CARDIOSURGERY
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) has proven to be an effective alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement, especially for patients with high and moderate surgical risk.
- Long-term outcomes of TAVR, especially for younger patients, remain limited. Valve durability and survival require further research, especially in low surgical risk groups.
- Studies such as PARTNER 3 have limitations in extrapolating results to younger patients. In real-world practice, patients and physicians are more likely to choose TAVR despite the lack of long-term data.
In recent decades, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) has become a revolutionary method for the treatment of severe aortic stenosis, especially for patients at high surgical risk. Studies such as PARTNER and SURTAVI have confirmed the non-inferiority or superiority of TAVR compared with surgical aortic valve replacement in various risk categories. Newer technologies, including third-generation valve systems, have improved durability and reduced complications such as paravalvular regurgitation. However, long-term survival data remain limited, especially for younger patients and groups with anatomical peculiarities. International association guidelines have long favored TAVR for older patients, while surgery remains the preferred option for younger patients with low surgical risk. However, the latter point is increasingly being questioned. The article analyzes key studies, discusses current limitations, and highlights the need for long-term data to inform clinical practice. In conclusion, TAVR is a remarkable achievement in interventional cardiology, but its optimal use requires consideration of individual patient factors.
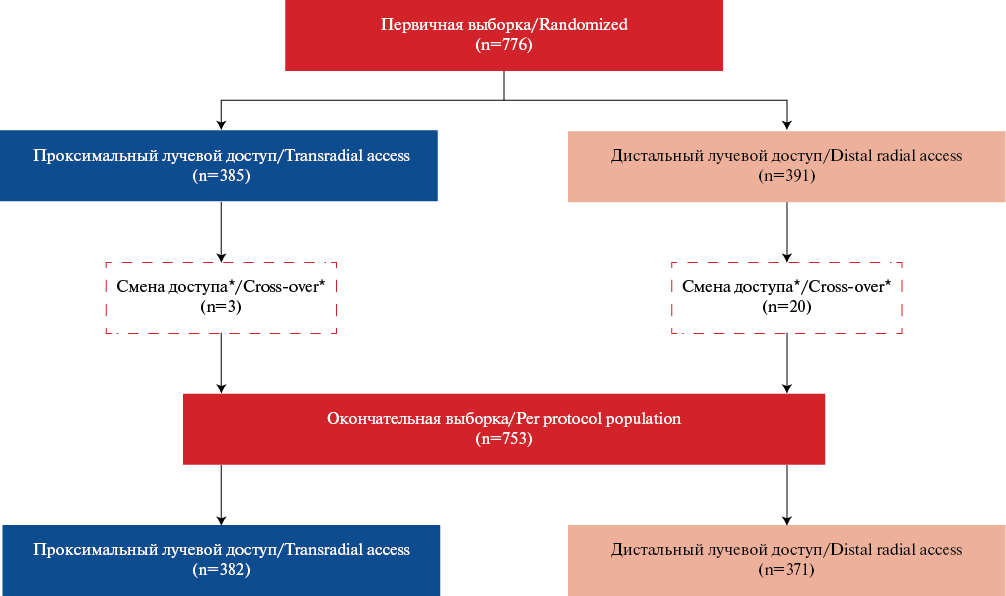
- For the first time, mid-term outcomes (3 months) of a prospective randomized study on distal radial access compared with conventional radial access in therapeutic and diagnostic interventions on coronary vessels are presented.
- A significantly lower number of radial artery occlusions was found when performing interventional procedures through the distal radial access, as well as cases of distal radial artery occlusion on dorsum of hand with a patent forearm radial artery.
Aim. To evaluate immediate and medium-term (3 months) results of safety and effectiveness of distal versus proximal radial access for coronary interventions.
Material and methods. An analysis of 776 patients of the prospective randomized TENDERA trial was performed: distal radial access (DRA) group — 1391 patients; proximal radial access (PRA) group — 385 patients. After excluding patients with failed primary access, the primary sample sizes decreased (DRA — 371, PRA — 382). Access-site crossover rate was statistically higher in the DRA group (5,1% and 0,8%, p<0,001). The primary endpoint was immediate (inhospital) or long-term radial artery (RA) thrombosis/occlusion. There were following secondary endpoints: 1 — composite endpoint including complications from the access artery; 2 — access parameters.
Results. Significant differences were obtained for the primary endpoint: DRA 2,7% (n=10), PRA 6,8% (n=26), p=0,008. Distal RA occlusion with patent RA: DRA: 1,3% (n=5), PRA: 0 (n=0), p=0,023. The secondary composite point showed significant differences in the following groups of complications: BARC type I bleeding (DRA: 3,8% (n=14), PRA: 21,7% (n=83), p<0,001); hematoma >5 cm on day 1 (DRA: 10% (n=37), PRA: 25,9% (n=98), p<0,001); hematoma >5 cm on day 7 (DRA: 12,4% (n=45), PRA: 34,6% (n=132), p<0,001). The following access parameters showed significant differences: distal RA puncture time — 19,0 (8,0; 50), proximal RA puncture time — 13,5 (5,0; 29), p<0,001; introducer insertion by DRA 42,0 (26,0; 84,0), PRA 35,0 (23,0; 55,0), p<0,001; duration of access artery hemostasis (min): DRA 180,0 (120,0; 480,0), PRA 155,0 (115,0; 195,0), p<0,001. Duration of the procedure and fluoroscopy, radiation dose, and RA spasm in both groups did not have significant differences.
Conclusion. In the TENDERA study, DRA demonstrated efficacy and safety in interventional coronary procedures compared to PRA in the mid-term follow-up period — significantly lower incidence of RA occlusions and local complications.
- The accumulation of surgical experience, the active implementation of patient-oriented techniques for the transcatheter aortic valve implantation, as well as the optimization of postoperative patient management, have made it possible to achieve high technical success rates in the transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
- The presented domestic experience of transcatheter aortic valve implantation for severe aortic stenosis in 500 patients demonstrates optimal long-term outcomes in terms of overall survival, cardiovascular death, implantation of a permanent pacemaker, and repeat valve replacement.
Aim. To evaluate remote outcomes of transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI), including overall survival, freedom from cardiovascular death, permanent pacemaker implantation, and repeat valve replacement.
Material and methods. This retrospective observational study included 535 patients who underwent TAVI from April 2015 to January 2024. Patients who underwent TAVI for moderate aortic stenosis or severe aortic valve regurgitation (n=35) were excluded from the analysis. A total of 500 patients were included in the final analysis. Males accounted for 40,8%. Most patients had intermediate EuroSCORE II risk (5,2%), as well as low STS-PROM score risk (2,9%). The median follow-up period was 2,2 (0,6;4,1) years.
Results. Overall patient survival was 94%, 88%, 86%, and 58% at 1, 3, 5, and 8 years, respectively. Freedom from cardiovascular death was 97%, 90%, 78%, and 61% at 1, 3, 5, and 8 years, respectively. The cumulative freedom from permanent pacemaker implantation over the entire follow-up period was 89,4%, and from repeat pacemaker replacement — 98,8%. The factors influencing the long-term all-cause mortality were male sex, smoking, cancer, and left ventricular mass index. The only independent predictor of cardiovascular death was the STS-PROM score.
Conclusion. Our experience demonstrates satisfactory long-term outcomes of transcatheter aortic valve implantation in patients with severe aortic stenosis in terms of overall survival, cardiovascular death, permanent pacemaker implantation, and repeat pacemaker replacement. Independent predictors of all-cause death were male sex, smoking, cancer, and left ventricular mass index. The only independent predictor of cardiovascular death in the long-term period was the STS-PROM score.
- The combination of AVNeo surgery with coronary artery bypass grafting is a promising procedure. It does not require the use of consumables, such as synthetic grafts, preserves the natural annulus operation in the cardiac cycle, thereby leading to excellent hemodynamic parameters and provides myocardial revascularization in case of concomitant coronary artery disease.
Aim. To evaluate immediate outcomes of the Ozaki procedure in patients with coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Material and methods. This retrospective study included 416 patients operated on at the Federal Center of Cardiovascular Surgery (Penza). The patients were divided into two groups. The first group included 139 patients who underwent the AVNeo procedure in combination with CABG. The second group included 277 patients who underwent a single AVNeo procedure.
Results. The median time of cardiopulmonary bypass and myocardial ischemia in the AVNeo+CABG group was 146 (134-165) and 115 (104-125), respectively, while in the AVNeo group — 117 (102-136) and 96 (82-109), respectively. The mean aortic valve pressure gradient immediately after surgery in the AVNeo+CABG group was 5,9±3,3, while in the AVNeo group — 6,4±3,1. Mortality in the AVNeo+CABG group was 2,8% (n=4), while in the AVNeo group — 0,3% (n=1). Inhospital survival in the AVNeo+CABG group was 97,1%, while in the AVNeo group — 99,6%. In the AVNeo+CABG group, there were following death causes: perioperative myocardial infarction (n=2), pneumonia (n=1), multiple organ failure (n=1). In the AVNeo group, the cause of the only fatal outcome was multiple organ failure. Only one predictor of inhospital mortality was identified — resternotomy for bleeding. In the case of resternotomy, inhospital death risk increases by 1,3 times for each day of the postoperative period. Cardiopulmonary bypass time, myocardial infarction, and operation duration do not affect mortality. The combination of AVNeo with CABG also does not affect inhospital mortality (p=0,1).
Conclusion. The combination of the AVNeo procedure with CABG is an effective and safe procedure in the immediate period.
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is the most common infectious complication of the early postoperative period in cardiac surgery patients.
- HAP development is accompanied by an increase in the risk of an unfavorable clinical outcome and an increase in economic costs.
- The most significant risk factors for HAP in a modern cohort of cardiac surgery patients are preoperative atrial fibrillation, on-pump duration ≥96 min and artificial ventilation ≥14 hours.
Aim. To study the prevalence and risk factors (RF) for hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) after on-pump cardiac surgery in a modern cohort of patients.
Material and methods. This retrospective analysis of the medical records of cardiovascular surgery patients, operated on in the period from January 1, 2022 to December 31, 2022. The study consistently included 417 patients who underwent on-pump cardiac surgery. The incidence and timing of HAP development were assessed. The influence of the main demographic, clinical, and perioperative factors on HAP risk was studied.
Results. The pneumonia prevalence per year was 27,6%, including after the Frozen Elephant Trunk (FET) procedure — 32%, after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) — 29,5%, after combined CABG and heart valve surgery — 26,2%, after isolated valve surgery — 25,9%, after thoracic aortic hemiarch replacement — 19,5%. Pneumonia developed on the 4,6±2,9 day after surgery. The risk of pneumonia increased with atrial fibrillation (AF) before surgery (odds ratio (OR) 3,17; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1,67; 6,02, p=0,0002), on-pump duration (OR 1,01; 95% CI: 1,00; 1,01; p=0,0006), aortic cross-clamping (OR 1,01; 95% CI: 1,00; 1,01; p=0,0002) and mechanical ventilation (OR 1,03; 95% CI: 1,01; 1,05; p=0,005). Pneumonia predictors were on-pump duration ≥96 min (sensitivity 67,7%, specificity 64,6%, AUC=0,681, p=0,0006) and mechanical ventilation ≥14 h (sensitivity 63,1%, specificity 69,3%, AUC=0,641, p=0,005), as well as preoperative AF (sensitivity 61%, specificity 75%, p=0,0002).
Conclusion. Preoperative AF, on-pump duration ≥96 min and mechanical ventilation ≥14 h serve as categorical and quantitative predictors of postoperative HAP in a modern cohort of patients.
CORONARY HEART DISEASE, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
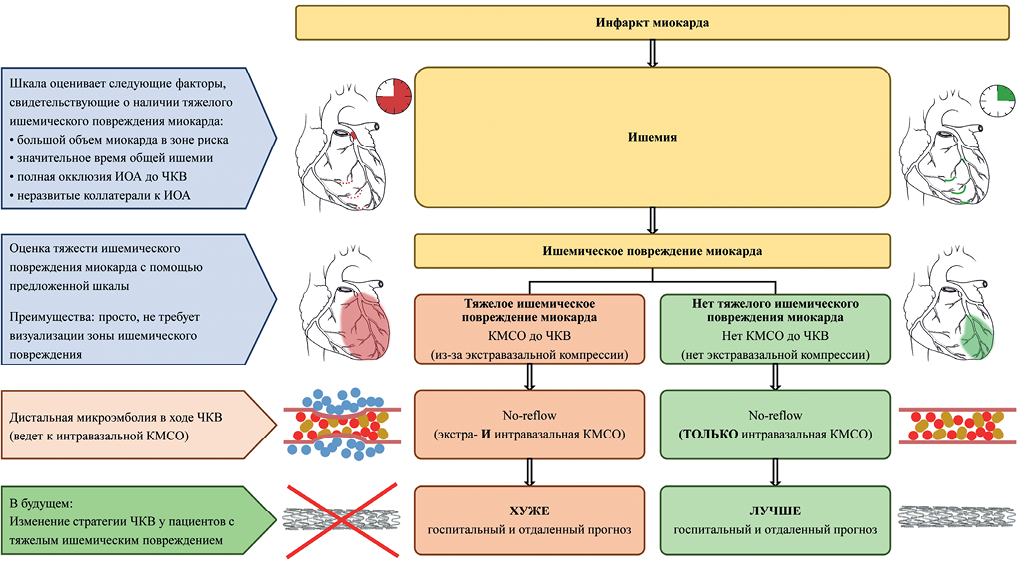
- Patients with myocardial infarction may have severe ischemic myocardial injury at the time of admission for percutaneous coronary intervention.
- Accurate methods for myocardial ischemia imaging in vascular centers are rarely available.
- Ischemic injury is one of the no-reflow causes. Distal microembolism during surgery also leads to no-reflow.
- Patients with no-reflow of combined (ischemia and embolism) nature are presumably have an unfavorable prognosis, which may be an argument for refusing the intervention.
- We proposed a scale for assessing the severity of ischemic myocardial injury and studied the long-term prognosis in groups of patients with and without severe ischemia.
Aim. To create a scale for assessing the myocardial ischemia severity and to study the effect of concomitant ischemia on the prognosis of myocardial infarction (MI) complicated by no-reflow phenomenon during percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Material and methods. A single-center cohort study was conducted. There were following inclusion criteria: MI, PCI, total ischemic time <48 h and no-reflow (TIMI flow grade <3 or Myocardial blush grade <2 or ST segment resolution <70%). The proposed scale included infarction-related lesion in the left main coronary artery or proximal left anterior descending artery — 2 points; total ischemic time >12 h — 1 point; TIMI flow grade 0-1 before PCI — 1 point; Rentrop collateral circulation grade 0-1 — 1 point. Severe ischemia — more than 3 points. Propensity score matching was used to correct differences between the groups. Median follow-up was 979 [743; 1318] days.
Results. A total of 18079 patients with acute coronary syndrome were analyzed, while 219 were included. After comparison, 105 patients remained as follows: group 1 — 75 patients without assessed severe ischemia; group 2 — 30 patients with assessed severe ischemia. During the hospital stage, 6 (8,0%) and 9 (30,0%) patients died, respectively, p<0,001. The left ventricular ejection fraction was 47 [42; 50]% and 41 [39; 45]%, respectively, p<0,001. Severe ischemia was associated with a 4,15-fold increase in the long-term death risk (95% confidence interval 1,87-9,20; p<0,001).
Conclusion. Concomitant severe ischemic damage in MI complicated by no-reflow during PCI is associated with worse left ventricular function and a higher death risk at the hospital stage and in the long-term follow-up period.
- Adrenergic reactivity of the body plays an important role in heart failure progression.
- An indirect indicator of body adrenergic reactivity is β-adrenergic reactivity of erythrocyte membranes.
- In a sample with past myocardial infarction, β-adrenergic reactivity of erythrocyte membranes did not differ in patients with preserved and reduced ejection fraction.
- Patients with preserved ejection fraction and left ventricular hypertrophy were distinguished by reduced adrenergic reactivity of the body.
Aim. To evaluate β-adrenergic reactivity of erythrocyte membranes (β-ARM) depending on clinical parameters in patients with heart failure (HF) with preserved and reduced ejection fraction (EF), who had prior myocardial infarction.
Material and methods. The sample included 89 patients with HF and past myocardial infarction. Preserved EF (HFpEF) group included 64 (71,9%) patients, while reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) — 25 (28,1%) patients. All patients underwent β-ARM assessment using an inhibition of hemolysis in a hypoosmotic medium with β-blocker.
Results. The groups with HFpEF and HFrEF were comparable in β-ARM values. There was no linear relationship between β-ARM and LVEF. In the HFpEF group, following differences in β-ARM were revealed depending on the HF functional class (p=0,049): 42,5 (24,1; 61,9) CU in class I, 25,9 (17,1; 36,9) CU in class II, 22,2 (14,9; 27,3) CU in class III. This was not observed in the HFrEF group (p=0,143). In HFpEF, patients with LV hypertrophy had (p=0,049) higher β-ARM values than patients without it (36,9 (24,2; 58,6) CU vs 23,3 (16,0; 29,8) CU). At the same time, in HFrEF, β-ARM was the same (p=0,364) in patients with and without LV hypertrophy. In the HFpEF group, patients taking angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers at admission had 2-fold lower β-ARM (p=0,035) than patients who did not take it.
Conclusion. In the sample with past myocardial infarction, patients with HF with preserved and low EF had comparable β-ARM. At the same time, individuals with HFpEF and LV hypertrophy differed from patients without hypertrophy in increased β-ARM, i.e., higher sympathoadrenal system intensity and reduced adrenergic reactivity, which was not observed in the HFrEF group. In the HFrEF group, taking angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers was associated with more favorable indicators of adrenergic reactivity.
- The novel haSTART vascular stiffness index has prognostic value in long-term follow-up of patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) after coronary artery bypass grafting.
- With haSTART index above the median, CAD patients were more likely to have all-cause death, cardiovascular death, and combined endpoint during the follow-up period.
- CAD patients with haSTART index below the median had better survival and better event-free survival according to Kaplan-Meier analysis.
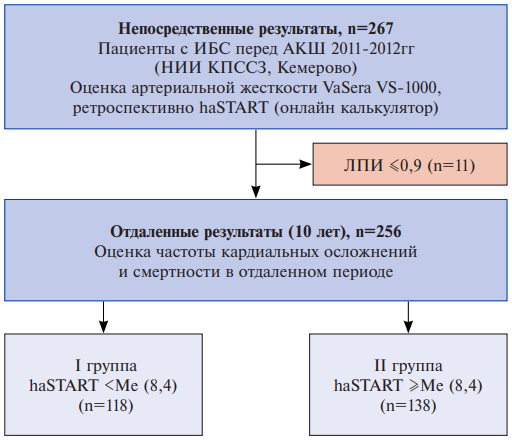
Aim. To study the long-term prognostic value of the novel START vascular stiffness index in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Material and methods. The study included 256 patients with CAD who underwent CABG at the Kemerovo Research Institute for Complex Issues of Cardiovascular Diseases. Before surgery, vascular stiffness was assessed using the haSTART cardio-ankle index. The mean follow-up period was 9,7±0,9 years. Two following study groups were formed: Group I — haSTART < the median (Me) index of 8,4 (haSTART <Me (n=118)); group II — haSTART ≥ the median (haSTART ≥Me, n=138). The prognostic value of haSTART was studied in relation to the following composite end point (CEP): death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, or stroke.
Results. Patients in the haSTART ≥Me group were significantly older than in the haSTART <Me group (p<0,001). In both groups, men predominated (76,2%). During the follow-up period, all-cause death was significantly more common in the haSTART ≥Me group (34,1%) than in the haSTART <Me group (19,5%), p=0,009. Cardiovascular death was also more common in the haSTART ≥Me group than in the haSTART <Me group (23,2% vs 8,5%, p=0,001). In patients with haSTART ≥Ме, CEP was observed in 45,7% of cases, compared to patients with haSTART <Ме (30,5%), p=0,013. Among patients with fatal outcome, the prevalence of patients with haSTART ≥Ме values was higher than in the group of survivors (67,1% and 48,9%, p=0,009). Among patients with CEP — the detection rate of haSTART ≥Ме was 63,6%, which was significantly higher than in the group of survivors without cardiovascular events (47,8%, p=0,013). Kaplan-Meier curves revealed a better long-term prognosis in the haSTART <Me group to the haSTART ≥Me group (p>0,05).
Conclusion. Evaluation of the haSTART stiffness index before CABG surgery may have prognostic value in the long-term follow-up period in patients with CAD.
- Of the 6 risk scores analyzed, only 4 (mc2HEST, COM-AF, CHA2DS2-VASc and HATCH) have acceptable predictive potential for new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention.
- The PAFAC and POAF scales have insufficient prognostic accuracy.
- An integrated model based on an artificial neural network, combining the prognostic resource of 6 scores, demonstrated higher accuracy than models developed using a decision tree and multivariate logistic regression.
Aim. To compare the effectiveness of the POAF, PAFAC, COM-AF, HATCH, ms2HEST and CHA2DS2-VASc scores for predicting new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), as well as to develop novel prognostic models based on machine learning methods.
Material and methods. This single-center retrospective study was conducted using data from 3449 electronic health records of patients with STEMI. Two groups of individuals were identified, the first of which included 312 (9%) patients with new-onset AF in the postoperative period of PCI, and the second — 3139 (91%) patients without cardiac arrhythmia. To predict AF, univariate and multivariate logistic regression (ULR and MLR), decision tree (DT), artificial neural networks (ANN) were used.
Results. The study results showed that of the 6 analyzed scores, only 4 (mc2HEST, COM-AF, CHA2DS2-VASc and HATCH) have an acceptable prognostic potential for new-onset AF after PCI, which was documented by the AUC metrics in the ULR models developed on the basis of the sum of points of each score (AUC — 0,736, 0,731, 0,71 and 0,702, respectively). The integrative ANN model, combining the prognostic resource of 6 scores, demonstrated higher accuracy than the DT and MLR models (AUC — 0,759 vs 0,745 and 0,755, p-value<0,0001).
Conclusion. Further studies aimed at improving the quality of AF prognostic models in patients with STEMI after PCI may involve searching for novel predictors characterizing severity of coronary involvement and effectiveness of its restoration, inflammatory response, myocardial electrophysiological status, etc.
RESEARCH METHODS
- Quantitative analysis of coronary atherosclerosis according to computed tomography coronary angiography allows identifying the calcified and soft tissue atherosclerotic components.
- An association was found between the soft tissue component of atherosclerotic plaque and the severity of coronary atherosclerosis and myocardial damage in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
- Soft tissue burden predicts greater myocardial damage as measured by cardiac biomarkers.
Aim. To study quantitative parameters of coronary atherosclerosis, according to computed tomography coronary angiography (CTCA), and to identify their association with the level of cardiac biomarkers in patients with acute myocardial infarction (MI).
Material and methods. The study included patients with newly diagnosed MI. Depending on the coronary artery (CA) stenosis, two groups were formed: 1) MI with obstructive CA ≥50% (MICAD); 2) MI with non-obstructive CA <50% (MINOCA). All patients were assessed for cardiac biomarkers and underwent CTCA.
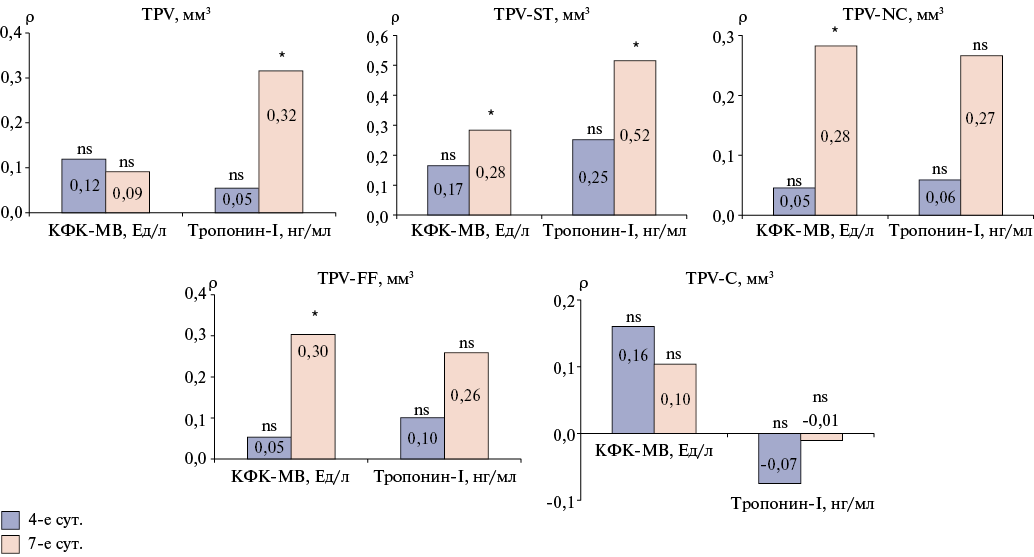
Results. The study included 31 patients as follows: MINOCA group consisted of 10 patients (5 men aged 68 (57; 79) years); MICAD group — 21 patients (13 men aged 62 (56; 68) years). When analyzing cardiac biomarker levels, a significant increase in cardiac troponin I (cTnI) levels was noted on the 4th (p=0,04) and on the 7th day (p=0,0009) in MICAD patients. A significant predominance of the volume (p=0,01) and burden (p=0,004) of low-density plaques was revealed in the MICAD group compared to MINOCA. In addition, MICAD patients had significantly increased values of the total atherosclerotic burden (p=0,01) and the total burden of the soft tissue component of plaques (p=0,04). A significant correlation was found between the plaque volume with cTnI on day 7 (ρ=0,52, p<0,05) and the plaque burden with cTnI on day 7 (ρ=0,43, p<0,05).
Conclusion. According to CTCA, the soft tissue component of plaques is associated with coronary atherosclerosis severity and myocardial damage in patients with MI. Soft tissue burden is a predictor of more severe myocardial damage, according to the cardiac biomarker data.
- Patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease may have reduced myocardial flow reserve in ~40% of cases, as determined by dynamic myocardial single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).
- Dynamic myocardial SPECT allows ~30% identification of microvascular dysfunction in patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease and normal results of standard myocardial perfusion scintigraphy.
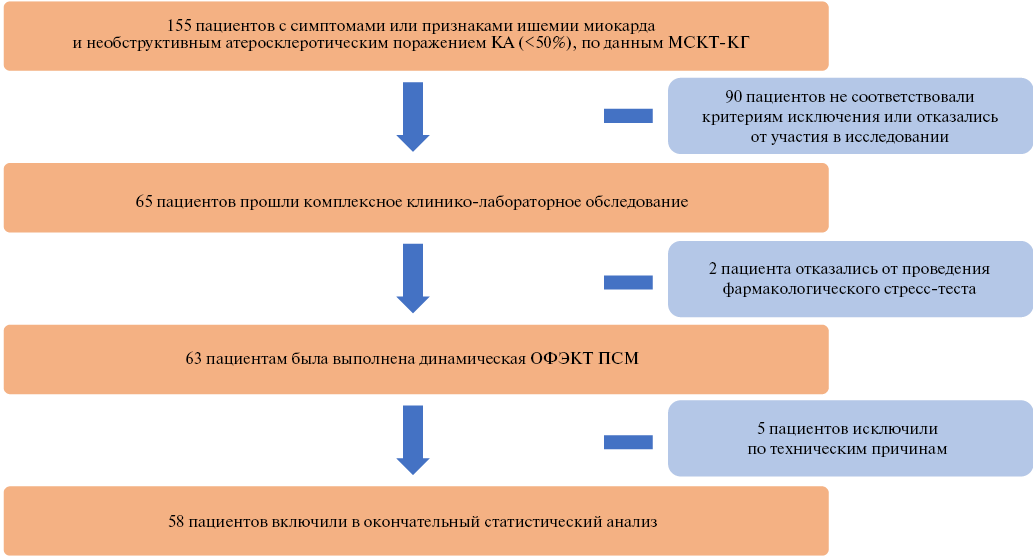
Aim. To compare standard indices of myocardial perfusion scintigraphy (MPS) and quantitative indicators of myocardial dynamic single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease (NOCAD).
Material and methods. The study included patients with symptoms or signs of myocardial ischemia and NOCAD (<50%). All patients underwent dynamic myocardial SPECT with assessment of standard MPS indices (summed stress score (SSS), summed rest score (SRS), summed difference score (SDS)) and quantitative indicators (stress and rest myocardial blood flow (MBF), myocardial flow reserve (MFR) and stress/rest MBF difference (ΔMBF)).
Results. According to MPS, 15 (26%) patients had signs of myocardial perfusion dysfunction (SSS ≥2,0). Standard MPS indices had low values as follows: SSS 0,0 (0,0; 2,0), SRS 0,0 (0,0; 0,0), SDS 0,0 (0,0; 2,0). According to dynamic myocardial SPECT, 22 (38%) patients had a reduced MFR <2,0. Quantitative indicators were characterized by greater variability compared to the MPS data as follows: stress MBF 1,34 (1,03; 1,64) ml/min/g, rest MBF 0,58 (0,42; 0,73) ml/min/g, MFR 2,42 (1,48; 2,85), ΔMBF 0,68 (0,36; 1,09). In 7 (12%) patients, ischemic myocardial changes (SSS ≥2,0) was associated with a reduced MFR <2,0, and in 28 (48%) without signs of ischemia (SSS <2,0) the MFR was within normal values ≥2,0. However, 15 (26%) had a normal radiopharmaceutical distribution and a reduced MFR, which may indicate the initial stages of microvascular dysfunction, which did not lead to myocardial ischemia.
Conclusion. The dynamic SPECT allows in ~30% of cases to identify MBF and MFR disorders in NOCAD patients with normal results of standard SFM.
METHODS OF TREATMENT AND DIAGNOSIS
- Diagnosis of elevated Lp(a) levels is important for early therapy and modification of risk factors to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Lipoprotein(a) assessment may be appropriate in the context of ongoing PSCK9-targeted therapy.
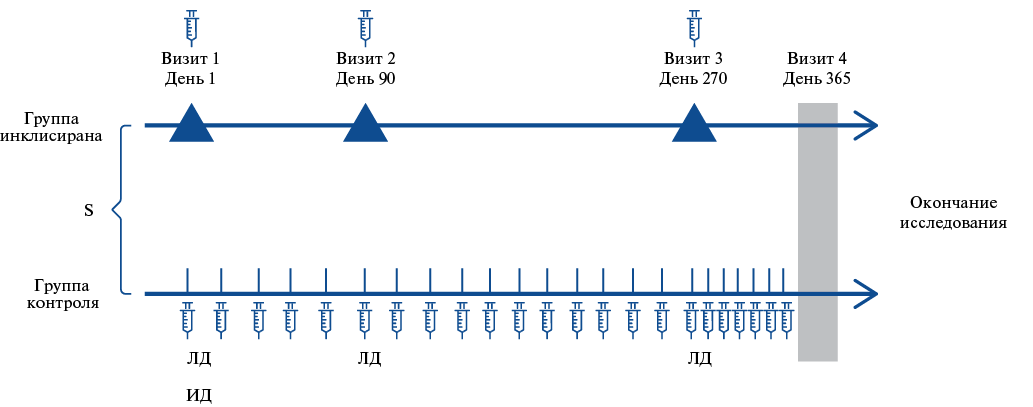
Aim. To evaluate the effect of PCSK9-targeted therapy on lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) levels in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases who have not achieved the target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level (statins at maximum tolerated doses and/or ezetimibe).
Material and methods. The study involved 3 Moscow medical facilities of the state healthcare system. The study included 50 people who received inclisiran therapy, 30 people — PCSK9 inhibitors (alirocumab, n=1; evolocumab, n=29). This analysis presents the results of Lp(a) level changes over 12-month inclisiran therapy. Lp(a) was determined by turbidimetry. Elevated Lp(a) level was defined as ≥50 mg/dL (125 nmol/L).
Results. Normal Lp(a) levels were determined in 16 subjects (34,8%), moderate — in 9 subjects (19,6%), high — in 21 subjects (45,7%), and extremely high (>180 mg/dL) — in 8 subjects (17,4%). Inclisiran therapy was associated with a significant (p<0,001) decrease in both LDL-C and Lp(a) levels by 52% and 54,7%, respectively. During therapy, normal Lp(a) levels remained within baseline values. In almost half of the cases with moderate Lp(a) values, its concentration decreased to normal values, and in cases with elevated Lp(a), its level decreased in 9 out of 10 patients. The proportion of patients in the group with Lp(a) levels <30 mg/dl increased from 35% to 41%. No patient had extreme values by the end of the study.
Conclusion. Lp(a) assessment may be appropriate with ongoing PSCK9-targeted therapy. Diagnosis of hyper-Lp(a) is important for early intensive combination lipid-lowering therapy and modification of risk factors in order to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
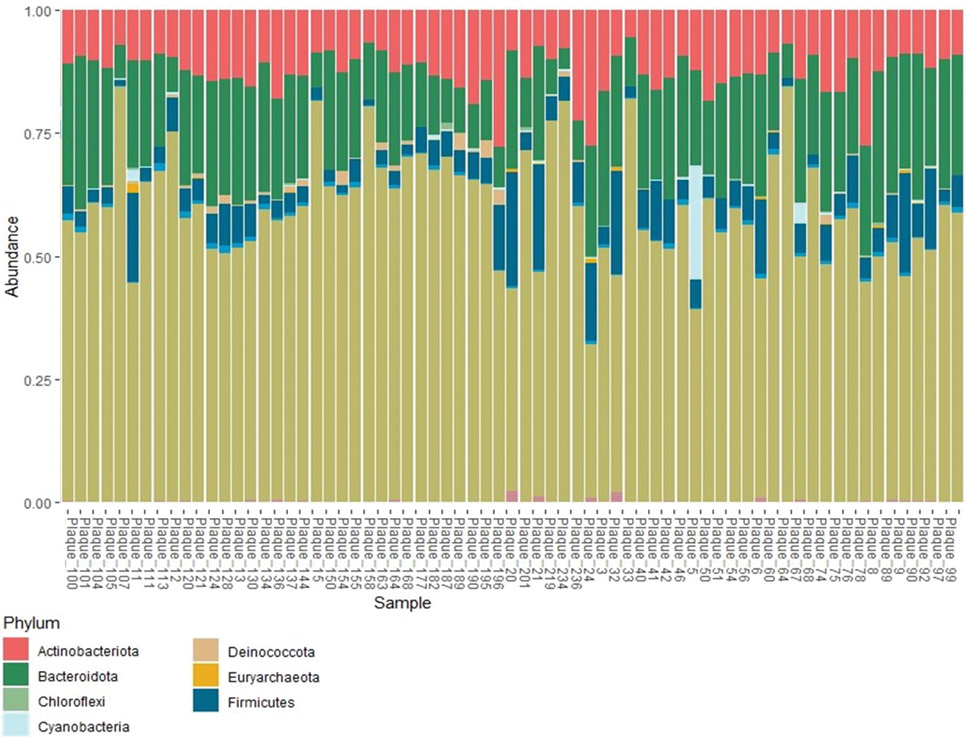
- Using the high-throughput sequencing of the 16SrRNA V4 region, the microbiota profile of 76 samples of atherosclerotic plaques obtained during carotid endarterectomy was analyzed, and taxonomic differences between the groups of patients with developed postoperative restenosis and without restenosis were determined.
- Four following bacterial families were the most represented: Caulobacteraceae, Rhizobiaceae, Sphingobacteriaceaeand Weeksellaceae.
- Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) revealed a significantly higher representation of the microbial marker OTU_21, belonging to the Sphingomonadaceaefamily, in patients with restenosis ≥50%, as well as Cloacibacterium(OTU_67), belonging to the Weeksellaceae family, in patients with restenosis >70%.
- The detection of a wide variety of Gram-negative bacteria in plaque, including those widely distributed in the environment, indicates a potential role of microorganisms of different origins in both plaque and restenosis development.
Aim. To study the microbiome of atherosclerotic plaque biopsies in patients who underwent carotid endarterectomy (CEA).
Material and methods. In this study, the microbiota profile of 76 atherosclerotic plaque samples obtained during CEA was analyzed using high-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA V4 region. The proportion of patients without restenosis included in the study was 20%. The median follow-up of patients was 1,9 years (range, 1,4-2,25).
Results. Taxonomic analysis revealed that the plaque microbiome is characterized by a wide diversity of gram-negative bacteria, including bacteria that are widespread in the environment. Bacteria most represented in plaques belong to four following families: Caulobacteraceae, Rhizobiaceae, Sphingobacteriaceae and Weeksellaceae. Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) revealed a significantly higher representation of the microbial marker OTU_21, belonging to the Sphingomonadaceae family, in the atherosclerotic plaque microbiome of patients with ≥50% restenosis and Cloacibacterium (OTU_67), belonging to the Weeksellaceae family, in patients with >70% restenosis.
Conclusion. The obtained data emphasize the importance of studying the atherosclerotic plaque microbiome and suggest that microorganisms of various origins, including those that have not previously been considered as risk factors, can play a pathogenetic role in both atherogenesis and restenosis.
- In patients with obstructive sleep apnea combined with atrial fibrillation (AF), more pronounced nocturnal hypoxemia (NH) was established compared to patients without AF.
- Echocardiographic parameters in patients with AF and obstructive sleep apnea combined with NH are characterized by more pronounced atrial remodeling and higher pulmonary hypertension than in those examined without NH.
- Patients with obstructive sleep apnea, NH, and AF are characterized by higher blood levels of fibrosis biomarkers, galectin-3 and growth differentiation factor-15, than patients without NH.
Aim. To study cardiac remodeling, blood concentrations of fibrosis biomarkers depending on nocturnal hypoxemia (NH) in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Material and methods. This case-control cross-sectional comparative study included 334 subjects as follows: 122 patients with AF(+)/OSA(+), 117 patients with AF(-)/OSA(+), 95 patients with AF(+)/OSA(-). The subjects underwent respiratory monitoring during sleep and transthoracic echocardiography. The blood concentrations of profibrogenic biomarkers were determined.
Results. The mean blood saturation level is lower, and the proportion of sleep time with saturation less than 90% is higher in patients with a combination of AF and OSA compared to patients without arrhythmia. The left atrial diameter, volumes and volume indices of both atria, pulmonary artery size, and pulmonary artery pressure in patients with AF combined with NH are greater than in patients with AF without NH. The blood levels of galectin-3 and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) are higher in patients with AF combined with NH than in patients with AF without NH and then in patients with NH without AF. In patients with AF in combination with OSA, an increased probability of NH is associated with a high blood concentration of GDF-15 (odds ratio =1,21, 95% confidence interval 1,001-1,34, p=0,002). NH increased the AF probability by 2,6 times (odds ratio =2,57, 95% confidence interval 1,47-4,46, p<0,001).
Conclusion. AF in patients with OSA in combination with NH is characterized by more significant cardiac remodeling (greater left and right atrial dilation), higher pulmonary hypertension and higher blood levels of profibrogenic factors (galectin-3 and GDF-15) than in patients without NH.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY
- Azilsartan has a stronger antihypertensive effect than other angiotensin II receptor blockers, including in comorbid patients. There is experimental evidence of pleiotropic effects of azilsartan.
- The data that allowed low diuretic doses taking the place of first-line antihypertensive drugs were mainly obtained in randomized clinical trials using chlorthalidone.
- Chlorthalidone showed greater antihypertensive efficacy compared to hydrochlorothiazide.
- Azilsartan medoxomil/chlorthalidone combination proved its greater antihypertensive efficacy compared to both the combination of olmesartan medoxomil/hydrochlorothiazide and azilsartan medoxomil/hydrochlorothiazide.
The article analyzes data from clinical studies on the efficacy and safety of azilsartan medoxomil/chlorthalidone combination and its components. According to the analyzed sources, both individual components and their combination have proven their efficacy and safety in patients with hypertension, including those with comorbid pathology. Azilsartan medoxomil demonstrated greater efficacy with comparable safety in terms of lowering blood pressure, both office and ambulatory, compared to candesartan, valsartan, olmesartan. Chlorthalidone showed greater hypotensive efficacy compared to hydrochlorothiazide and proved its protective effect in cardiovascular risk reduction. The combination of azilsartan medoxomil/chlorthalidone, in turn, has proven its safety and greater hypotensive efficacy compared to both the combination of olmesartan medoxomil/hydrochlorothiazide and azilsartan medoxomil/hydrochlorothiazide.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)