,2-35,57, with p<0,001), as well as "Age is not a hindrance" questionnaire score ≥3 (OR 9,62, 95% CI 2,96-31,25, with p<0,001), Charlson Comorbidity Index score ≥6 (OR 10,4, 95% CI 2,84-38,12, with p<0,001), NT-proBNP ≥1400 pg/ml (OR 7,09, 95% CI 2,53-19,89, with p<0,001) and ST2 ≥8,2 ng/ml (OR 9,13, 95% CI 2,79-29,89, p<0,001). Percutaneous coronary intervention during the current hospitalization reduced the risk of adverse outcomes (OR 0,24, 95% CI 0,09-0,69, p=0,015). Predictive model for unfavorable outcome within 12 months after MI for patients over 70 years of age based on the "Age is not a hindrance" questionnaire score, serum ST2 level in ng/ml and left ventricular ejection fraction in % in ROC analysis has an area under the curve of 0,87 (95% CI 0,79-0,95), sensitivity — 86%, specificity — 71% (p<0,001).
Conclusion. Prediction of an unfavorable outcome based on the "Age is not a hindrance" questionnaire score, Simpson's left ventricular ejection fraction in %, and ST2 concentration can improve risk stratification for adverse outcomes within 12 months after MI in patients over 70 years.
- In patients with hypertension and aortic aneurysm, after endovascular aneurysm repair, regardless of its location, the carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity significantly increases.
- After aortic repair, the central pulse wave shape changes, reflecting a decrease in aortic distensibility and a deterioration in the damping function.
- Implantation of longer stent grafts, as well as a lower heart rate after surgery, leads to an increase in the time to return of the reflected pressure wave.
Aim. To assess the changes of arterial stiffness, central blood pressure (CBP), and determine the factors potentially influencing them in patients with descending thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysm, in combination with hypertension, one year after endovascular aneurysm repair ((T)EVAR).
Material and methods. Patients ≥18 years of age without clinically significant cardiac arrhythmias were included. Before surgery and a year later, we determined peripheral blood pressure, heart rate (HR), CBP, augmentation index (AIx), pressure at the point of maximum rise of the direct pulse wave (PT1h), time to return of the reflected pressure wave (Tr) and carotid femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV).
Results. Fifty patients were included (mean age, 68±9 years; 41 men; 16 with descending thoracic aortic aneurysm, 34 with abdominal aortic aneurysm), 23 patients were reexamined. After (T)EVAR, an increase in cfPWV (+2,6 m/s, p<0,001), PT1h (+5 mm Hg, p=0,026), peripheral pulse pressure (+7 mm Hg, p=0,039), heart rate (+5 beats/min, p=0,025). The CBP and AIx values have not changed. The dependence of Tr decrease on the stent-graft length (β=0,42) and the decrease in heart rate (β=-0,52) was found. During the year, 6 cardiovascular events were registered.
Conclusion. Graft implantation is accompanied by an increase in cfPWV, regardless of aneurysm location. An increase in PT1h one year after (T)EVAR may reflect a decrease in aortic distensibility and worsening damping function. No changes of CBP and AIx is probably explained by reflected wave characteristics after surgery. Predictors of Tr are — increase in heart rate and implantation of longer stent grafts.
- The choice of a method with high long-term effectiveness in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease remains debatable.
- Bilateral inthernal thoracic artery grafting was associated with significantly better patient survival and fewer major cardiovascular events during 33-month follow-up.
- Patient age over 58 years, body mass index over 30,72 and left ventricular ejection fraction <48% are independent predictors of a higher long-term death risk.
- A trial fibrillation increases the long-term death risk in relative to patients with sinus rhythm by 4,7 times.
Aim. To evaluate the long-term results of complete bilateral internal thoracic artery (BITA) grafting and traditional coronary bypass grafting (CABG) in patients with multivessel CAD.
Material and methods. From June 2018 to December 2021, 646 CABG operations were performed in patients with multivessel CAD at the Federal Center for Cardiovascular Surgery (Krasnoyarsk). There were 178 patients receiving BITA grafting and 468 — traditional revascularization technique. After propensity score matching, 356 patients were selected, of which 99 had on-pump BITA (group 1), 178 — on-pump traditional revascularization (group 2), and 79 — off-pump BITA (group 3). There were more males (p=0,143 and p=0,547). The groups were comparable in age (p=0,343 and p=0,104), body mass index (p=0,532 and p=0,759), diabetes (p= 0,705 and p=0,667), the number of hemodynamically significant coronary stenoses (p=0,370 and p=0,595).
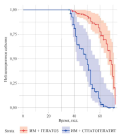
Results. The follow-up period lasted 32,8±8,52 months. Long-term patient survival was 83,9% in group 2,93% in group 1 (p=0,041) and 94% in group 3 (p=0,039). Freedom from cardiovascular mortality was 100% in both groups of BITA grafting and 92,5% in group 2 (p=0,001 and p=0,039), freedom from major cardiovascular events was 94,2% in group 1, 85,1% in group 2 and 98,5% in group 3 (p=0,032 and p=0,03).
Conclusion. BITA grafting is a modern effective and safe method of surgical myocardial revascularization both on- and off-pump. Up to 33 months. BITA grafting was associated with significantly better patient survival, complete freedom from cardiovascular mortality and a lower incidence of major cardiovascular events.
GUIDELINES FOR THE PRACTITIONER
- The costs of achieving a 1% target for reducing cardiovascular mortality of the State Program "Health Development" in 2023-2024 were determined.
Aim. To assess cost-effectiveness of valsartan+sakubitril, dapagliflosin and empagliflosin for prevention of cardiovascular death and achieving the target indicator "reduction of cardiovascular mortality" of the State Program "Health Development" in patients with heart failure (HF) of the entire profile of left ventricular ejection fraction in 2023-2024
Material and methods. The target population was Russian patients who had acute cardiovascular disease (CVD) and a verified diagnosis of HF and received subsidized drug coverage. Parametric modeling was used to predict cardiovascular mortality. In the corresponding comparative pair, the amount of drug costs required to prevent one cardiovascular death (CVD) was calculated, as well as to achieve a 1% target for reducing cardiovascular mortality in the whole country and separately in each region.
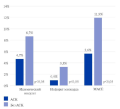
Results. To prevent one cardiovascular event, the costs of 1-year val-sartan+sacubitril therapy was RUB11,80 million, dapagliflozin — RUB7,07 million, empagliflozin — RUB13,83 million. The costs required to achieve a 1% target for reducing cardiovascular mortality for valsartan+sacubitril, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin were:
• in 2023, RUB6534,0 million, RUB3915,0 million and RUB7654,2 million, respectively;
• in 2024, RUB1100,6 million, RUB659,5 million and RUB1289,7 million, respectively.
Conclusion. The use of dapagliflozin is characterized by the lowest costs for preventing one cardiovascular event and achieving a 1% target for reducing cardiovascular mortality in 2023-2024.
The publication reflects the modern strategy and potential of various fixed-dose combinations in comorbid patients with hypertension and lipid metabolism disorders. Based on guidelines and key randomized studies, algorithms for prescribing combination drugs are proposed depending on the clinical characteristics of patients. The priority is both to achieve target blood pressure and low-density lipoprotein levels and to maximize the impact on cardiovascular prognosis and outcomes. Of course, these algorithms are not mandatory, and in a specific clinical situation there may be any deviations even from standard treatment regimens as follows: an alternative decision of a practitioner, intolerance to therapy, special indications, and much more. However, differentiated approach to fixed-dose combinations is extremely useful in cases where it is necessary to quickly make the right decision to prescribe optimal therapy for hypertension and dyslipidemia in lack of time to comprehensively weigh all the pros and cons underlying any clinical guidelines.
The prevalence of hypertension (HTN) in the Russian Federation and the world continues to grow. This is largely due to the epidemic of obesity and related conditions — metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. The most common and proven hypothesis of the relationship between hypertension and obesity is the activation of the sympathetic nervous system. However, modern research shows that the consequences of sympathetic hyperactivation are not limited only to hemodynamic effects, but extend to many organs and systems. Long-term sympathetic hyperactivation can lead to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Neurotransmitters affect fat cells by increasing lipolysis and leading to increased fatty acid release, the liver by increasing gluconeogenesis, and pancreatic β-cells by decreasing insulin secretion. The sympathetic nervous system plays an important role in energy management by regulating metabolic rate. Obese individuals have significantly less pronounced postprandial thermogenesis, despite a higher insulin response, while the hemodynamic response to isometric or heterometric exercise is reduced. Chronic stress serves not only as a trigger for behavioral disorders, but also directly leads to various physiological disorders, including through sympathetic activation. However, the choice of antihypertensive agents affecting the sympathetic activity in patients with obesity and metabolic disorders is very limited. According to current guidelines, β-blockers are not the drugs of choice in patients with uncomplicated HTN, since it has a weaker evidence base compared to other classes of drugs and have metabolic and other side effects. Therefore, selective I1-imidazoline receptor agonists, and in particular, moxonidine may be the drugs of choice in this category of patients. Moxonidine in combination therapy of patients with HTN and metabolic disorders, including metabolic disorders in menopause, as well as with a physiological estrogen decrease, significantly improves the effectiveness of antihypertensive therapy and increases the achievement of target blood pressure. In addition, its metabolic effects improve prognosis of such patients.
REVIEW
- In recent years, more and more data have emerged on the differences in the development, course, progression and treatment of hypertension (HTN) between males and females.
- By informing and educating health care providers about sex differences in cardiovascular prognosis, the implementation of a differential approach in HTN diagnosis and treatment, as well as adherence to therapy among patients, is stimulated.
The diagnosis of hypertension (HTN) has been known to doctors for many years. Current clinical guidelines represent a unified approach to the treatment and prevention of hypertension in patients of both sexes. Meanwhile, there are data that the development, course, progression and treatment of the disease may differ depending on sex. The aim of the review was to systematize modern ideas about sex differences in hypertension, as well as to substantiate the differentiated treatment among men and women. A literature search for 2013-2023 was conducted in the PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, Google Scholar, eLibrary databases using the search phrase "sex differences in hypertension". This work reflects current data regarding sex-specific differences in hypertension, including its development, blood pressure regulation, sex characteristics of risk factors, target organ damage, and features of antihypertensive treatment. Differentiated approach considering sex differences may provide novel strategies for preventing the progression of cardiovascular disease.
- Aging is accompanied by a decrease in growth and mineral density of bone tissue (osteopenia and osteoporosis), a progressive muscle decrease, and an increase in adipose tissue (sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity).
- Serum markers of bone turnover, muscle function and inflammation may be used as additional diagnostic criteria for osteosarcopenic obesity.
Osteosarcopenic obesity syndrome involves the simultaneous deterioration of bone, muscle, and excess fat accumulation, resulting in systemic metabolic dysregulation. Currently, the relevance of this problem is increasing due to the global population aging, the high incidence of obesity, type 2 diabetes, sarcopenia and frailty in developed countries of the modern world. In this regard, novel diagnosis methods for this condition, including laboratory markers, should be developed. The review examines modern biomarkers of osteosarcopenic obesity.
What is already known about the subject?
- Worsening of heart failure (HF) remains a serious problem due to limited opportunities for timely diagnosis and treatment, especially in the prehospital stage.
What might this study add?
- Exacerbation episodes are varied, and the risk of repeated HF deterioration is determined by residual congestion (clinical or subclinical).
- Due to the unfavorable prognosis, the phenotype of "hospitalized patients with decompensated HF" should be distinguished.
How might this impact on clinical practice?
- The introduction of a Russian- language analogue of the term "worsening HF" seems rational to identify a cohort of patients with HF exacerbation and an established diagnosis of HF in order to unify terminology and optimize management tactics.
The article presents a brief analytical review of the European Society of Cardiology consensus statement on the definition and clinical features of heart failure (HF) with a summary of the latest results on the treatment and prevention of exacerbation. The main viewpoints are compared with existing approaches in the Russian Federation. The definition and classification of worsening HF (WHF), as well as its main clinical manifestations, epidemiology, outcomes, pathophysiology, approaches to early detection, patterns of in- and outpatient treatment of WHF are discussed. Attention is paid to the terminology necessary to identify a cohort of patients with HF exacerbation with a previously established diagnosis of HF in order to unify approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
This review article considers the role of sutureless aortic valve replacement in the era of transcatheter replacement. Modern data regarding the outcomes of treatment with these two methods and its comparison are considered. Their main disadvantages and the cohorts of patients suitable for each technique are determined.
OBITUARY
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)