CORONARY HEART DISEASE, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
- The development of heart failure (CHF) after myocardial infarction significantly worsens exercise tolerance, quality of life and survival of patients.
- The prognosis of patients with HF is one of the most unfavorable, despite the introduction of effective treatment methods into practice.
- Involvement of patients with HF in cardiac rehabilitation programs based on physical training leads to an increase in exercise tolerance, improvement of clinical symptoms and quality of life after 3 months with an effect increase after 6 months.
Aim. To study the effectiveness of a 6-month training program in patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II-III heart failure (HF) after myocardial infarction (MI).
Material and methods. Patients (n=40) with left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) <45% after MI were included. Patients were randomized into the main group (n=20) with training and drug therapy and the control group (n=20) with therapy only. Training program and follow-up lasted 6 months.
Results. According to the bicycle ergometry after 6 months, the main group patients demonstrated a significant increase in the intensity (by 16,4%, p<0,01) and duration (by 21,3%, p<0,01) of physical activity (PA) against a decrease in these parameters in patients of control group (by 13,9%, p<0,01 and 20,4%, p<0,01, respectively). Only in the trained patients, LVEF increased after 6 months (by 6,5%, p=0,03) versus decrease (by 8,6%, p=0,024) in the control group. Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) against the background of physical training after 6 months decreased by 180±64 dyn·s·cm−5 (p=0,001) and did not change in the control group. Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire parameters improved after 6 months with PA (by 28,4±3,8%, p=0,001) and worsened without it (by 26,9±3,6%, p=0,001). With the training program, there was a decrease in the number of angina attacks (by 31,1%, p=0,022), complaints of dyspnea (by 15%, p=0,044) and muscle fatigue (by 21,6%, p=0,039). In the control group, these indicators did not change.
Conclusion. The 6-month training program for patients with NYHA class II-III HF contributed to a decrease in the severity of clinical symptoms, improved tolerance to PT, echocardiography parameters and quality of life. It is advisable to involve patients with HF and reduced LVEF in cardiac rehabilitation programs based on physical training.
CARDIOSURGERY
- The study describes the positive experience of iVAC 2L device use in high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention, including acute coronary syndrome.
- Under mechanical circulatory support with the iVAC 2L device, the technical success of the percutaneous coronary intervention procedure was achieved in 100% of cases.
- One of the most common complications of using the device are arrhythmias, which are benign in nature.
Aim. To analyze the multicenter international experience of high-risk protected percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) procedures using the transaortic temporary pulsatile mechanical circulatory support (MCS) device iVAC 2L (PulseCath B. V., Amsterdam, the Netherlands).
Material and methods. The pilot prospective-retrospective international multi-center observational study included patients with multivessel and/or complex coronary lesions, indications for coronary revascularization and refusal of the heart team from coronary artery bypass grafting and unprotected PCI due to a high risk of complications. PCI was performed with a temporary MCS using the iVAC 2L device in five clinics in Russia and Belarus.
Results. From February 2023 to February 2024, 24 patients were included in the study. The median age was 69,0 years (interquartile range (IQR): 63,5-71,8); 87,5% were men. Twenty patients (83,3%) underwent elective PCI and four patients (16,7%) due to acute coronary syndrome (ACS) as follows: three with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and one with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The patient with STEMI underwent PCI against the background of acute heart failure (AHF). The median MCS time was 66,0 min (IQR: 43,0-98,0). Technical success of PCI was achieved in 100% of patients. The median initial and residual SYNTAX scores were 35,0 (IQR: 25,6-41,4) and 8,0 (IQR: 5,0-17,5), respectively. The median left ventricular ejection fraction before PCI and 7 days after was 44,0% (IQR: 31,0-54,0) and 48,0% (IQR: 36,5-53,5), respectively. In two cases (8,3%), major bleeding from the access site of the MCS device was observed. There were 2 fatal outcomes as follows: during elective PCI due to progression of acute left ventricular failure and in the late period due to septic shock after emergency PCI.
Conclusion. PCI with MCP by the iVAC 2L device is an applicable and relatively safe tactic of coronary revascularization in patients with a high risk of complications, including in the conditions of ACS and AHF.
PROGNOSIS AND DIAGNOSTICS
What is already known about the subject?
- Increased plasma osmolarity is associated with the risk of adverse outcomes in acute heart failure or myocardial infarction.
What might this study add?
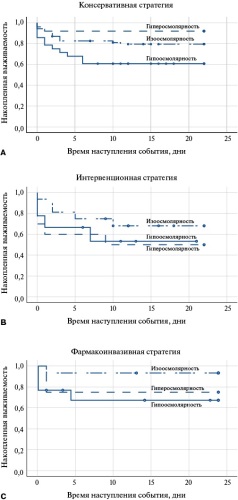
- Plasma hypoosmolarity is accompanied by an increased risk of inhospital mortality, which is significant in the conservative management of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction complicated by acute heart failure.
How might this impact on clinical practice?
- Assessment of plasma osmolarity upon admission to hospital in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction complicated by acute heart failure allows predicting inhospital mortality and potentially extends the time frame for myocardial revascularization in high-risk patients.
Aim. To assess the clinical significance of plasma osmolarity and its regulation in acute heart failure in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) under various revascularization strategies.
Material and methods. The study included patients hospitalized with a preliminary diagnosis of STEMI and clinically significant dyspnea (n=198). Plasma osmolarity was determined upon admission by estimation. To assess the intensity of vasopressin synthesis, the copeptin level was determined using an enzyme immunoassay. The study endpoints were inhospital mortality and early complications of MI.
Results. The patients in the sample were comparable by sex, age, major cardiovascular risk factors and clinical phenotype of MI that served as a reason for hospitalization. The highest rate of MI early complications and inhospital mortality was among patients with initial plasma hypoosmolarity (68,6 and 40,4%, respectively). Serum copeptin levels tended to increase in patients with initially low plasma osmolarity (p=0,178). Low baseline plasma osmolarity was associated with an increased risk of death (odds ratio (OR) 0,465, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0,238; 0,911, p=0,024), mainly due to the subgroup of patients with a conservative management strategy (OR 0,335, 95% CI 0,140; 0,803, p=0,012).
Conclusion. Plasma osmolarity assessed upon admission can be used to predict inhospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure and STEMI.
- Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) can help to understand the plaque vulnerability criteria.
- Combined use of CCTA and various serum and tissue biomarkers may be the key to identifying a vulnerable plaque.
- Microcalcifications in patients after acute coronary syndrome have a significant relationship with the level of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), as well as monocyte-to-HDL-C ratio.
Aim. To assess the relationship between simple inflammation markers and plaque vulnerability criteria according to coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), as well as lipid profile parameters in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Material and methods. This prospective, randomized, single-center study included 125 patients admitted urgently with the clinical performance of ACS (myocardial infarction (MI) — 94 patients; unstable angina (UA) — 31). All patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention of the infarct-related artery. In addition, all patients had atherosclerotic plaques with stenosis <50% in one or two non-infarct-related arteries. Treatment of ACS was carried out according to the guidelines. One month after ACS, all patients underwent CCTA to detect vulnerable plaques, as well as lipid profile analysis (total cholesterol (TC), lowdensity lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol), simple inflammatory biomarkers C-reactive protein (CRP), neutrophilto-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), monocyte-to-HDL-C ratio (MHR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), lymphocyte-to-CRP ratio (LCR).
Results. Of the 125 patients included in the study, MI was diagnosed in 94 (75%) patients, and UA in the remaining cases. In the acute period, in patients with MI, the HDL-C value was significantly lower 1,2 (1,03; 1,5) mmol/L than in the group of patients with UA (1,4 (1,24; 1,58) mmol/L), p=0,044. NLR was higher in patients with MI — 2,96 (2,09; 3,99) versus 2,21 (1,69; 2,71) in the UA group (p=0,018). One month after the index event, the HDL-C level remained significantly lower in the MI group 1,08 (0,95; 1,34) mmol/L, and the MHR was higher (0,52 (0,37; 0,64)) than in UA (1,25 (1,15; 1,34) mmol/L and 0,41 (0,31; 0,52)), respectively. The LCR after 1 month was almost 2 times higher in the UA group — 1,32 (0,65; 2,28) versus 0,66 (0,34; 1,28) in the MI group (p=0,028). The vulnerability criteria of plaques according to CCTA data were identified in 55 (44%) patients in the general group with ACS, of which positive remodeling was detected in 35 patients, a low-density area — in 30, and punctate calcifications (PC) — in 11. Patients in the general ACS group were divided by vulnerability criteria. Patients with PC had a significantly (p=0,004) higher level of HDL-C 1,22 (1,02; 1,34), compared to those without it 0,97 (0,77; 1,13). The MHR was higher (p=0,024) in the presence of PC (0,61 (0,48; 0,86)) than without it (0,46 (0,35; 0,63)). No significant differences were found for other indicators. When conducting the ROC analysis in patients with PC, the threshold level of HDL-C was 0,98 (AUC: 0,76, Sensitivity 66,7%, Specificity 77,4%), the threshold level of HDL-C in the presence of low-density area simultaneously with PC was also 0,98 (AUC: 0,83, Sensitivity 75%, Specificity 75,7%).
Conclusion. The HDL-C and MHR indicators significantly changed in patients who had ACS and microcalcifications in the plaques.
- Patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy are indicated for taking the selective transthyretin stabilizer tafamidis.
- During therapy, monitoring for disease progression is necessary.
- A case series demonstrates the importance of myocardial scintigraphy as a tool in assessing disease progression and demonstrates a previously undescribed effect of therapy in reducing the myocardial radiopharmaceutical uptake.
Introduction. In recent years, the detection rate of transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy has been rapidly increasing. The only drug registered as a pathogenetic therapy in Russia is tafamidis. To date, there is no single protocol for assessing disease progression, and the role of scintigraphy with phosphate complexes is not reflected in current documents due to the lack of evidence.
Brief description. The article presents a case series including patients who received tafamidis therapy for at least 12 months. During therapy, there were no signs of disease progression, and in some cases, according to myocardial scintigraphy with phosphate complexes, a decrease in radiopharmaceutical uptake was noted.
Discussion. The role of myocardial scintigraphy with phosphate complexes for monitoring the effectiveness of tafamidis therapy was discussed.
- For the first time, a scoring system has been proposed to assess the contribution of various factors (metabolic and cardiogenic) to increased liver stiffness in patients with cardiometabolic risks.
- Multiparametric ultrasound examination of the liver (B-mode, elastography, steatometry) allows you to differentiate the causes of changes in liver stiffness: steatosis, fibrosis, venous congestion or a combination thereof.
- The use of a scoring system ensures the accuracy and reproducibility of diagnosis, which contributes to a more personalized approach to the treatment of patients with metabolically associated steatosis liver disease.
- The results of the study confirm the value of ultrasound diagnostic methods for determining the severity of changes in the liver associated with venous congestion in patients with chronic heart failure.
- The developed ultrasound examination protocol can become the basis for standardization of diagnostics in clinical practice and scientific research.
Aim. To evaluate the feasibility of using multiparametric liver ultrasound to determine the pathophysiological causes of increased stiffness in patients with cardio-metabolic risks.
Material and methods. A study was conducted involving 104 cardiology patients, including 48 men (46,2%) and 56 women (53,8%), aged 49 to 73 years, of Caucasian ethnicity. Inclusion criteria included chronic heart failure stage IIB (II, III functional classes according to NYHA), main and additional criteria of metabolic syndrome containing cardiometabolic risks for the development of metabolically associated fatty liver disease. All patients were examined according to a unified diagnostic algorithm consisting of two stages: Stage 1 — clinical and laboratory assessment, Stage 2 — instrumental assessment using liver ultrasound methods (B-mode, color Doppler imaging, two-dimensional shear wave elastography, quantitative steatometry).
Results. A scoring system has been proposed to assess the predominant contribution to liver fibrosis development based on data from multiparametric ultrasound examination of the liver. Total score 0-8: predominant liver involvement — in this case, characteristic signs of liver involvement, such as increased echogenicity and absence of significant venous vessel dilation, are observed. Total score 9-14: combined involvement — the signs include both liver-related changes (e.g., steatosis) and signs of venous congestion. Total score 15-16: predominant cardiovascular involvement — in this case, significant venous vessel dilation and other signs of congestive hepatopathy are the main features, indicating venous congestion as the primary cause of liver changes.
Conclusion. Multiparametric ultrasound examination of the liver combined with the developed scoring system can be used to differentiate the causes of increased liver stiffness and the severity of liver steatosis in patients with cardiometabolic risks. Standardization of the ultrasound protocol improves the reproducibility of the method.
RISK FACTORS
- Adjuvant chemotherapy with a combination of doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide in breast cancer (BC) in women is associated with an increase in the level of atherogenic lipoproteins and visceral obesity parameters, which is more pronounced in patients with comorbidity of BC and hypertension (HTN).
- In patients with BC, metabolic status disorders are recorded 7-14 days after the completion of chemotherapy and can persist for up to 3-4 months, which indicates the need for long-term monitoring of changes.
- A comprehensive assessment of the potentially adverse effects of chemotherapy is a prerequisite for the effective prevention of cardiovascular complications in BC, especially in cases of its combination with masked or primary HTN.
Aim. To evaluate cardiometabolic risk (CMR) factors in women with breast cancer (BC) before and after chemotherapy (CT) with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide.
Material and methods. This prospective cohort study included 154 women with a median age of 43 years with newly diagnosed stage IIA-IIIB BC. Three following groups were identified among the examined women: with normal blood pressure (BP), masked hypertension (MH) and primary hypertension (HTN). All patients after BC surgery underwent 4 courses of chemotherapy with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide lasting about 3 months. The assessment of CMR factors was carried out at 3 following stages: I — before chemotherapy; II and III — 7-14 days and 90-120 days after its completion. Fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TGs), high-density (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and non-HDL-C were determined. The atherogenicity coefficient, visceral obesity index (VAI) and lipid accumulation product (LAP) index were calculated.
Results. In women with comorbidity of BC and HTN, the body mass index (BMI) decreased at stage II and returned to the initial level at stage III, while class I obesity was recorded in almost a third of patients. In the MH group, an increase in BMI was observed 90-120 days after the end of chemotherapy. In patients with normal BP, TC level did not change significantly during the follow-up, and among women with HTN, a significant increase in TC compared to the baseline was determined 90-120 days after the completion of chemotherapy. In patients with comorbidity of BC and HTN at stage III, the highest concentration of LDL-C, non-HDL-C and the lowest concentration of HDL-C in the blood were established, which distinguished them from individuals with normotension and MH. Hypertriglyceridemia was recorded in most patients with MH and hypertension after the completion of chemotherapy. The median values of TGs, VAI and LAP index in individuals with normal BP were significantly lower than in the comparison groups at all stages.
Conclusion. In patients with BC after adjuvant chemotherapy with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide, an increase in the level of atherogenic lipids and visceral obesity indicators is recorded, which is more pronounced in the case of comorbidity of BC and HTN. Metabolic status disorders after chemotherapy persisted for up to 3-4 months, which indicates the need for long-term monitoring of changes.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY
- Patients with diabetes often have platelet hyperreactivity and, as a rule, a reduced response to acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) therapy.
- In all patients with stable coronary artery disease, the need for antiplatelet therapy for secondary cardiovascular prevention is beyond doubt.
- There is still no "gold standard" for assessing the effectiveness of ASA, but at the moment, high expectations are associated with platelet aggregometry and its various modifications.
- Up to 60% of patients are resistant to ASA therapy, one of the possible factors for the development of resistance may be enteric coating.
- The buffered ASA, which is absorbed in the stomach, is potentially more effective in patients with diabetes and coronary artery disease compared to the enteric-coated form without any loss in safety.
Aim. Enteric-coated acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is released more slowly and is absorbed in smaller quantities and over a longer period of time, which may lead to bioavailability and antiplatelet effect decrease compared to conventional ASA. Patients with diabetes are characterized by increased platelet reactivity and a reduced pharmacodynamic response to ASA compared to individuals without diabetes. It seems rational to test the hypothesis that the use of ASA absorbed in the stomach may be more effective in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) and stable coronary artery disease (CAD).
Material and methods. This single-center, non-interventional comparative study will randomly select 200 adult patients of both sexes with stable CAD and T2D who were routinely prescribed a gastro-soluble ASA (Cardiomagnyl 75 mg/day) or an enteric-soluble ASA (Aspirin® Cardio 100 mg/day or Thrombo ASS® 100 mg/day) before inclusion in the study. According to the routinely prescribed therapy, patients will be divided into 2 following groups: patients taking Cardiomagnyl 75 mg/day and patients taking Aspirin® Cardio 100 mg/day or Thrombo ASS® 100 mg/day. The primary endpoint is the incidence of high residual platelet reactivity (HRPR) while taking ASA (resistance to ASA) according to the VerifyNow Aspirin Test.
Conclusion. CASCADE is the first study to evaluate the HRPR using the VerifyNow Aspirin Test in patients with stable CAD and T2D.
- Angiotensin II receptor blocker therapy in patients with mitral valve prolapse resulted in decreased expression of transforming growth factor-β (serum concentration and density of TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 expressing valvular interstitial cells) and severity of myxomatous degeneration (expression of type III collagen, but not fibulin-5, thickness and length of leaflets according to echocardiographic and pathological examination).
- Angiotensin II receptor blocker therapy is associated with improved left ventricular strain and reduced severity of mitral regurgitation in patients with mitral valve prolapse.
- These studies indicate the potential of angiotensin II receptor blockers for the development of new approaches to pathogenetic therapy of mitral valve prolapse.
Aim. To evaluate the effect of angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) therapy on the expression of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) in the myxomatous mitral valve, on the serum levels of TGF-β1/TGF-β2 and the left ventricular (LV) systolic function in patients with mitral valve prolapse (MVP).
Material and methods. The retrospective non-randomized single-center study included 233 patients who underwent surgical treatment of severe mitral regurgitation due to MVP. Preoperative drug therapy was assessed using case records. Transthoracic echocardiography was performed in all patients before surgery. Pathological and immunohistochemical analysis of mitral valve fragments removed during surgery were performed. The serum content of TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 was determined by the enzyme immunoassay.
Results. According to echocardiography, mitral valve leaflets were significantly longer and thicker in patients in the control group than in the ARB group. These data were confirmed by pathological study — most patients in the control group had excessive myxomatous mitral valve leaflets (χ2=7,9; p=0,005). In the ARB group, the expression of type III collagen in the mitral valve leaflets was lower compared to the control group and the expression of fibulin-5 did not differ. Also, in the main group, an increased density of valvular interstitial cells was found, including those expressing TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 compared to the control group. The serum level of TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 was significantly higher in the control group than in the ARB group.
Despite the absence of differences in LV ejection fraction between the groups, global longitudinal systolic strain and strain rate were significantly higher in the main group.
Conclusion. This is the first study to reveal a positive effect of ARB therapy on myxomatous mitral valve degeneration and LV function due to inhibition of the TGF-β signaling pathway, which opens up potential for pathogenetic therapy in patients with MVP.
EXPERT COUNCIL OPINION
The aim of the expert council "First star duo of telmisartan and indapamide in the Russian Federation", dedicated to the introduction of a new fixed-dose combination of telmisartan and indapamide (modified-release tablets) into clinical practice was to formulate an expert opinion on the potential use of novel fixed-dose combination of telmisartan and indapamide in the treatment of hypertensive patients.
LIPID METABOLISM DISORDERS
- Skeletal muscle disorders in patients with coronary artery disease can be represented by dynapenia and presarcopenia and occur in approximately a quarter of patients.
- Presarcopenia and dynapenia can be considered not only as components of sarcopenia, but also as independent pathologies that are not always interconnected.
Aim. To assess the prevalence of dynapenia, presarcopenia and their relationship with structural and functional parameters of the heart in patients with coronary atherosclerosis.
Material and methods. The study included 136 people with stable types of coronary artery disease (CAD). Hand grip test was performed to measure muscle strength. In women, a decrease in grip strength of <16 kg was a sign of decreased muscle strength, while in men — <27 kg (according to the guidelines of the Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 of 2019). All patients underwent computed tomography with skeletal muscle index (SMI, cm2/m2) estimation. The threshold values of SMI, a decrease in which was regarded as a decrease in muscle volume, were 52,4 cm2/m2 for men and 38,5 cm2/m2 for women. If patients had an isolated decrease in SMI according to computed tomography, the condition was classified as presarcopenia. With a decrease in muscle strength according to the hand grip test, the condition was classified as dynapenia. All patients underwent echocardiography using a standard technique.
Results. The analysis revealed that individuals with presarcopenia were exclusively male and were taller (175 (168; 179) cm) than those with normal muscle mass (166 (159; 172,5) cm (p=0,001)), but the body mass index in presarcopenia was lower (27,3 (24,4; 30,3) kg/m2 and 29,5 (25,8; 33,1) kg/m2) in individuals without this pathology (p=0,02). When comparing echocardiographic parameters, a lower left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction was found among patients with presarcopenia. The LV end-diastolic volume (EDV), LV end-systolic volume (ESV), LV end-diastolic dimension (EDD), and LV end-systolic dimension (ESD) were greater in the group of patients with presarcopenia compared to other patients (p<0,05). Patients with presarcopenia were more likely to have prior myocardial infarction — 24 patients (68,6%) versus 41 (46,6%) in the group without presarcopenia (p=0,02). Patients with dynapenia differed in the following parameters: they were older (68 (65,6; 71,4) years versus 65 years (63; 67,9) in rest of the sample), mostly women (74,2%) and shorter (164 (159,6; 165,4) cm) compared to individuals without dynapenia (170 (168; 172) cm (p<0,05)). Patients with dynapenia were more likely to have prior type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (p<0,05).
Conclusion. Patients with presarcopenia and CAD more often have prior myocardial infarction and larger LV size and volume. Patients with dynapenia and coronary atherosclerosis are more often female, have shorter stature, and more often had chronic kidney disease and diabetes.
- Aortic stenosis (AS) diagnosed at a young age without infectious and congenital etiology may be a manifestation of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH).
- The development of AS in FH is associated with both non-lipid risk factors, such as age and hypertension, and lipid ones, with metabolic factors influencing the progression of aortic valve disease (total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, triglycerides, lipoprotein(a) levels and cumulative indicators).
Aim. To analyze factors influencing the development of aortic stenosis (AS) in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (heFH).
Material and methods. A total of 114 patients with heFH were examined (mean age 54,3±2,7 years, 85 men (69,1%)), of whom 10 (8,8%) had AS. FH was diagnosed according to the Dutch Lipid Clinic Network criteria. Lipid profile parameters, lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) level, age, family history of cardiovascular disease, smoking, hypertension (AH), hyperglycemia were analyzed. The history of coronary artery disease (CAD), myocardial infarction (MI), and ischemic stroke was taken into account. Cumulative levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and non-HDL cholesterol were calculated as the total LDL-C over the patient's life, taking into account the levels achieved during lipid-lowering therapy.
Results. AS development was influenced by age (odds ratio (OR) 1,1 [1,02; 1,15], p=0,009), HTN (OR 8,15 [1,50; 44,08], p=0,017), lipid profile parameters: total cholesterol (OR 2,09 [1,38; 3,10], p=0,0006; LDL-C (OR 2,8 [1,59; 4,79], p=0,0004), non-HDL-C (OR 1,012 [1,005; 1,019], p=0,003), triglycerides (OR 1,97 [1,33; 2,87], p=0,0007). Cumulative indicators also influenced the risk of AS: cumulative LDL accumulated over the years of life (OR 2,13 [1,31; 3,54], p=0,003), cumulative non-HDL-C level accumulated over life (OR 1,56 [1,01; 2,18], p=0,013), Lp(a) level (AS risk increases by 10,6 times with an increase in Lp(a) by 1 unit of measurement (1 g/l) (OR 10,5 [5,0; 21,9], p=0,0017). The presence of CAD and MI in FH increases the risk of AS (for CAD, OR 8,62 [1,07; 69,113], p=0,044; for MI, OR 3,93 [1,08; 14,36], p=0,034). The combination of MI and cerebrovascular accident increases the risk of AS by 4,94 (OR 4,94 [1,23; 19,62], p=0,021). Tendon xanthomas significantly affects the AS (OR 50,2 [6,03; 413,00], p<0,001).
Conclusion. AS detected at a young age can be a manifestation of FH. The development of AS in FH is influenced by age and HTN, and following lipid factors: total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides, as well as Lp(a) levels and cumulative indicators.
- Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events and acute and chronic pancreatitis.
- The profile of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, the pathogenesis of lipid disorders and hypertriglyceridemia-associated risks vary significantly, which requires differentiated approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
Numerous studies demonstrate an independent relationship between an increase in the blood content of triglyceride-rich particles and the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases and acute pancreatitis. This review article presents in detail aspects of the pathogenesis of various types of primary and most relevant secondary hypertriglyceridemias (HTGs). Classifications are provided depending on the etiology, phenotype of dyslipidemia and severity. Approaches to HTG diagnosis are described. Special attention is paid to the potential of HTG therapy.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)