REVIEW
- The review presents all types of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) used in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
- Endovascular interventions for STEMI are divided depending on the disease duration, persistent symptoms of the disease, and the preliminary use of thrombolytic therapy.
- Different types of PCI for STEMI have different benefits.
- The review, based on the evidence base, substantiates the priority role of primary PCI within 12 hours from the symptom onset among all types of reperfusion in patients with STEMI, which has been enshrined in modern guidelines since 2003.
In ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), various types of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) are performed depending on the disease duration, persistent disease symptoms, and prior thrombolytic therapy.
The aim of this review is to present all PCI types that can be performed in the treatment of patients with STEMI, substantiate the indications for their use, and the optimal option for endovascular intervention.
Basically, three following types of PCI used in patients with STEMI are distinguished: primary PCI (PPCI), late PCI (after 48 hours from the disease onset), and PCI after thrombolytic therapy. Different types of PCI in STEMI have different benefits. Current guidelines substantiate absolute indications for stenting with the highest level of evidence for 12-hour PPCI, rescue PCI, and routine early PCI after thrombolytic therapy. At the same time, the priority role in reperfusion in STEMI is assigned to 12-hour PPCI. That is why this indicator is a target in the European Stent for Life (SFL) initiative — the national/regional indicator of 12-hour PPCI should be 70% or higher of the number of patients hospitalized with STEMI.
What is already known about the subject?
- The clinical guidelines for heart failure present the criteria for healthcare quality.
- The published registry results provide an average idea of the quality of health care. The results of individual centers may differ significantly. When planning improvements in a specific health facility, more accurate data on existing deficiencies is needed.
What might this study add?
- The characteristics of 27 multicenter Russian and foreign registries of heart failure are presented.
- The key requirements for a heart failure registry designed to monitor the implementation of clinical guidelines in everyday practice are outlined.
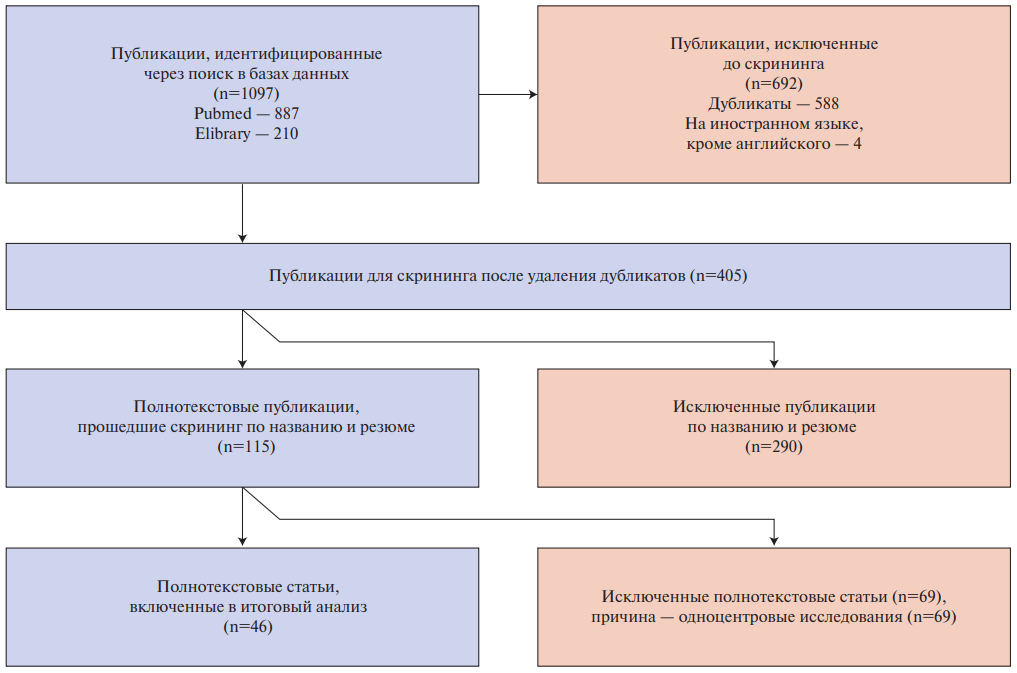
The aim was to determine the key requirements for a heart failure (HF) registry designed to monitor the implementation of clinical guidelines in everyday practice. A systematic literature review was conducted using the PRISMA methodology to identify multicenter HF registries. The PubMed and eLibrary databases were used. The search depth was 2015-2025. For the final analysis, 46 sources were selected, which presented data from 27 multicenter registries (19 foreign and 8 Russian). An assessment of the registers’ compliance with the main quality criteria was carried out according to guidelines of Martsevich SYu, et al., 2023. Registry designed for routine monitoring of the implementation of clinical guidelines should be: 1) continuously operational; 2) accessible 24/7 in real-time; 3) results are presented in terms of approved quality criteria; 4) achieved results compared to the average result of the reference group; 5) the organizational structure of the registry and algorithms for calculating indicators are universal and publicly available; 6) the organizational structure and calculation algorithms are based on quality measures presented in clinical guidelines but adapted (selected and detailed) for the purposes of maintaining the registry. It should also meet the basic quality criteria for a register as a tool of evidence-based medicine.
- Based on the analysis of animal models, a hypothesis has been put forward on different types of fibrosis — hot and cold.
- The hot phenotype is characteristic of chronic exposure to a damaging factor — hypertension, chronic coronary artery disease, etc.
- Cold fibrosis develops after a single exposure to an intense damaging factor (for example, in myocardial infarction) and is represented almost exclusively by myofibroblasts with minimal participation of immune cells.
Fibrosis is a process characterized by excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components in response to injury, ischemia, and chronic metabolic and immune inflammation. Normally, extracellular matrix homeostasis is regulated by maintaining a balance between the intensity of fibrogenesis and fibrolysis. In this review, for the first time in the Russian literature, a new concept of "cold" and "hot" fibrosis is highlighted, based on the peculiarities of the interaction of the extracellular matrix and the immune system. The role of biologically active substances acting as candidate biomarkers for fibrosis and antifibrotic response is discussed. The development of such a biomarker concept can be considered as a basis for the creation of antifibrotic therapy strategies relevant for the treatment of various cardiac diseases.
- The use of photoplethysmography (PPG) at the outpatient stage for remote heart rate monitoring is not inferior to traditional methods of monitoring indicators.
- The diagnostic value of PPG for the early diagnosis of atrial fibrillation, as well as the accuracy of remote blood pressure monitoring systems, are emphasized.
Aim. To analyze literature data on use of photoplethysmography (PPG) at the outpatient stage for remote monitoring of heart rate, arrhythmias, blood pressure (BP), temperature, respiratory rate.
Research design. The search was carried out using the PubMed/Medline, Web of Science, Scopus and Google Scholar databases from 2015 to 2025.
Results. A small number of studies were included in the meta-analysis. Mean values of systolic and diastolic BP depending on the measurement method used were presented in two studies, which implies high inconsistency in the presented studies and determines the need for a balanced interpretation of the pooled estimate of the difference in mean values for these studies.
Absolute values determining the incidence of AF are indicated in four studies.
Conclusion. Our systematic review and meta-analysis showed PPG effectiveness for arrhythmia and controlling systolic and diastolic BP at the outpatient stage.
- Parkinson’s disease is accompanied not only by motor but also by pronounced cardiovascular disorders.
- Disorders in the autonomic nervous system, especially cardiac sympathetic denervation, play an important role in pathogenesis.
- Accumulation of alpha-synuclein is found in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Orthostatic hypotension is associated not only with nervous system damage, but also with external factors — a decrease in fluid volume and drug exposure.
- Cardiovascular symptoms significantly worsen the quality of life of patients.
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common progressive neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s disease, characterized by selective loss of dopaminergic neurons in the compact part of the substantia nigra. This leads to striatal dopamine deficiency and motor symptoms. Along with this, non-motor disorders, in particular cardiovascular dysfunctions, play a significant role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease, which have a significant impact on the quality of life of patients.
Neurogenic mechanisms include pathological accumulation and aggregation of alpha-synuclein with the formation of Lewy bodies and neurites, detected in both the central and peripheral autonomic nervous systems, including the heart sympathetic innervation. Additionally, non-neurogenic factors (decreased intravascular volume due to dysphagia and inadequate fluid intake, heart failure, and antiparkinsonian-induced hypotension) contribute to orthostatic hypotension and other cardiovascular events, increasing the risk of stroke and other complications.
In addition to autonomic and motor manifestations, mental and cognitive impairment is of paramount importance in Parkinson’s disease. Depression, anxiety, and dementia are found in 40-50% of patients, often in the early stages of the disease, and through activation of the sympathoadrenal system, increased cortisol levels, and baroreflex dysfunction can exacerbate arrhythmias, ischemic episodes, and other cardiac events. In addition, decreased motivation and adherence to therapy with mental symptoms further increases the risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in this group of patients.
- Computer vision is widely used for routing patients with ischemic stroke.
- The accuracy of machine learning models for diagnosing ischemic stroke based on neuroimaging is comparable to the accuracy of radiologists.
- Publications on the accuracy of AI systems often contain systematic bias.
- AI systems for ischemic stroke diagnosis do not show an impact on patient outcomes in clinical trials.
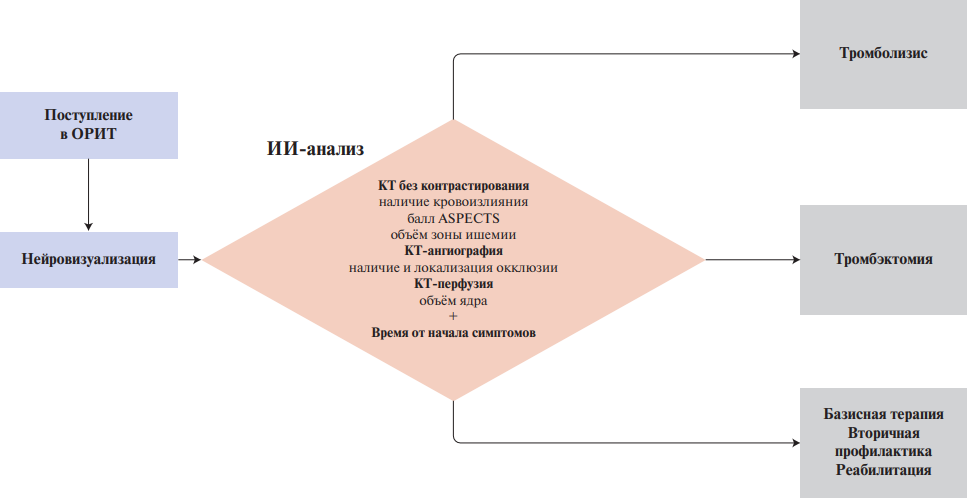
Artificial intelligence (AI) is actively used in the diagnosis of ischemic stroke, allowing speeding up the decision-making process and improving the accuracy of diagnosis. Machine learning models are able to identify ischemic areas based on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging data, as well as indicate the volume of damage and calculate the ASPECTS score. Modern AI systems demonstrate high diagnostic accuracy, comparable to the accuracy of radiologists. According to clinical studies, these systems significantly reduce the time from the patient admission to the vascular center to treatment, but their impact on clinical outcomes remains unclear. The review discusses the problems of assessing the clinical effectiveness of AI in the diagnosis of ischemic stroke, including systematic bias in model training and choice of study design, as well as publication bias. To integrate AI into clinical practice, randomized controlled trials with clinically relevant endpoints, as well as standardization of data and methods for assessing effectiveness, are needed. Despite significant AI advances in diagnosing ischemic stroke, their effectiveness in real-world practice requires further study and validation.
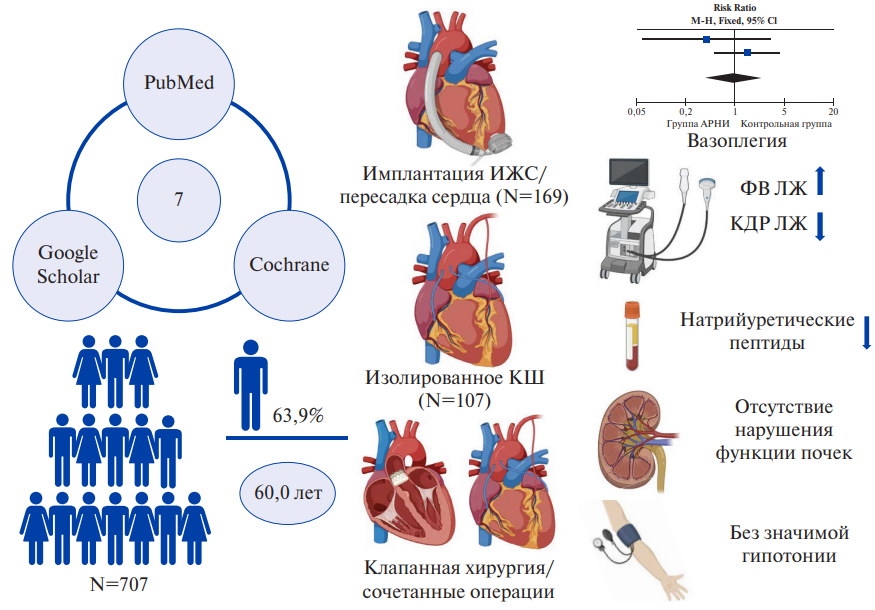
- The use of angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors in the perioperative period in cardiac surgery has been studied in a limited and heterogeneous series of studies.
- According to the conducted systematic review, therapy with a combination of sacubitril/valsartan in the perioperative period demonstrated safety and efficacy.
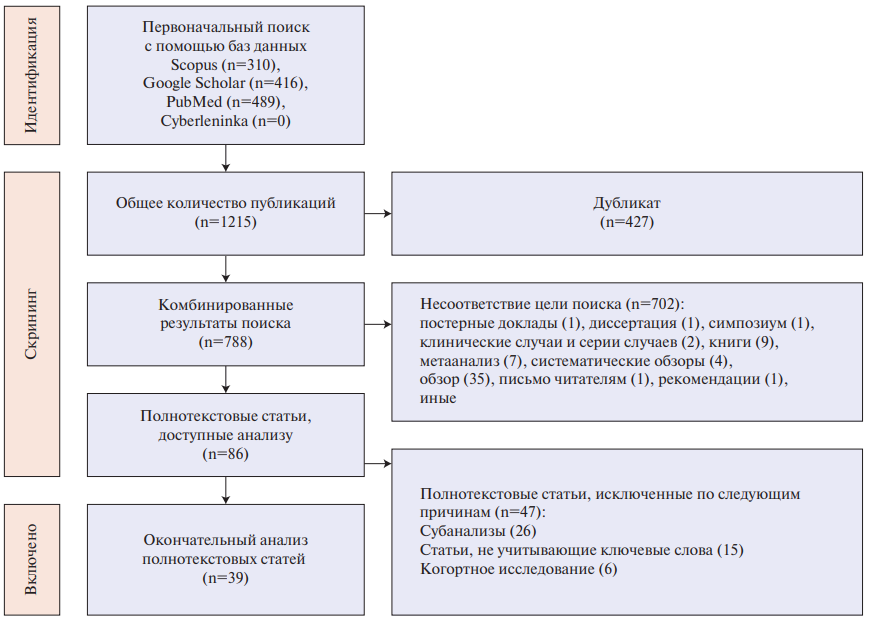
Aim. To conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies to determine the efficacy and safety of using sacubitril/valsartan combination in the perioperative period in adult patients undergoing cardiac surgery.
Material and methods. The search for studies was carried out in the PubMed (MEDLINE), Google Scholar and Cochrane library databases. The inclusion criteria for studies were the use of sacubitril/valsartan combination in the perioperative period in adult patients undergoing open-heart cardiac surgery with adequately presented baseline parameters and clinical outcome data.
Results. Seven studies from 459 publications were selected for this systematic review. The total number of patients was 707, of which 452 were men (63,9%). Two studies described the use of angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI) in the implantation of left ventricular assist device or heart transplant. A meta-analysis was performed on these studies, which demonstrated that the incidence of vasoplegic syndrome after these operations did not differ significantly between the ARNI group and the control group (relative risk 0,69; 95% confidence interval: 0,40-2,30; p=0,92). Also, two studies considered the results of therapy during coronary bypass grafting, while three studies — during the valve defect treatment. All studies demonstrated improvement in certain clinical parameters (ejection fraction and left ventricular (LV) size, cardiac index, natriuretic peptide levels, 6-minute walk test, etc.), as well as the safety of ARNI administration (no significant renal dysfunction and hypotension), including its early initiation after cardiac surgery.
Conclusion. ARNI administration in the perioperative period has been studied in a limited and heterogeneous series of studies with small sample sizes, which are devoted to surgical treatment of end-stage heart failure, coronary artery disease and valve defects. Sacubitril/valsartan combination therapy demonstrated safety and efficacy in all groups considered. Further large controlled clinical trials are required to formulate reliable recommendations regarding the use of ARNI in the perioperative period.
ПРОБЛЕМНАЯ СТАТЬЯ
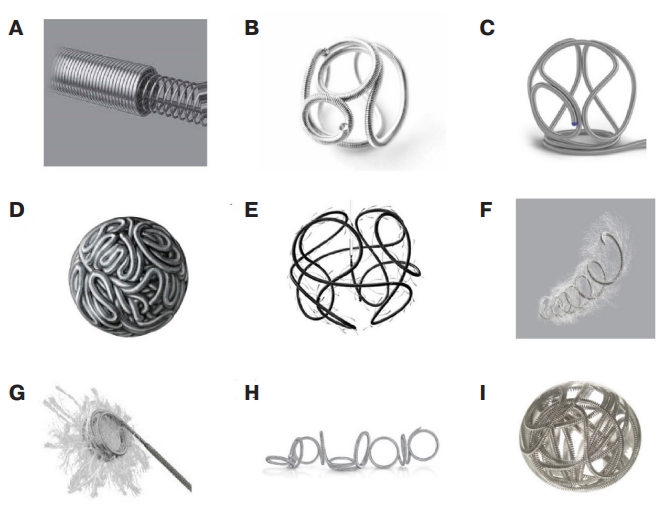
- Both clinical experience and literary data shows that endovascular coils are an important tool in modern interventional radiology.
- Modern developments continue to expand the capabilities of this technology, increasing the accuracy of delivery, controllability and safety.
Although the term "target organ damage" is used primarily in relation to the diagnosis of hypertension, the fact that vessels are involved in a wider range of diseases is beyond doubt. Over the past 30 years, arterial stiffness has moved from the area of scientific interest to clinical guidelines. The ankle-brachial index is widely used to assess target organ damage. In a number of conditions (diabetes, chronic kidney disease, especially in the end-stage renal failure and hemodialysis), severe medial calcification of the arterial walls develops. As a result, the arteries become non-compressible, which leads to falsely elevated ankle-brachial index (>1,4). Toe vessels are less susceptible to vascular stiffness, which makes the toe-brachial index an accessible alternative in such a situation. The literature review highlights the history of toe-brachial index development as a research method, as well as the predictive value and prospects for further application. Its use offers opportunities for deepening and expanding understanding of the pathogenesis of a wide range of diseases, searching for and testing correction methods and developing effective prevention methods.
- The evidence base for the ankle-brachial index has been forming for several decades, and the need for its measurement is covered in many clinical guidelines. However, it turned out to be uninformative in patients with severe arterial stiffness, since it does not allow to detect early arteriosclerosis; in addition, even in limbs with a normal index, microvascular dysfunction may develop.
- There is a pressing need to find a new tool for assessing blood flow in lower limb arteries. Toe vessels are less susceptible to vascular stiffness, which makes the toe-brachial index an accessible alternative in such a situation.
- Due to the likelihood of the significant compaction of lower limb arteries, the predictive value of ankle-brachial index may be reduced, while the assessment of toe-brachial index has virtually no such limitations.
The article presents a review on dilated cardiomyopathy in patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. It is shown that in young children with the Wolff-Par-kinson-White syndrome, the most pronounced pre-excitation on the electrocardiogram and the right septal or right lateral location of accessory atrioventricular pathways, hypotrophy and dyskinesia of the interventricular septum may occur, with subsequent left ventricular dilation and dysfunction. However, these factors are not specific and cardiomyopathy development is possible in patients of any age and with other locations of additional conduction pathways. In addition, the current classifications of cardiomyopathies in children do not include a concept that includes this condition, and there are no criteria for making this diagnosis.
- Diagnosis of dyssynchrony cardiomyopathy in patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome is traditionally based on the data of the standard transthoracic echocardiography with determination of heart chamber volumes and sizes and left ventricle ejection fraction.
- New research data has shown the role of global longitudinal strain according to Speckle tracking in the diagnosis of dyssynchrony and subclinical myocardial contractility disorders.
- Generalization of experience in this area will help to identify predictors left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with the WPW syndrome and optimal indications for radiofrequency ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways in children.
Endovascular embolization using coils is a widely used method for treating various vascular pathologies. There are many types of coils, differing in design, material and technical characteristics, which allows choosing the best options depending on the clinical setting. The article discusses the main types of endovascular coils and their technical features. The final part presents cases of successful use of endovascular embolization coils and stopping bleeding, demonstrating its high potential and important role in modern interventional therapy.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)