ОЦЕНКА РИСКА
Aim. To evaluate the relationship between leukocyte telomere length (LTL) and cardiovascular risk factors in young and middle-aged patients without cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Material and methods. This cross-sectional study involved 450 patients aged 30 [21;42] years. Risk factors and possible exclusion criteria was assessed through questionnaires and anthropometric examination. In all subjects, glucose concentration and lipid profile were assessed using the CardioChekPA express analyzer (USA, 2017), followed by calculation of integral metabolic indices: visceral adiposity index (VAI), body fat percentage, body adiposity index (BAI), lipid accumulation product (LAP). LTL was measured in whole blood samples using fluorimetry (Qubit 4 Singapore 2020) and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (QIAamp Blood Mini Kit, German 2022). Statistical analysis was carried out using the Statistica 10 program.
Results. The prevalence of the studied risk factors in the main group corresponded to the general population. According to the correlation analysis, LTL was associated with age (r=-0,26; p<0,05), smoking (r=-0,35; p<0,05), obesity (r=-0,19; p>0,05), neck circumference (NC) (r=-0,53; p<0,05), diastolic blood pressure (r=-0,31; p<0,05), cholesterol (r=-0,64; p<0,05), high-density lipoproteins (HDL) (r=0,59; p<0,05) and low-density lipoproteins (r=-0,52; p<0,05), triglycerides (r=-0,46; p<0,05), glucose (r=-0,33; p<0,05), LAP (r=-0,4; p<0,05), VAI (r=-0,57; p<0,05) and BAI (r=-0,32; p<0,05). According to the multivariate regression analysis, LTL was associated with age (B=-0,04, Std. Err. of B=0,02, p=0,03), smoking (B=-0,87, Std. Err. of B=0,26, p=0,001), NC (B=-0,23, Std. Err. of B=0,07, p=0,001), total cholesterol levels (B=-0,37, Std. Err. of B=0,87, p<0,001), HDL (B=0,59, Std. Err. of B=0,24, p=0,018), LAP (B=-0,01, Std. Err. of B=0,02, p<0,011), VAI (B=-0,37, Std. Err. of B=0,16, p=0,025).
Conclusion. LTL is interconnected with cardiovascular risk factors, which determines the significance of their participation in CVD development and biological aging in young and middle-aged people.
- Interval hypoxic-hyperoxic exposures in the hypoxic preconditioning mode reduces the incidence of peri- and postoperative complications.
- The study did not register cerebrovascular accidents in patients after hypoxic preconditioning in the peri- and postoperative periods, with a higher level of cognitive function being maintained compared to the placebo group.
- Compared with the control group, patients who underwent preoperative hypoxic-hyperoxic conditioning procedures showed frequent spontaneous restoration of sinus rhythm, which was accompanied by significantly lower values of myocardial injury, endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress 24 hours after surgery.
Aim. To assess the effect of intermittent hypoxic-hyperoxic exposures (IHHE) on the outcomes of on-pump cardiac surgery.
Material and methods. This prospective, single-center, randomized, controlled study was conducted in 110 patients with heart valve defects and/or aortic pathology from the cardiac surgery clinic of the I. M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University. The total sample was randomly divided into a group of patients who underwent IHHE (n=66) and a control group of patients who underwent placebo procedures with ambient air (n=44). The frequency and structure of intra-and postoperative complications were analyzed within 30 days after surgery. The presence of cognitive impairment, as well as serum troponin I and lactate concentrations were analyzed before and after surgery.
Results. Peri- and early postoperative complications such as cardiac death, non-fatal infarction and acute heart failure occurred significantly less frequently in patients treated with IHHE compared with placebo group (1,6% vs 16,7%, p=0,009; 1,6% vs 16,7%, p=0,009; 6,3% vs 33,3%, p<0,001, respectively). The median troponin I values 24 hours after surgery were 1,068 ng/ml (0,388-1,397 ng/ml) in the IHHE group and were significantly lower compared to the control group (1,980 ng/ml (1,068-3,239 ng/ml)). The serum lactate level after surgery was 1,8±0,7 mmol/l in the IHHE group and was significantly lower compared to the control group — 2,4±1,2 (p=0,05). Cognitive function, assessed by MOCA and MMSE tests, turned out to be significantly higher in patients who underwent a preoperative IHHE. No significant complications or serious adverse events were observed during the IHHE procedures.
Conclusion. The use of individually adapted hypoxic preconditioning procedures reduces the incidence of peri- and postoperative complications, which is accompanied by a lower ischemia-reperfusion myocardial injury during artificial circulation with preservation of cognitive functions. IHHE procedures ramp up prehabilitation of patients referred for on-pump surgery of heart defects and aortic pathology.
- The majority of patients with coronary artery disease referred for coronary artery bypass surgery have reduced left atrial strain characteristics. Impaired conduit and reservoir functions are predominantly detected.
- The data obtained may indicate no significant relationships between the parameters of left atrial myocardial strain and the risk of postoperative atrial fibrillation in patients who underwent off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting, which may be explained by the surgical characteristics performed.
Aim. To explore the potential of using left atrial strain parameters obtained through transthoracic speckle-tracking echocardiography for predicting new-onset postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF) in patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Material and methods. The study included 111 patients with coronary artery disease referred for elective CABG. There were following exclusion criteria: recurrent or combined cardiac surgery, cerebral stroke, prior atrial tachyarrhythmia episodes, on-pump CABG, patients with NYHA class 4 heart failure. Patients included in the study underwent transthoracic speckle tracking echocardiography before surgery to assess the reservoir, conduit and contractile left atrial (LA) functions. After off-pump CABG, patients were prospectively observed until discharge from the hospital to record the primary end point — the first-time persistent POAF episode.
Results. During follow-up, POAF was recorded in 11 patients (10%). The median endpoint registration was 4 days. The groups formed depending on the end point achievement were comparable in basic clinical and demographic characteristics and analyzed ultrasound parameters. In the majority of the patients studied, a decrease in LA function was detected. Disorders of the conduit (n=94, 85%) and reservoir functions (n=85) were dominant.
Conclusion. The results obtained may indicate that there is no relationship between the LA myocardial strain parameters obtained during preoperative screening and the risk of POAF in patients with coronary artery disease who underwent off-pump CABG.
- White blood cell count in the sample with myocardial infarction (MI) with an active cancer was higher than in patients with MI and a history of cancer, while the white blood cell count in people with MI and a history of cancer was higher than in those with MI without cancer.
- Total cholesterol level was lower in MI patients with active cancer compared with MI without cancer or with a history of cancer.
Hokkaido University (Tsumita T, 2022) researchers found that endothelial cells accumulate low-density lipoproteins (LDL) in tumor blood vessels. At the same time, the endothelium carries out neutrophil chemotaxis, which perform an immunosuppressive function contributing to cancer progression.
Aim. To search for the relationship between the white blood cell (WBC) count and some lipid profile parameters in cancer patients with myocardial infarction (MI).
Material and methods. We examined 319 patients who were treated at Dzhanelidze Research Institute of Emergency Medicine in 2018-2023, which were divided into three groups: MI in combination with an active cancer — 132 patients (Group I), MI+cancer in history — 58 patients (Group II), MI without cancer — 129 patients (Group III). Following laboratory data used in routine practice were assessed: WBC count, relative neutrophil count, total cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins.
Results. Cancer patients with MI are characterized by higher WBC and neutrophil count than in other samples However, the total cholesterol level was significantly lower in this sample, and the LDL level was not significantly different. Patients with MI and previous cancer occupied an intermediate position between groups I and III in terms of studied parameters.
Conclusion. In general, data on the role of cholesterol levels in cancer patients are contradictory. In particular, some studies have shown that elevated cholesterol levels are a potential risk factor for cancer. In our study, as in a number of others, no significant associations were identified between elevated cholesterol levels and the presence of cancer. Our study is a step towards understanding the connection between the cholesterol concentration and the immune response in cancer patients with MI.
- In a cohort of patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF), a high incidence of clinically significant obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) was revealed.
- In the group of patients with a combination of OSA and AF undergoing conservative treatment, more unfavorable cardiovascular characteristics of the system and more severe comorbid status were revealed compared to the group of patients undergoing surgical treatment.
- Along with the known risk factors for AF, OSA in patients with paroxysmal AF should be diagnosed and treated in order to influence the AF recurrence. According to our data, priority attention should be paid to patients undergoing conservative treatment of arrhythmia.
Aim. To compare the clinical characteristics of two groups of patients with a combination of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF), undergoing conservative treatment for arrhythmia and after pulmonary vein isolation.
Material and methods. The study included 362 patients with paroxysmal AF who underwent respiratory sleep monitoring.
Results. A predominance of clinically significant OSA was revealed (moderate and severe — 37% and 29%, respectively), as well as a higher drug burden and comorbidity in the group of patients receiving drug treatment for AF. The threshold value of body mass index (BMI), at which a high risk of severe OSA was predicted, corresponded to class 1 obesity (BMI ≥31 kg/m2). The results obtained demonstrated an association between an increase in the left atrium anteroposterior size and the severity of OSA (4,1 [3,8-4,4] cm, r=0,28; p<0,001), which may be due to cardiac structural remodeling in patients with a combination of paroxysmal AF and severe OSA.
Conclusion. In a cohort of patients with paroxysmal AF, a high incidence of clinically significant OSA was revealed. In the group of patients with a combination of OSA and AF undergoing conservative treatment, more unfavorable cardiovascular characteristics and a more severe comorbid status were revealed compared to the group of patients undergoing surgical treatment.
GUIDELINES FOR THE PRACTITIONER
Aim. To evaluate the dapagliflozin as part of various treatment regimens in patients with heart failure (HF) with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) ≤40% receiving medications within federal preferential drug program to achieve the "Reduction of cardiovascular mortality" of the State Program "HealthCare Development". To estimate the costs of reducing the cardiovascular mortality rate by 1 death per 100 thousand of population and achieving 1 percentage point of the target indicator "Reduction of cardiovascular mortality".
Material and methods. The target patient population was Russian patients aged over 18 years diagnosed with NYHA class II-IV HFrEF (≤40%), included in the federal preferential drug program. We used model developed based on the DAPA-HF study results. We assessed the costs of drugs, the number of lives saved, the impact of therapy on achievement of the target indicator "Reduction of cardiovascular mortality" and other indicators in the Russian Federation (RF) as a whole and in each subject of the Russian Federation while using dapagliflozin as part of various treatment regimens for HFrEF including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi)/angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARB) or angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNi), beta blockers, diuretics, mineralocorticoid antagonists, cardiac glycosides.
Results. In 2024, the treatment cost of 181351 patients with HFrEF included in the federal preferential drug program with dapagliflozin in combination with standard therapy (ST) will be RUB9265,4 million; in combination with ST without ARNi (ST including ACEi/ARB) — RUB8161,7 million; in combination with ST including ARNi — RUB17837,3 million. The additional number of lives saved when using dapagliflozin in combination with standard therapy was 2394, in combination with standard therapy without ARNi — 2340, in combination with standard therapy, including ARNi — 2913. Costs of therapy per patient per year when using dapagliflozin in combination with standard therapy amounted to RUB51090,90; in combination with standard therapy without ARNI — RUB45004,72; in combination with standard therapy, including ARNI — RUB98358,00. In 2024, the percentage (%) of achievement of the federal target for dapagliflozin in combination with ST is 11,22%, while in combination with standard therapy without ARNi (ST including ACEi/ARB) — 10,96%, in combination with ST including ARNi — 13,65%. Achievement of a 1% target reduction in cardiovascular mortality in 2024 reqiored RUB828,1 million for dapagliflozin in combination with ST, while in combination with ST without ARNI (ST including ACEi/ARB) — RUB748,2 million, in combination with ST including ARNi — RUB1293,3 million.
Conclusion. Among the 3 options considered for adding dapagliflozin to ST (ARNi or ACEi/ARB, including ACEi/ARB, including ARNi), ST without ARNI (ST including ACEi/ARB) has the lowest cost required to achieve a 1% target reduction in cardiovascular mortality. At the same time, the standard therapy with ARNI has the highest cost required to achieve a 1% target reduction in cardiovascular mortality, which indicates its least cost-effectiveness.
- Over the past decades, alongside with the increase in the hypertension (HTN) prevalence, there has been a progressive increase in the prevalence of overweight/obesity and diabetes. There is strong evidence of a relationship between body mass index and the risk of cardiovascular events.
- The importance of early initiation of antihypertensive therapy is recognized, including in persons with overweight/obesity and concomitant diabetes.
- Data from subanalyses of the TRICOLOR study in patients with overweight/obesity and diabetes demonstrate the high antihypertensive effectiveness of amlodipine/indapamide/perindopril in patients with hypertension, the clinical effectiveness of which did not depend on the presence of diabetes, overweight or obesity.
Aim. To describe antihypertensive effectiveness of triple fixed-dose combination of am lo dipine/indapamide/perindopril and assess predictors of its clinical effectiveness in pati ents depending on body mass index (BMI) and presence of type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Material and methods. This observational prospective study TRICOLOR (NCT03722524) (n=1247) demonstrated high antihypertensive effectiveness and good tolerability of amlodipine/indapamide/perindopril fixed-dose combination. Subgroup analyzes based on BMI included data from 1144 patients. In a second subgroup analysis, 1128 patients were stratified according to concomitant T2D.
Results. In patients with overweight/obesity and diabetes, good antihypertensive effectiveness of amlodipine/indapamide/perindopril was observed, comparable in blood pressure (BP) reduction with the comparison groups (patients with normal BMI and patients without diabetes). At the same time, patients with normal BMI, compared with patients with overweight and obesity, had significantly lower systolic BP (SBP) (after 4 and 12 weeks) and diastolic BP (DBP) (after 2 and 12 weeks). In the subgroups, depending on the diabetes status, there were no significant differences in the decrease in SBP and DBP levels at all follow-up points. By the 12th week, BP decrease in the group of patients with normal BMI was 32,9 (10,5)/15,3 (8,6) mm Hg, in the group with overweight — 33,2 (11,3)/14,2 (8,5) mm Hg, in the obesity group — 33,9 (12,3)/14,1 (8,8) mm Hg (p>0,05 for intergroup comparison). Target BP <140/90 mm Hg already after 2 weeks of therapy achieved a higher number of patients with a normal BMI compared to overweight group (50,8% vs 37,2%, p=0,009). By the 12th week, the vast majority of patients, regardless of BMI and diabetes status, achieved a target BP <140/90 mm Hg, which demonstrates a good and rapid response to triple fixed-dose therapy.
Conclusion. Thus, additional analyzes of the TRICOLOR study demonstrate the high antihypertensive effectiveness of amlodipine/indapamide/perindopril in hypertensive patients, regardless of the presence of diabetes, overweight or obesity.
PROGNOSIS AND DIAGNOSTICS
- The study provided evidence of the association of systemic inflammation with early adverse outcomes of myocardial infarction (MI) in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
- The potential of cellular indices of systemic inflammation (neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, systemic inflammation index and systemic inflammation response index) as predictors of adverse events in patients with myocardial infarction and type 2 diabetes has been demonstrated.
- The developed model for predicting in-hospital mortality, including cellular indices of systemic inflammation and traditional risk factors, will optimize risk stratification for MI in combination with type 2 diabetes.
Aim. To assess the value of cellular indices of systemic inflammation in the prognosis of in-hospital mortality in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (MI) in combination with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Material and methods. The retrospective case-control study included 125 patients with myocardial infarction and T2D, 25 of whom died during the index hospitalization. The cellular composition of the blood and the level of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) were determined on the first and third days of hospitalization. In the groups of deceased and surviving patients, cellular indices of systemic inflammation were calculated and compared (neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), neutrophil-monocyte ratio (NMR), monocyte-lymphocyte ratio (MLR), platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), systemic inflammation index (SII), systemic inflammation response index (SIRI)) and average hsCRP levels). The prognostic role of the studied parameters was assessed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression.
Results. Deceased patients, compared with survived ones, had higher Killip class, body mass index, number of stents implanted, higher hsCRP levels, and lower left ventricular ejection fraction. Inhospital mortality was associated with hsCRP (odds ratio of 1,03 with 95% confidence interval of 1,003-1,05, p=0,029), NLR (2,56 [1,73-9,78], p<0,001), NMR (1,16 [1,001-1,35], p=0,04), MLR (23,7 [3,1-182,6], p=0,002), SII (1,001 [1,0-1,001], p=0,028), SIRI (1,29 [1,09-1,52], p=0,003) 48 hours after admission, as well as with the degree of hsCRP change (1,03 [1,003-1,05], p=0,025), NLR (1,58 [1,21-2,06], p=0,001), SII (1,001 [1,0-1,001], p=0,028) during the first three days. Adjusted multivariate regression analysis identified a set of independent predictors with greatest accuracy in assessing the death probability: NLR, SII and SIRI 48 hours after admission, the degree of hsCRP change, body mass index and the num ber of implanted stents.
Conclusion. The work demonstrated the significance of cellular indices of systemic inflammation (NLR, SII and SIRI) in assessing the prognosis of in-hospital mortality in patients with MI combined with T2D.
- Increased survival of patients with myocardial infarction (MI) has led to an increase in the number of patients with MI complications. One of these complications is left ventricular (LV) aneurysm, the formation of which increases in-hospital mortality in patients with MI, the incidence of arrhythmias and heart failure.
- The incidence of dilatation and post-infarction LV aneurysm according to our work was 18,1%.
- Anterior MI location and the level of stimulating growth factor are predictors of dilatation and post-infarction LV aneurysm development.
Aim. To establish predictors of left ventricular (LV) dilatation and post-infarction left ventricular aneurysm (LVA) development in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and/or with Q wave.
Material and methods. This registry study included patients admitted with STEMI and/or with Q wave in the first 24 hours from the disease onset in the period from November 1, 2022 to March 31, 2023. The study included 138 patients. The mean age of the patients was 62±11 years. Treatment and examination were carried out in accordance with the current Russian clinical guidelines (2020) on STEMI. The levels of stimulating growth factor expressed by genome 2 (sST2), proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein were determined in patients by enzyme immunoassay on the first day of the disease. The patients were divided into two following groups: group 1 — patients with LV dilatation/LVA, n=25 (18,1%), group 2 — patients without LV geometry disorders, n=113 (81,9%). Univariate and multivariate regression analyzes were performed to determine independent predictors of LV dilation/postinfarction LVA.
Results. This study showed that with an increase in sST2 levels by 1 ng/L, the probability of LV dilation/LVA formation increase by 1,53 times. Anterior location of myocardial infarction increases the probability of LV dilation/LVA formation by 63,55 times. An increase in eGFR on day 2 of hospitalization by 1 ml/min/1,73 m2 reduces the probability of LV dilatation/LVA formation by 1,07 times.
Conclusion. The study showed that anterior location of myocardial infarction and increased sST2 levels increase the probability of LV dilation/LVA formation.
- Contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and speckle tracking echocardiography make it possible to quantitatively assess the morphofunctional characteristics of post-infarction cardiosclerosis.
- Only patients with left ventricular ejection fraction ≥50% showed favorable regression of ischemia-reperfusion injury and global wasted work.
- Severe ischemia-reperfusion injury according to magnetic resonance imaging, as well as global work efficiency and global work index on echocardiography are predictors of a left ventricular ejection fraction decrease less than 50% in the medium term.
Aim. To analyze ischemic and reperfusion injury characteristics, as well as myocardial performance, to identify predictors of reduced left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) <50% 24 weeks after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in patients who underwent revascularization.
Material and methods. The study included were 65 patients (age 58 (52; 60) years), who were examined on days 7-10 and after 24 weeks. Based on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), parameters of ischemic and reperfusion injury were determined. Speckle tracking echocardiography was used to evaluate the myocardial function.
Results. All 65 patients completed the study. Based on echocardiography, patients were divided into following groups: 1 — 45 people with LVEF ≥50%, 2 — 20 patients with LVEF <50%. In patients with LVEF ≥50% 24 weeks after STEMI, there was a decrease in the ischemia injury mass by 32,3% (p=0,001) due to regression of the scar mass by 28% (p=0,008) and the peri-infarct heterogeneous zone by 33,3% (p=0,020). In group 2, the indicators did not change. At the repeat visit, there was a decrease in the number of people with microvascular obstruction in the group of LVEF ≥50% from 44 to 16% (p<0,001), while in LVEF <50% — from 65 to 40% (p=0,045). According to echocardiography, global wasted work in group 1 decreased from 77 (50,5; 105,5) to 59 (43; 92) mm Hg% (p=0,042), while in group 2, it increased from 99,5 (59; 181) to 104,5 (58,5; 156,5) mm Hg% (p=0,765). Global work efficiency and global work index prevailed in patients with LVEF ≥50% at two visits (p<0,05). The following predictors of decreased LVEF were determined 24 weeks after STEMI: ischemia injury mass, scar tissue, microvascular obstruction, global contrast index according to MRI; global work efficiency and global work index on echo cardiography.
Conclusion. Contrast-enhanced cardiac MRI and speckle tracking echocardiography are complementary methods that allow quantitative morphofunctional assessment of post-infarction cardiosclerosis and predict the development of mildly reduced and reduced LVEF in the medium term.
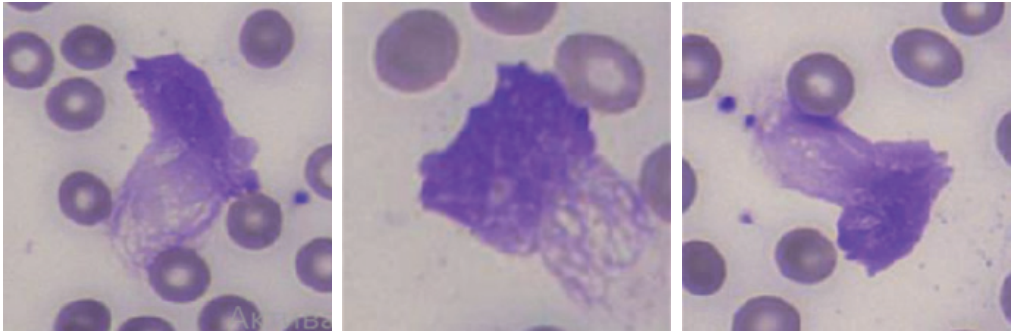
- Neutrophil extracellular traps in blood smears represent a novel prognostic marker for complicated infective endocarditis.
- Level of neutrophil extracellular traps in blood smears of patients with infective endocarditis above 11,2% increase the probability of in-hospital mortality by 24 times and postoperative sepsis by 22 times.
- The presented data makes it possible to discuss the significant contribution of neutrophil extracellular traps to the pathogenesis of infective endocarditis and complications.
Aim. To assess the prognostic value of the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in blood smears of operated patients with infective endocarditis (IE).
Material and methods. We prospectively included 46 patients with verified IE and 50 patients with valvular heart disease without IE, hospitalized in a cardiac surgery hospital in 2021-2022 (Moscow), comparable by sex and age. In all patients, NETs were determined upon admission and 7 days after surgery using the MECOS-Ts2 automated microscope (Russia). Patients included in the study were prospectively followed during the in-hospital period (ME [IQR] 30,0 [21,0-41,0] days) for the primary composite endpoint (in-hospital all-cause mortality, embolic, intracardiac, infectious complications) and its individual components.
Results. Patients with IE were predominantly male (n=37, 80,4%) with a median age of 55,5 [44,0-70,0] years. The primary combined endpoint was recorded in 76,1% (n=35) of those examined with IE. The NET level after 7 days was significantly higher in patients with IE who had primary combined endpoint events than in the group of operated patients with heart defects without IE (Me [IQR] 4,4 [0,6-26,6] vs 2,9 [1,1-4,3], respectively, p<0,05). Patients with IE who died in the hospital had a significantly higher NET level compared with surviving patients with IE and the control group as at admission (9,2 [1,8-18,9] vs 4,2 [0,3-28 ,5] and 3,4 [1,76,9], respectively, p<0,05), and in dynamics (18,2 [5,2-26,6] vs 4,0 [1, 0-26,6] and 2,9 [1,1-4,3], respectively, p<0,001). The threshold value of dynamic NET ≥11,2% predicted in-hospital death with high accuracy (sensitivity 80,0%, specificity 90,0%, positive predictive value 66,7%, negative predictive value 100,0%, area under the curve 0,915, p=0,003) and the development of postoperative sepsis (sensitivity 75,0%, specificity 88,0%, positive predictive value 60,0%, negative predictive value 100,0%, area under the curve 0,884, p=0,01). The obtained cut-off values significantly predicted the death (OR 23,9 (95% CI 1,7-344,8, p=0,02)) and sepsis (OR 22,0 (95% CI 1,9-256,8, p=0,01)) in the hospital in operated patients with IE.
Conclusion. The NET level in blood smears of operated patients with IE is a new promising marker for predicting the disease complicated course. NETs ≥11,2% in operated patients with IE increase the probability of hospital mortality by 24 times and postoperative sepsis by 22 times.
- Non-small cell lung cancer and cardiovascular diseases occur together in most patients, increasing the cumulative risk of fatal cardiovascular outcome.
- The author's risk assessment model of a fatal cardiovascular outcome is proposed, constructed using the regression analysis of clinical, functional, biochemical, and pathomorphological parameters.
- The risk assessment model of a fatal cardiovascular outcome is easy to use and allows for personalized management of patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
Aim. To study risk factors for fatal cardiovascular events in patients with non-small cell lung cancer over two years of standard treatment.
Material and methods. This pilot retrospective non-randomized cohort study included 179 patients who were consecutively admitted to the chemotherapy department of City Clinical Hospital 1 from January to December 2020 with a confirmed diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer based on the comprehensive examination and morphological verification according to the 2018 clinical guidelines on bronchial and lung cancer. Diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases were carried out according to national clinical guidelines. The follow-up period for non-small cell lung cancer and cardiovascular disease was 2 years. Logistic regression models were considered to assess the risk of cardiovascular death. The model accuracy was assessed by a cross-validation.
Results. The best model in terms of the sensitivity and specificity sum according to a cross-validation was the model with the following explanatory variables: sex, cancer stage, platinum-based chemotherapy, etoposide, immunotherapy, surgical treatment. This model showed a sensitivity of 70,1% and a specificity of 82,1%.
Conclusion. This approach is easy to implement and may optimize treatment for patients with non-small cell lung cancer.
- Patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome are a heterogeneous group differing in clinical and laboratory data.
- Clusters with high platelet function, high monocyte count and low hemoglobin values included older patients with significant comorbidities, which had a higher incidence of adverse cardiovascular events.
Aim. To identify clusters of patients with non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) depending on the laboratory data, including platelet function tests.
Material and methods. The study included 109 patients hospitalized in the cardiology department with NSTE-ACS. All patients underwent a standard examination, including a complete blood count. In addition, the platelet function was assessed using impedance aggregometry with various inducers (adenosine diphosphate (5 and 10 μmol/L), collagen (2 μmol/L)). We assessed the P-selectin expression level using flow cytometry. Patients were followed up for 6 months. As a statistical method, we performed сluster analysis by K-means algorithm.
Results. We registered 18 adverse outcomes (myocardial infarction, unstable angina) during 6-month follow-up. Cluster analysis revealed 3 clusters. The first cluster included 39 (36%) patients with higher monocyte values and lower hemoglobin values, probably indicating chronic inflammation and a tendency towards anemia. The second cluster included 13 older patients (12%) with high comorbidity and high platelet function. Both the first and second clusters recorded 23% adverse outcomes. Third cluster, on the contrary, included mostly younger patients with fewer comorbidities, which had more favorable course of ACS (no signs of platelet hyperaggregation, chronic inflammation and anemia). This cluster included more than half (n=57, 52%) of all patients; adverse outcomes at 6 months in these patients developed 2-fold less frequently than in the other clusters (11% vs 23%).
Conclusion. Among patients with NSTE-ACS, groups differing in laboratory parameters were identified, based on which clusters were formed using the k-means method. Clusters with high levels of platelet functional activity, monocyte count and low hemoglobin values included older patients with severe comorbidity and showed a tendency towards more frequent adverse outcomes of the disease.
- The paper presents the first results of the AURA real-world data registry.
- A group of people with previously undiagnosed chronic kidney disease was identified, who had a higher incidence of albuminuria and no diabetes of any type.
- Albuminuria was more common in males, over 40 years of age, with metabolic syndrome, hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.
Aim. To present data from the AURA Registry (real-world data registry on AlbUminuRia detection rate among patients with previously undiAgnosed chronic kidney disease). It is important to perform population studies both to study the occurrence of markers (albuminuria (AU), decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR)) and the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD), which will provide information on the actual detection rate of CKD and the related markers in territories included in the registry of research centers.
Material and methods. The article presents the first data from the AURA registry. Recruitment was carried out from March 6, 2023 to January 23, 2024. Thirty-four research centers in various federal districts of the Russian Federation and 104 doctors took part in the recruitment. We included 4580 subjects over the age of 40 years who had no previously established diagnosis of CKD and did not have type 1 or type 2 diabetes. During recruitment, the researchers were guided by the AURA study protocol (Version 1.7/12-26-2022).
Results. AU more than 20 mg/g was detected in 64,9% of cases. At the same time, AU is more common at GFR values that may correspond to stage 3A of CKD. The rarer occurrence of AU in those examined with GFR >60 ml/min/1,73 m2 may be explained by less severe renal damage at this CKD stage. The incidence of AU was significantly higher in men, older people, smokers, people with metabolic syndrome, hypertension (HTN), prediabetes and overweight. The occurrence of AU also increased as HTN grade increased. AU detection rate was associated with hypertriglyceridemia, a high blood level of C-reactive protein, which is an integrative marker of inflammation that negatively affects cardiovascular risk.
Conclusion. The presented first data from the AURA registry demonstrated the high AU prevalence in people over 40 years of age. A high incidence of AU was typical for patients with HTN, coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and prediabetes. An association has been demonstrated between the high incidence of AU and male sex, age, overweight, hyperuricemia, dyslipidemia, and a number of other cardiovascular risk factors.
МЕДИЦИНСКАЯ ИНФОРМАТИКА
- For patients at risk of sudden cardiac death (SCD), early prevention is possible with timely diagnosis and identification of subcritical and critical conditions.
- The use of fuzzy logic decision making makes it possible to improve the quality of diagnosis and prediction of the SCD risk.
- A prognostic algorithm based on membership functions and risk factors makes it possible to assess the severity of subcritical and critical conditions as predictors of SCD and timely modify treatment measures during follow-up.
Aim. To develop a method for early diagnosis of subcritical homeostasis disorders leading to sudden cardiac death (SCD). The basis is to improve the efficiency of predictive algorithms.
Material and methods. This pilot, controlled, open-label, randomized, prospective clinical trial included 220 patients at risk of SCD and 150 patients without risk of SCD. Main and control groups was formed according to the global cardiovascular risk score. Based on the informative features proposed by specialized experts using multivariate statistics methods (discriminant analysis), two condition classes were formed. The conducted exploratory analysis confirmed the significance of diagnostic criteria in relation to SCD manifestation (manifestation of cardiac arrest — MCA), which is an integral assessment of a fatal complication. The development of decision rules was carried out on the basis of soft computing technology.
Results. Taking into account the priority of clinical research, namely, the identification of subcritical stages of MCA, a classifier is proposed according to basic severity of patients — the severity of critical condition risk (SCCR). The discriminant function and intersection areas between MCA subclasses in the conditions of early SCD diagnosis determine the transition to soft computing technology. Membership functions for severe MCA are formed, followed by their iteration according to E. Shortliffe. The final decision rule, using a fuzzy classifier, differentiates the MCA into stages with different SCCR. In parallel with standard protocols for the management of severe somatic patients (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, hepatocellular failure), based on the proposed algorithm with an integral assessment of critical conditions, using the MCA decision rule in the main group in 30,5% of cases, subcritical stage was revealed, followed by targeted treatment and preventive support. In the first group, a subcritical condition was detected in 67 patients (30,5%); a critical condition without SCD — in 3 patients (1,4%). In all noted cases, early prevention of SCD was successfully carried out (these patients were transferred to a class with a lower SCD degree). Using conventional prognostic scores in this group, 46 patients (20,9%) were identified with a subcritical condition and 1 (0,4%) with a critical condition. In the control group, subcritical condition was determined in 35 patients (23,3%), of which 17 patients (11,3%) had a moderate risk of SCD. Using conventional prognostic scores, 23 patients (15,3%) with subcritical condition were identified.
Conclusion. In the conditions of intensive care unit, general medicine departments, hemodialysis department, cardiac surgery, and organ transplantation department, an algorithm for early diagnosis and risk stratification of SCD with an integral assessment (MCA) should be used. The fuzzy classifier MCA according to SCCR makes it possible to carry out timely correction of treatment measures in addition to standard protocols.
METHODS OF STUDY
- Focused echocardiography is noninferior to pulmonary artery catheterization in monitoring cardiac index and total peripheral vascular resistance in patients with myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock.
- We consider the left ventricular outflow tract VTI measurement to be a more preferable method for cardiac index estimation.
Aim. To compare main central hemodynamic parameters obtained by pulmonary artery catheterization and transthoracic echocardiography (TTE).
Material and methods. This prospective study included 20 patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by true cardiogenic shock. In all patients, number of central hemodynamic parameters was measured using a Swan-Ganz catheter and TTE. Comparison of both methods was carried out by Spearman correlation analysis and Bland-Altman plots using the STATISTICA 8.0 program.
Results. We found quite a lot of agreement between the parameters measured by the two methods in the same patient at approximately the same time. Thus, the cardiac index (CI) is well measured by both methods. At the same time, the correlation coefficient was significantly higher when measuring CI using VTI (r=0,81 vs r=0,81) compared to LV volumes. Therefore, we consider the first method to be preferable. The values of total peripheral vascular resistance (TPVR), estimated by right atrial pressure, did not reveal agreement between methods. At the same time, there was agreement in case of central venous pressure. Measurement of pulmonary wedge pressure did not show agreement in me thods. We believe that this is due to the fact that diastolic function assessment in intensive care patients in the focal TTE mode may be difficult and not sufficiently correct.
Conclusion. TTE can be used to monitor central hemodynamics in cases of satisfactory and moderately reduced cardiac imaging. Both the results of CI measurement using the Bernoulli formula and left ventricular volumes, as well as measuring TPVR using central venous pressure, are statistically consistent. Measurement of TPVR using right atrial pressure and measurement of pulmonary wedge pressure did not demonstrate agreement between the different techniques. We believe that TTE can be used to monitor CI and TPVR in patients with myocardial infarction complicated by true cardiogenic shock.
- The increasing prevalence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), high rates of hospitalization for acute decompensated HFpEF (ADHFpEF) and associated mortality rates make the search for novel diagnostic approaches urgent.
- The concentration of NT-proBNP, the dose of diuretics, inhospital mortality and fluid volume are significantly higher with severe congestion; an association between inhospital mortality and markers of venous congestion, such as VExUS grade and fluid volume was demonstrated.
- The use of the VExUS protocol, pulmonary ultrasound, and bioimpedance analysis should be considered as potentially the most accurate means of congestion severity in patients with ADHFpEF.
Aim. To characterize the potental of additional paraclinical research methods (ultrasound, determination of body composition) for assessing the congestion severity in patients with acute decompensated heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (ADHFpEF) in the intensive care unit.
Material and methods. We examined 82 patients with ADHFpEF aged from 50 to 85 years, who were hospitalized in the intensive care unit of the Veresaev City Clinical Hospital (Moscow). All patients underwent a standard clinical and laboratory examination, including determination of NT-proBNP, as well as echocardiography, chest radiography, bioimpedance analysis, Venous Excess Ultrasound (VExUS), lung ultrasound. Depending on the congestion degree visualized by VExUS, patients were divided into three groups.
Results. The median levels of NT-proBNP, E/A and E/e', number of B-lines in one lung segment, ECW and TBW, and the diuretics' dose used in the hospital in pa tients with ADHFpEF and severe congestion were significantly higher. Signs of congestion obtained as a result of X-ray examination did not differ significantly between groups. In-hospital death was associated with higher values of NT-proBNP, E/A ratio, IVC diameter, number of B-lines in one lung segment, ECW and TBW. The odds of death in patients with VExUS Grade 3 increased 20,9 times compared to Grade 1 (95% CI: 1,125-387,688).
Conclusion. Higher levels of NT-proBNP, the dose of diuretics used in the hospital, and ECW and TBW were associated with congestion severity. The severity of congestion assessed by VExUS and ECW/TBW are positively associated with inhospital mortality
- Myocardial bridges may be associated with serious cardiovascular events.
- Left ventricular peak global longitudinal strain of -20,55% or less negative, measured with two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography, has demonstrated high informative value in predicting myocardial bridges.
- Computed tomography myocardial perfusion makes it possible to detect coronary circulatory defects in asymptomatic patients with myocardial bridges at an early stage.
Aim. To evaluate the effectiveness of left ventricular (LV) peak global longitudinal strain and potential of computed tomography myocardial perfusion (CT perfusion) for the early diagnosis of asymptomatic patients with myocardial bridges (MBs).
Material and methods. Forty patients were examined (20 with asymptomatic MBs in the area of the left anterior descending (LAD) artery and 20 without MBs) at the S. M. Kirov Military Medical Academy in the period from 2021 to 2023. The patients were divided into 2 equal groups consisting of 20 people (10 with MBs — the main group; 10 without MBs — the comparison group), one of which underwent speckle tracking echocardiography (STE), and the other — stress CT perfusion performed (adenosine triphosphate 160 mg/kg). The results were assessed in accordance with the 17-segment classification of LV proposed by the American Heart Association (2002).
Results. When performing STE, 5 (50%) patients with MBs showed a decrease in LV local strain in the segments, the blood supply of which comes from the LAD artery and its branches, while in the comparison group — 1 (10%) (x2=5; p=0,025). When assessing the global longitudinal peak strain (GLPS), a significant difference was revealed among the study groups, amounting to -20,9±1,5% in patients with MBs and -22,1±0,9% in those without MBs (p=0,04). Using ROC analysis, the effectiveness of GLPS in prediction of asymptomatic MBs was calculated as follows: AUC=0,93 (95% confidence interval: 0,819-1,0; p=0,001), the cut-off point — -20,55% (sensitivity 80%, specificity 100%). According to CT perfusion data, impaired myocardial blood supply in the group of asymptomatic patients with MBs was noted in 6 (60%) cases, and in the comparison group — 2 (20%) (x2=9,8; p=0,002).
Conclusion. Imaging of initial LV changes according to two-dimensional STE and detection of coronary circulatory disorders according to CT myocardial perfusion in asymptomatic patients with MBs makes it possible to timely suspect intramyocardial course of the coronary artery, as well as to consider further management tactics and carry out early prevention of possible cardiovascular events.
OPINION ON THE ISSUE
- Myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock (MI CS) is the terminal stage of the cardiovascular disease continuum, leading to the death of every second patient in its severe course.
- The systemic inflammatory response is a key pathophysiological mechanism of initiation and progression of MI CS, despite timely and optimal coronary revascularization; MI CS time-dependent intervention may become a new goal in personalized treatment of MI CS.
- Efferent therapy, namely selective cytokine hemoadsorption, can be considered as one of the novel medical technologies in the management of patients with septic shock, and has great potential as personalized therapy for MI CS.
Myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock (MI CS) is the terminal stage of the cardiovascular disease continuum, leading to the death of every second patient in its severe course. Over the past decades, there are no improvement in inhospital mortality rates for MI CS, despite the widespread introduction of early and effective revascularization methods and intensive care techniques. Recently, more and more data have emerged on the significant contribution of the systemic inflammatory response (SIR) to the pathogenesis of acute coronary syndrome and its complications. The characteristics and impact of SIR in MI CS on its course and outcome have not been sufficiently studied. One of the strategies to influence the SIR course, along with the use of anti-inflammatory therapy, is efferent treatment. However, despite all the above-mentioned fundamental prerequisites for the use of an extracorporeal therapy in CS patients, the introduction of these techniques into clinical guidelines and practice requires exploratory and multicenter randomized studies. This review article summarizes modern ideas and characterizes the existing possibilities of using efferent therapy in MI CS.
The article discusses the adaptation of European Federation of Internal Medicine clinical guidelines for the management of patients with acute heart failure (AHF). An algorithm has been proposed for the differential diagnostic examination of patients with AHF and acute shortness of breath, signs of congestion, hypoxemia, including the determination of natriuretic peptides (NUPs) and/or cardiac troponin, assessment of the congestion severity using echocardiography, as well as the potential of chest radiography and lung ultrasound in certain clinical situations. Special attention is paid to methods for assessing and treating signs of fluid congestion, which have the most accurate prognostic value in patients hospitalized due to AHF. Assessment of the prognosis and the need for hospitalization of AHF patients in the intensive care unit are highlighted. Treatment strategies for patients with hypotension and low cardiac output are discussed. The latest guidelines for the treatment of patients with AHF, taking into account concomitant diseases, are presented. Indications for hospital discharge of patients with AHF, optimization of the further treatment plan, effective strategies for reducing the risk of rehospitalization and mortality, both at the hospital discharge and outpatient stage, are discussed.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)