Перейти к:
Проблемы оценки клинической эффективности применения искусственного интеллекта в диагностике ишемического инсульта
https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6357
EDN: CBNZRM
Аннотация
Искусственный интеллект (ИИ) активно используется в диагностике ишемического инсульта, позволяя ускорить процесс принятия решений и повысить точность диагностики. Модели машинного обучения способны выявлять зоны ишемии по данным компьютерной томографии и магнитно-резонансной томографии, а также указывать объём поражения и рассчитывать балл по шкале ASPECTS. Современные ИИ-системы демонстрируют высокую диагностическую точность, сравнимую с точностью врачей-рентгенологов. По результатам клинических исследований, эти системы значимо сокращают время от поступления пациента с симптомами острого нарушения мозгового кровообращения в сосудистый центр до момента проведения лечения, однако их влияние на клинические исходы остаётся неясным. В обзоре рассматриваются проблемы оценки клинической эффективности ИИ в диагностике ишемического инсульта, включая систематические ошибки (bias) при обучении модели и выборе дизайна исследования, а также публикационная предвзятость. Для интеграции ИИ в клиническую практику необходимы рандомизированные контролируемые исследования с клинически значимыми конечными точками, а также стандартизация данных и методов оценки эффективности. Несмотря на значительный прогресс в разработке ИИ-решений для диагностики ишемического инсульта, их эффективность в реальной клинической практике требует дальнейшего изучения и валидации.
Ключевые слова
Для цитирования:
Балунов И.О. Проблемы оценки клинической эффективности применения искусственного интеллекта в диагностике ишемического инсульта. Российский кардиологический журнал. 2025;30(9S):6357. https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6357. EDN: CBNZRM
For citation:
Balunov I.O. Problems of assessing the clinical efficiency of artificial intelligence systemsin diagnosing ischemic stroke. Russian Journal of Cardiology. 2025;30(9S):6357. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6357. EDN: CBNZRM
Основная область применения искусственного интеллекта (ИИ) в медицине — это анализ медицинских изображений. Нейронные сети позволяют ускорить интерпретацию исследования и повысить точность врача в постановке диагноза. В первую очередь ИИ в радиологии используется для диагностики патологий, требующих быстрого принятия решения.
Одна из таких патологий — ишемический инсульт. Скорость принятия решения играет важную роль в терапии острого ишемического инсульта, поскольку от времени начала симптомов до начала лечения зависит прогноз пациента. Согласно российским клиническим рекомендациям, опубликованным в 2024г, для проведения внутривенной тромболитической терапии у врача есть 4,5 ч от появления первых симптомов инсульта, а для проведения тромбэкстракции — 6 ч. Также в России действует приказ Минздрава России "Об утверждении Порядка оказания медицинской помощи больным с острыми нарушениями мозгового кровообращения", согласно которому время от поступления пациента с симптомами острого нарушения мозгового кровообращения (ОНМК) до интерпретации компьютерной томографии (КТ) или магнитно-резонансной томографии (МРТ) головного мозга рентгенологом не должно превышать 40 мин.
Для более оперативного оказания помощи пациентам с ОНМК разрабатываются модели машинного обучения, автоматизирующие работу врачей на различных этапах оказания помощи. ИИ позволяет как оптимизировать процесс оказания помощи, так и увеличить точность в постановке диагноза и выборе лечения.
ИИ-сервисы для диагностики ишемического инсульта представляют собой медицинское программное обеспечение, предназначенное для автоматизации работы врача при помощи методов ИИ. Сервисы ИИ для диагностики ишемического инсульта используются в двух сценариях: сервис для "второго мнения" и инструмент для маршрутизации пациентов (рис. 1).
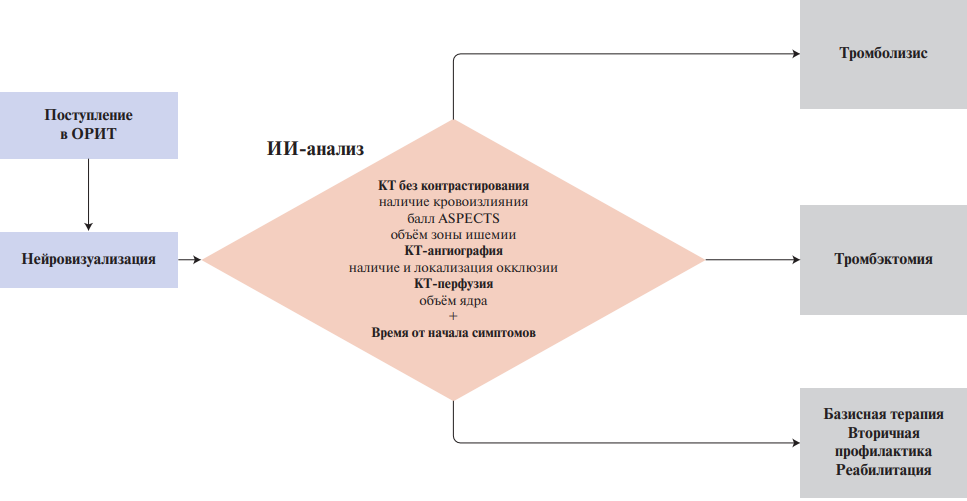
Рис. 1. ИИ для триажа пациентов с симптомами ОНМК.
Примечание: ИИ-сервисы для поддержки принятия врачебных решений автоматически интерпретируют данные визуализации и оценивают параметры, на основании которых лечащий врач выбирает дальнейшую тактику ведения пациента.
Сокращения: ИИ — искусственный интеллект, КТ — компьютерная томография, ОРИТ — отделение реанимации и интенсивной терапии.
В первом сценарии сервис ИИ анализирует данные визуализации и автоматически формирует заключение. Такое решение предназначено для снижения количества "пропущенных" патологий.
Во втором сценарии сервис ИИ автоматически анализирует данные визуализации и при нахождении патологии оповещает врача. Такие модели могут быть интегрированы в медицинскую информационную систему и маркировать пациентов в зависимости от вероятности патологии по данным КТ или КТ-ангиографии [1]. Врач, работающий на потоке, получает уведомление о пациенте с более вероятным наличием и рассматривает его исследование в приоритетном порядке. Такое решение даёт возможность в более короткие сроки провести тромболитическую терапию или тромбэкстракцию пациентам с острым ишемическим инсультом.
Большинство опубликованных клинических исследований показывают высокую диагностическую точность нейронных сетей, сравнимую с точностью врачей-рентгенологов. Сервисы маршрутизации пациентов с использованием ИИ многократно доказали способность сократить время от поступления в медицинское учреждение до проведения реканализации сосуда, однако в данный момент недостаточно доказательств положительного влияния ИИ на клинические исходы. Для оценки эффективности ИИ необходимы рандомизированные клинические исследования с клинически значимыми конечными точками. Более того, в исследованиях медицинского ИИ, в частности, для диагностики ишемического инсульта, встречаются систематические ошибки (bias), вызывающие опасения относительно безопасности и эффективности использования моделей ИИ.
Цель обзора — изучить доказательства клинической эффективности применения ИИ для диагностики ишемического инсульта и описать ограничения, влияющие на интерпретацию этих доказательств.
Что такое ИИ и машинное обучение?
ИИ — это область компьютерных наук, изучающая создание искусственных систем, способных выполнять задачи, традиционно требующие человеческого интеллекта. ИИ в медицине решает такие задачи, как распознавание образов, анализ данных и принятие решений на их основе. Термин "искусственный интеллект" был введён в 1950-е годы как новое направление в компьютерных науках [2].
Одним из ключевых подходов в ИИ является машинное обучение, которое позволяет алгоритмам автоматически обучаться на основе данных, выявляя в них закономерности [3]. Нейронные сети — это один из классов алгоритмов машинного обучения, вдохновлённых структурой нейронных связей человеческого мозга. Нейронные сети состоят из множества взаимосвязанных слоев, обрабатывающих входные данные, преобразуя их в сложные представления, что позволяет решать задачи высокой сложности, такие как классификация изображений или анализ медицинских данных.
Компьютерное зрение (computer vision) — это область ИИ, решающая задачи на основе анализа изображений и видео [4]. В области компьютерного зрения используются нейронные сети, осуществляющие детекцию и сегментацию объектов, а также классификацию изображений. Большая часть медицинских задач, в которых ИИ нашёл своё применение, относятся к анализу медицинских изображений. Модели машинного обучения используются в лучевой диагностике, офтальмологии, кардиологии, дерматологии, онкологии, патоморфологии, хирургии [5].
Методология исследования
Поиск публикаций на русском и английском языках производился по базам данных научной литературы PubMed и eLIBRARY. В анализ включались статьи, содержащие ключевые слова "ischemic stroke", "artificial intelligence", "radiology", "ишемический инсульт", "искусственный интеллект", "рентгенология", опубликованные с 2019 по 2025гг. Критерии исключения: статьи, опубликованные в "хищнических" журналах, согласно списку Билла. Дата последнего поиска — 21.03.2025.
В результате были получены 103 публикации. После скрининга статей по аннотациям были исключены 66 публикаций из-за несоответствия теме обзора. В финальный анализ были включены 39 обзоров, метаанализов и клинических исследований, изучающих тему эффективности ИИ для диагностики ишемического инсульта.
Результаты
Использование ИИ на каждом этапе диагностики ишемического инсульта
Нейронные сети используются как системы поддержки принятия решения для диагностики и выбора лечения при ОНМК рентгенологами, неврологами и сосудистыми хирургами. Чаще всего врачи в клинической практике сталкиваются с моделями ИИ для анализа изображений. Для автоматизированной диагностики острого ишемического инсульта разработаны сервисы, анализирующие данные бесконтрастной КТ, КТ-ангиографии, КТ-перфузии, МРТ.
Большая часть систем для диагностики ишемического инсульта детектируют и/или выделяют контуром зоны предполагаемой ишемии на бесконтрастных КТ. Примерами таких сервисов являются Rapid, Viz, qER, Avicenna, Brainomix, Deep01 и Annalise AI. Также эту задачу выполняют системы, разработанные российскими компаниями: Третье мнение КТ ГМ комплекс, NtechMed CT Brain, Sciberia Head, Цельс КС КТ ГМ и "КТ ГМ комплекс" от СберМедИИ. Помимо сегментации изображений, некоторые модели ИИ автоматически подсчитывают объём и размеры предполагаемой зоны ишемии.
Для принятия решения о проведении внутрисосудистой тромбоэкстракции при острейшей ишемии используется шкала Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS). Модели машинного обучения способны предсказывать локализацию зон ASPECTS и зоны ишемии на бесконтрастной КТ. При сопоставлении этих зон модель определяет балл по шкале ASPECTS, подобно врачу-рентгенологу. Примерами сервисов для оценки баллов ASPECTS являются Rapid-ASPECTS и e-ASPECTS [6, 7], получившие одобрение Управления по санитарному надзору за качеством пищевых продуктов и медикаментов (FDA). По данным метаанализа Adamou A, et al. [8], ИИ способен более точно оценивать балл по шкале ASPECT, чем врач-рентгенолог. При сравнении истинной оценки (ground truth) по шкале ASPECTS с оценкой врача-рентгенолога коэффициент межклассовой корреляции (ICC) в среднем составил 0,62, при сравнении с ИИ-сервисом — 0,72.
Помимо бесконтрастной КТ, в диагностике инсульта широко применяется КТ-ангиография, позволяющая определить локализацию поражения и выбрать тактику лечения. В практике уже используются сервисы Rapid LVO и Viz LVO [9, 10] для детектирования окклюзии больших сосудов по данным КТ-ангиографии. В исследовании Martinez JC, et al. [11] использование сервиса Viz LVO для автоматической диагностики окклюзии больших сосудов в сосудистых центрах позволило сократить время от поступления пациента до выполнения внутрисосудистой тромбэкстракции ("door-to-groin") на 11,2 мин по сравнению с центрами, в которых сервис не использовался. При прямом сравнении моделей Viz LVO и Rapid LVO на выборке из 360 исследований сервисы продемонстрировали специфичность 0,96 и 0,85, чувствительность 0,87 и 0,87, соответственно [12].
Одним из признаков острейшей ишемии является симптом гиперденсной средней мозговой артерии. Weyland CS, et al. [13] продемонстрировали способность нейронной сети детектировать симптом гиперденсной артерии с чувствительностью 0,77 и специфичностью 0,87, что сопоставимо с точностью врачей-рентгенологов.
Нейронные сети также используются для предсказания зоны пенумбры и ядра ишемии при КТ-перфузии. Одно из исследований продемонстрировало модель, определяющую зону ядра ишемии по данным КТ-перфузии со средней абсолютной ошибкой 13,8 мл при сравнении с диффузно-взвешенной МРТ [14].
Метод диффузно-взвешенной МРТ обладает 94% чувствительностью и 100% специфичностью при определении ишемического инсульта в первые 6 ч от начала развития симптомов, согласно Российским клиническим рекомендациям по лечению ишемического инсульта. Это наиболее эффективная модальность для проведения дифференциальной диагностики ишемического инсульта [15]. Для автоматической интерпретации МРТ-исследований также обучают новые модели ИИ. В метаанализ Bojsen JA, et al. [16] были включены 9 исследований, изучавших эффективность моделей машинного обучения для диагностики ишемии по данным МРТ. Чувствительность и специфичность детектирования ишемии на изображениях диффузионно-взвешенной МРТ составила 93% и 93%. По данным метаанализа Miceli G, et al. [17], ИИ-сервисы помогают определять класс инсульта по шкале TOAST по данным МРТ и КТ-ангиографии.
Помимо детектирования и сегментации зон ишемии, многие сервисы детектируют и сегментируют другие патологии, что помогает врачу-рентгенологу провести дифференциальную диагностику. Вазогенный отёк — одна из патологий, проявляющаяся на бесконтрастной КТ как гиподенсивная зона. В исследовании Newbury-Chaet I, et al. модель ИИ Annalise Enterprise CTB детектировала вазогенный отёк на КТ с чувствительностью 90,2% и специфичностью 93,5% [18]. Российский ИИ-сервис "Третье Мнение. КТ ГМ", помимо выделения зон ишемии, также определяет зоны кистозно-глиозной трансформации для дифференциации свежего ишемического инсульта вблизи участков хронических изменений.
Исследование нейровоспаления является перспективным направлением в диагностике ишемического инсульта и нейрореабилитации. Для исследования процесса нейровоспаления активно используется позитронно-эмиссионная томография с КТ с транслокационным белком 18 кДа (TSPO). Zatcepin A, et al. разработали метод количественной оценки с использованием алгоритма машинного обучения, позволяющий упростить и ускорить процесс интерпретации исследования на 10 мин по сравнению со стандартным протоколом [19].
Систематические ошибки в исследованиях ИИ для диагностики ишемического инсульта
Понятие "bias" в научных исследованиях представляет собой систематическую ошибку, приводящую к отклонению результатов от объективной истины. В контексте медицинского ИИ bias может проявляться на разных этапах разработки алгоритмов, включая сбор и обработку данных, выбор модели и интерпретацию результатов [20]. Основные источники bias в медицинском ИИ включают несбалансированные или нерепрезентативные выборки данных, методологические ошибки при обучении моделей, а также предвзятость исследователей. Такие искажения могут приводить к снижению точности диагностики и прогностических моделей для отдельных групп пациентов, что может усугублять существующие диспропорции в медицинской помощи. Выявление и минимизация bias являются критически важными задачами для обеспечения справедливости и надежности ИИ-решений в здравоохранении.
Для оценки эффективности ИИ-сервисов в клинических исследованиях необходимы новые структуры отчётов, учитывающие технические особенности моделей машинного обучения и связанные с ними риски. Для стандартизации отчетности и увеличения прозрачности данных в исследованиях ИИ были разработаны рекомендации MINIMAR (Minimum Information for Medical AI Reporting) [21], CONSORT-AI (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials–Artificial Intelligence) [22] и SPIRIT-AI (Standard Protocol Items: Recommendations for Interventional Trials–Artificial Intelligence) [21-23], а также специализированные рекомендации CLAIM для моделей ИИ, анализирующих изображения [24]. Все перечисленные рекомендации включают стандартные требования для исследования медицинских вмешательств и специфические требования, связанные с ИИ: описание модели, использованных данных для её разработки, процессов тестирования и валидации.
По данным систематического обзора Akay E, et al. [25], большинство исследований систем поддержки принятия врачебных решений с ИИ для диагностики ишемического инсульта не соответствуют стандартам отчётности. Только 58% исследований сообщили о разделении данных на обучающую и тестовую выборки, во многих исследованиях отсутствует информация о наличии отдельного набора данных для валидации модели. В 3% исследований информация о пациентах, чьи данные использовали для обучения модели, полностью отсутствовала. Многие исследования включали в себя неполные демографические данные пациентов в исследовании, в 8% исследований демографические данные отсутствовали.
Коммерческие нейронные сети, как правило, обучены на непубличных наборах данных. Фактически только компания-разработчик имеет информацию об алгоритмах обучения моделей, источниках данных для обучения и их количестве. Информация о частных наборах данных, приобретаемых компаниями-разработчиками, остаётся недоступной для научного и медицинского сообщества.
Использование публичных наборов данных не гарантирует высокую достоверность моделей, обученных на этих данных. Galanty M, et al. [26] выявили ряд проблем в публичных наборах данных с медицинскими изображениями и сигналами, используемых для обучения ИИ. Основные недостатки связаны с недостаточной документацией, в которой часто отсутствуют критерии включения данных, методы аннотирования, возможные ошибки и ограничения.
Разнообразие данных для обучения моделей машинного обучения — одна из наиболее распространённых проблем для медицинского ИИ [27-29]. Разработчики обязаны обеспечить не только адекватное распределение патологий, но и репрезентативную выборку по демографическим показателям. Недостаточное внимание к демографическим данным, таким как возраст, пол и раса, приводит к систематическим ошибкам в классификации и прогнозировании. Публичные наборы данных с исследованиями КТ головного мозга для обучения ИИ, такие как CQ500 [30], не содержат данных о расовой принадлежности и географическом распределении пациентов, чьи исследования вошли в набор данных.
Существуют разные подходы к распределению демографических параметров в наборе данных для обучения ИИ, и выбор правильного подхода неоднозначен. С одной стороны, тренировочный набор должен содержать достаточное количество данных, полученных от людей с разными демографическими показателями (пол, возраст, раса). С другой стороны, если распределение демографических данных будет соответствовать демографическому распределению в стране, использующей ИИ-сервис, ответы сервиса будут более достоверными.
Проблемы с аннотацией данных обусловлены отсутствием единых стандартов, что приводит к высокой вариативности разметки и ошибкам в обучении моделей. Также отмечается нехватка информации об источниках ошибок и их количественной оценке, что мешает разработчикам учитывать неопределенности при обучении. В документации часто отсутствует информация о сборе данных, включая условия их получения и личность сборщиков, что затрудняет воспроизводимость исследований.
Предвзятость публикации — один из типов bias, связанный со склонностью научных журналов и исследователей публиковать позитивные исследования чаще, чем негативные. Подавляющее большинство опубликованных исследований, изучающих эффективность ИИ в диагностике ишемического инсульта, оказываются положительными. Однако по данным систематического обзора [31] лишь 1% из всех клинических исследований медицинских ИИ-сервисов оказываются опубликованными. Поощрение публикации исследований с негативными результатами со стороны научных журналов может помочь преодолению предвзятости публикации в сфере ИИ.
Отсутствие опубликованных результатов работы не мешает сервису ИИ получить одобрение FDA или Европейского агентства медицинских средств (EMA). Leeuwen KG, et al. проанализировали 100 медицинских сервисов с ИИ, прошедших сертификацию Европейского соответствия (CE) и получивших разрешение к использованию в европейских странах [32]. 64 из 100 сервисов были одобрены на основании внутреннего анализа, проведённого разработчиками сервисов. 11 сервисов для диагностики ишемического инсульта, включённых в исследование, также вышли на рынок раньше, чем были опубликованы статьи с доказательствами их безопасности и эффективности.
Сложности оценки эффективности ИИ-сервисов
Для оценки качества работы ИИ необходима валидация на тестовой выборке исследований из источника, данные из которого не использовались для обучения модели. Благодаря внешней валидации можно определить генерализуемость модели ИИ. Kim DW, et al. [33] выявили лишь 31 исследование из 516 опубликованных исследований ИИ для анализа медицинских изображений, в которых использовался внешний набор данных для валидации моделей. При этом ни одно из исследований не включало 3 ключевых элемента дизайна: дизайн когортного исследования, многоцентровое исследование и проспективный сбор данных для валидации.
Исследования моделей ИИ, включающие валидацию на внешнем наборе данных, зачастую демонстрируют на нём более низкую точность. Анализ 83 публикаций, описывающих модели глубокого обучения для лучевой диагностики, показал, что 81% моделей имели более высокие метрики точности при внутреннем тестировании по сравнению с внешней валидацией [34].
По данным систематического обзора Mikhail P, et al. [35], большинство публикаций на тему ИИ-диагностики ишемического инсульта на бесконтрастной КТ содержали анализ чувствительности, специфичности и доли верных ответов моделей при сравнении с врачом-радиологом. Однако, чтобы оценить возможность использования ИИ в клинической практике, необходимы доказательства влияния ИИ на клинические исходы.
Самой распространённой конечной точкой в клинических исследованиях ИИ для диагностики ишемического инсульта является время "от двери до иглы" — от поступления пациента в стационар до проведения тромболитической терапии. По решению Национального симпозиума по быстрой идентификации и лечению острого инсульта (1996, Bethesda), этот показатель не должен превышать 60 мин. Большинство ИИ-сервисов, одобренных FDA и EMA, используются как инструмент маршрутизации пациентов в специализированных сосудистых центрах. Сервис автоматически анализирует исследование и при выявлении ишемического инсульта маркирует его в электронной медицинской карте. Маркировка сигнализирует врачу-рентгенологу, что исследование данного пациента необходимо рассмотреть в первую очередь, т.к. он с высокой вероятностью имеет патологию по данным КТ. Модель ИИ внутри подобной платформы для триажа пациента позволяет значимо уменьшить время до проведения тромболитической терапии и тромбэкстракции. Тем не менее в одном из исследований использование сервиса Rapid LVO для детектирования окклюзии больших сосудов по КТ-ангиографии, ранее одобренного FDA для использования в клинической практике, не позволило уменьшить время до лечения [36]. Изменение балла по шкале National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) через 36 ч после тромболитической терапии оказалось выше в группе, для которой не использовалась маршрутизация с ИИ (медиана 7 для группы без ИИ и 3 с ИИ, p<0,03). Время описания исследования резидентами-рентгенологами без большого опыта было значительно ниже в группе ИИ (31,70 мин без ИИ и 20,13 мин с ИИ, p<0,0003), статистически значимых различий в группе опытных нейрорадиологов не было. В похожем исследовании сервиса Viz LVO [37], аналогичного Rapid LVO по функциональным свойствам, в качестве первичной конечной точки для оценки эффективности использовался показатель door-in-door-out (DIDO) — время нахождения пациента в первичном сосудистом центре. Медианное время DIDO в группе без использования ИИ-маршрутизации составило 210 мин, в группе с использованием ИИ — 133 мин. В качестве вторичной конечной точки исследователи использовали вероятность проведения внутрисосудистой тромбэкстракции (EVT) после перевода пациента из первичного инсультного центра в специализированный центр. В группе ИИ этот показатель оказался выше, однако увеличение не достигло статистической значимости (отношение шансов 2,13; 95% доверительный интервал: 0,88-5,13; p=0,093), что может быть связано с малым объёмом выборки. Таким образом, ведущие модели ИИ позволяют ускорить оказание медицинской помощи пациентам с ишемическим инсультом, однако пока отсутствуют убедительные доказательства их влияния на клинические исходы.
Westwood M, et al. [38] в систематическом обзоре, посвящённом клинической и экономической эффективности программного обеспечения для диагностики ишемического инсульта, отмечают, что дизайн исследований не позволяет сделать выводы об эффек- тивности в реальной клинической практике. Ни одно из 22 проанализированных исследований не оценивало программное обеспечение с ИИ в условиях, соответствующих заявленному применению — в связке с врачом, как предполагается производителями. Практически все исследования изучали эффективность ИИ как автономной системы, что не отражает его предполагаемое использование в клинической практике. В другом случае, исследования ИИ-систем для триажа пациентов являются наблюдательными исследованиями, оценивающими время оказания помощи до и после внедрения ИИ в процесс маршрутизации. В данных исследованиях отсутствовала информация о ложноотрицательных ответах ИИ-моделей. Таким образом, нельзя сделать выводы о количестве случаев ишемического инсульта, пропущенных моделью ИИ.
В данный момент в Российской Федерации зарегистрированы 5 медицинских изделий с ИИ для автоматизации диагностики ишемического инсульта: Третье мнение КТ ГМ комплекс, NtechMed CT Brain, Sciberia Head, Цельс КС КТ ГМ, КТ ГМ комплекс от СберМедИИ. Каждый из этих сервисов осуществляет сегментацию зоны ишемии. Также данные сервисы детектируют и сегментируют кровоизлияния, что позволяет дифференцировать геморрагический и ишемический инсульт и выявить противопоказания для проведения тромболитической терапии.
Комплексный сервис "КТ головного мозга" компании-разработчика "СберМедИИ" — единственный российский сервис ИИ для диагностики ишемического инсульта, опубликовавший результаты исследования эффективности [39]. В рамках исследования сервис обработал 703 бесконтрастных КТ из одного медицинского центра и при ретроспективном сравнении с заключениями рентгенологов продемонстрировал высокую диагностическую точность: чувствительность — 89%, специфичность — 98%, точность — 98%. Значительным ограничением данного исследования являются критерии исключения. Из анализа исключались КТ-исследования с наличием "нецелевой патологии", что делает выборку нерепрезентативной.
Несмотря на отсутствие публикаций, посвящённых другим российским ИИ-сервисам для диагностики ишемического инсульта, их точность регулярно оценивается в ходе "Эксперимента по использованию инновационных технологий в области компьютерного зрения для анализа медицинских изображений и дальнейшего применения в системе здравоохранения города Москвы", запущенного в 2019г Правительством Москвы [40]. В рамках данного эксперимента лучевые исследования (в частности, КТ головного мозга), выполняемые в медицинских учреждениях города Москва, автоматически направляются разработчикам ИИ-сервисов для обработки ИИ-сервисом. Результаты обработки исследования становятся доступны врачу-рентгенологу, предоставляя "второе мнение". Оценка сервисов проводится экспертами ежеквартально. Сервисы оцениваются на основании параметра площади под кривой (AUC), отражающей способность модели различать положительные и отрицательные случаи ишемического инсульта и внутричерепных кровоизлияний. Показатели AUC участников Эксперимента в период 4 квартала 2024г1 для сервисов Третье мнение КТ ГМ комплекс, Цельс КС КТ ГМ, NTechMedCT Brain Complex составили 0,92; 0,8907; 0,8637, соответственно. Таким образом, разработанные в России модели ИИ для диагностики патологий на бесконтрастной КТ головного мозга имеют высокую диагностическую точность.
Заключение
Применение ИИ в диагностике ишемического инсульта является перспективным направлением, способным повысить оперативность и точность выявления патологии. Современные ИИ-модели демонстрируют сопоставимую с врачами-рентгенологами диагностическую точность.
Публикации, доказывающие эффективность ИИ в реальной клинической практике, имеют ряд ограничений. В большинстве публикаций, посвящённых ИИ-сервисам для диагностики ишемического инсульта, недостаточно описаны данные, использованные для обучения моделей ИИ, процессы разработки и тестирования моделей. Несмотря на положительное влияние ИИ-сервисов для маршрутизации пациентов на сокращение времени до начала лечения, влияние на исходы не доказано клиническими исследованиями. Проблема оценки эффективности особенно актуальна для моделей ИИ, разработанных в России, т.к. научные данные о точности и безопасности этих моделей, за исключением сервиса "КТ головного мозга", отсутствуют на момент написания данного обзора.
В связи с указанными выше ограничениями, оценка пользы применения ИИ-сервисов для диагностики инсульта в клинической практике остаётся нерешённой задачей на текущий момент. Для её решения необходим анализ влияния ИИ на клинические исходы в исследованиях и увеличение прозрачности данных в публикациях, посвящённых моделям для диагностики ишемического инсульта.
1 https://mosmed.ai/media/Матрица_зрелости_ИИ_сервисов_4_кв_2024_v.1.pdf.
Список литературы
1. Wolcott ZC, English SW. Artificial intelligence to enhance prehospital stroke diagnosis and triage: a perspective. Front Neurol. 2024;15:1389056. doi:10.3389/fneur.2024.1389056.
2. McCarthy JJ, Minsky M, Rochester N, Shannon CE. A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence. Ai Magazine. 2006;27(4):12. doi:10.1609/aimag.v27i4.1904.
3. Adlung L, Cohen Y, Mor U, et al. Machine learning in clinical decision making. Med. 2021;2(6):642-65. doi:10.1016/j.medj.2021.04.006.
4. Lindroth H, Nalaie K, Raghu R, et al. Applied Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: A Review of Computer Vision Technology Application in Hospital Settings. J Imaging. 2024;10(4):81. doi:10.3390/jimaging10040081.
5. Esteva A, Chou K, Yeung S, et al. Deep learning-enabled medical computer vision. NPJ Digit Med. 2021;4(1):5. doi:10.1038/s41746-020-00376-2.
6. Maegerlein C, Fischer J, Mönch S, et al. Automated Calculation of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score: Feasibility and Reliability. Radiology. 2019;291(1):141-8. doi:10.1148/radiol.2019181228.
7. Guberina N, Dietrich U, Radbruch A, et al. Detection of early infarction signs with machine learning-based diagnosis by means of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT score (ASPECTS) in the clinical routine. Neuroradiology. 2018;60(9):889-901. doi:10.1007/s00234-018-2066-5.
8. Adamou A, Beltsios ET, Bania A, et al. Artificial intelligence-driven ASPECTS for the detection of early stroke changes in non-contrast CT: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg. 2023;15(e2):e298-e304. doi:10.1136/jnis-2022-01944.
9. Amukotuwa SA, Straka M, Smith H, et al. Automated Detection of Intracranial Large Vessel Occlusions on Computed Tomography Angiography: A Single Center Experience. Stroke. 2019;50(10):2790-8. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.026259.
10. Yahav-Dovrat A, Saban M, Merhav G, et al. Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence-Powered Identification of Large-Vessel Occlusions in a Comprehensive Stroke Center. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021;42(2):247-54. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A6923.
11. Martinez-Gutierrez JC, Kim Y, Salazar-Marioni S, et al. Automated Large Vessel Occlusion Detection Software and Thrombectomy Treatment Times: A Cluster Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2023;80(11):1182-90. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.3206.
12. Delora A, Hadjialiakbari C, Percenti E, et al. Viz LVO versus Rapid LVO in detection of large vessel occlusion on CT angiography for acute stroke. J Neurointerv Surg. 2024;16(6):599-602. doi:10.1136/jnis-2023-020445.
13. Weyland CS, Papanagiotou P, Schmitt N, et al. Hyperdense Artery Sign in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke-Automated Detection With Artificial Intelligence-Driven Software. Front Neurol. 2022;13:807145. doi:10.3389/fneur.2022.807145.
14. Kasasbeh AS, Christensen S, Parsons MW, et al. Artificial Neural Network Computer Tomography Perfusion Prediction of Ischemic Core. Stroke. 2019;50(6):1578-81. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022649.
15. Vilela P. Acute stroke differential diagnosis: Stroke mimics. Eur J Radiol. 2017;96:133-44. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.05.008.
16. Bojsen JA, Elhakim MT, Graumann O, et al. Artificial intelligence for MRI stroke detection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Insights Imaging. 2024;15(1):160. doi:10.1186/s13244-024-01723-7.
17. Miceli G, Basso MG, Rizzo G, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Acute Ischemic Stroke Subtypes According to Toast Classification: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Biomedicines. 2023;11(4):1138. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11041138.
18. Newbury-Chaet I, Mercaldo SF, Chin JK, et al. Evaluation of an Artificial Intelligence Model for Identification of Mass Effect and Vasogenic Edema on CT of the Head. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2024;45(10):1528-35. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A8358.
19. Zatcepin A, Kopczak A, Holzgreve A, et al. Machine learning-based approach reveals essential features for simplified TSPO PET quantification in ischemic stroke patients. Z Med Phys. 2024;34(2):218-30. doi:10.1016/j.zemedi.2022.11.008.
20. Cross JL, Choma MA, Onofrey JA. Bias in medical AI: Implications for clinical decision-making. PLOS Digit Health. 2024;3(11):e0000651. doi:10.1371/journal.pdig.0000651.
21. Hernandez-Boussard T, Bozkurt S, Ioannidis JPA, et al. MINIMAR (MINimum Information for Medical AI Reporting): Developing reporting standards for artificial intelligence in health care. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2020;27(12):2011-5. doi:10.1093/jamia/ocaa088.
22. Liu X, Cruz Rivera S, Moher D, et al. Reporting guidelines for clinical trial reports for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the CONSORT-AI extension. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1364-74. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-1034-x.
23. Cruz Rivera S, Liu X, Chan AW, et al. Guidelines for clinical trial protocols for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the SPIRIT-AI extension. Lancet Digit Health. 2020;2(10):e549-e560. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30219-3.
24. Tejani AS, Klontzas ME, Gatti AA, et al. Checklist for Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging (CLAIM): 2024 Update. Radiol Artif Intell. 2024;6(4):e240300. doi:10.1148/ryai.240300.
25. Akay EMZ, Hilbert A, Carlisle BG, et al. Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Decision Support in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review. Stroke. 2023;54(6):1505-16. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.122.041442.
26. Galanty M, Luitse D, Noteboom SH, et al. Assessing the documentation of publicly available medical image and signal datasets and their impact on bias using the BEAMRAD tool. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):31846. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-83218-5.
27. Garin SP, Parekh VS, Sulam J, et al. Medical imaging data science competitions should report dataset demographics and evaluate for bias. Nat Med. 2023;29(5):1038-9. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02264-0.
28. Obermeyer Z, Powers B, Vogeli C, et al. Dissecting racial bias in an algorithm used to manage the health of populations. Science. 2019;366(6464):447-53. doi:10.1126/science.aax2342.
29. Larrazabal AJ, Nieto N, Peterson V, et al. Gender imbalance in medical imaging datasets produces biased classifiers for computer-aided diagnosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(23):12592-4. doi:10.1073/pnas.1919012117.
30. Chilamkurthy S, Ghosh R, Tanamala S, et al. Development and validation of deep learning algorithms for detection of critical findings in head CT scans. arXiv preprint. 2018. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1803.05854.
31. Pearce FJ, Cruz Rivera S, Liu X, et al. The role of patient-reported outcome measures in trials of artificial intelligence health technologies: a systematic evaluation of ClinicalTrials.gov records (1997-2022). Lancet Digit Health. 2023;5(3):e160-e167. doi:10.1016/S2589-7500(22)00249-7.
32. van Leeuwen KG, Schalekamp S, Rutten MJCM, et al. Artificial intelligence in radiology: 100 commercially available products and their scientific evidence. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(6):3797-804. doi:10.1007/s00330-021-07892-z.
33. Kim DW, Jang HY, Kim KW, et al. Design Characteristics of Studies Reporting the Performance of Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Diagnostic Analysis of Medical Images: Results from Recently Published Papers. Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(3):405-10. doi:10.3348/kjr.2019.0025.
34. Yu AC, Mohajer B, Eng J. External Validation of Deep Learning Algorithms for Radiologic Diagnosis: A Systematic Review. Radiol Artif Intell. 2022;4(3):e210064. doi:10.1148/ryai.210064.
35. Mikhail P, Le MGD, Mair G. Computational Image Analysis of Nonenhanced Computed Tomography for Acute Ischaemic Stroke: A Systematic Review. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020;29(5):104715. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104715.
36. Soun JE, Zolyan A, McLouth J, et al. Impact of an automated large vessel occlusion detection tool on clinical workflow and patient outcomes. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1179250. doi:10.3389/fneur.2023.1179250.
37. Le NM, Iyyangar AS, Kim Y, et al. Machine Learning–Enabled Automated Large Vessel Occlusion Detection Improves Transfer Times at Primary Stroke Centers. Stroke: vascular and interventional neurology. 2024;4:e001119. doi:10.1161/svin.123.001119.
38. Westwood M, Ramaekers B, Grimm S, et al. Software with artificial intelligence-derived algorithms for analysing CT brain scans in people with a suspected acute stroke: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2024;28(11):1-204. doi:10.3310/RDPA1487.
39. Медведева Н. А., Казиева М. Ю., Сидорова А. А. и др. Совре-менные возможности комплексного алгоритма искусственного интеллекта в диагностике ишемического инсульта и внутричерепных кровоизлияний. Журнал Диагностическая и интервенционная радиология. 2024;18(2.1):152-9.
40. Тыров И. А., Васильев Ю. А., Арзамасов К. М. и др. Оценка зрелости технологий искусственного интеллекта для здравоохранения: методология и ее применение на материалах московского эксперимента по компьютерному зрению в лучевой диагностике. Врач и информационные технологии. 2022;4:76-92. doi:10.25881/18110193_2022_4_76.
Об авторе
И. О. БалуновРоссия
Илья Олегович Балунов — студент, кафедра медицинского права, этики и антропологии ИММ
Москва
Дополнительные файлы
- Компьютерное зрение широко используется для маршрутизации пациентов с ишемическим инсультом.
- Точность моделей машинного обучения для диагностики ишемического инсульта по данным нейровизуализации сопоставима с точностью врачей-рентгенологов.
- В публикациях на тему точности систем искусственного интеллекта часто содержатся систематические ошибки.
- Системы искусственного интеллекта для диагностики ишемического инсульта не демонстрируют влияния на исходы пациентов в клинических исследованиях.
Рецензия
Для цитирования:
Балунов И.О. Проблемы оценки клинической эффективности применения искусственного интеллекта в диагностике ишемического инсульта. Российский кардиологический журнал. 2025;30(9S):6357. https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6357. EDN: CBNZRM
For citation:
Balunov I.O. Problems of assessing the clinical efficiency of artificial intelligence systemsin diagnosing ischemic stroke. Russian Journal of Cardiology. 2025;30(9S):6357. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6357. EDN: CBNZRM
JATS XML

















































