MYOCARDITISES, VALVULAR AND NONCORONAROGENIC DISEASES
What is already known about the subject?
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is used to treat patients with heart failure and conduction disorders.
- Left ventricular (LV) non-compaction cardiomyopathy manifests as heart failure, rhythm and conduction disorders.
What might this study add?
- The role of magnetic resonance imaging in predicting the CRT effectiveness in patients with left ventricular non-compaction was assessed.
- The following factors influencing the CRT results were identified: familial form of the disease, sex and age of patients, myocardial fibrosis, myocardial non-compaction severity, LV volume index.
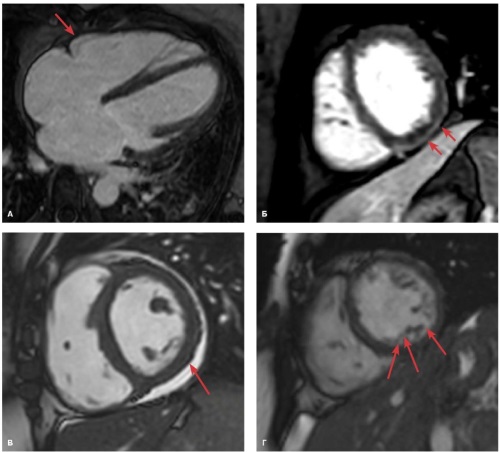
Aim. To evaluate the role of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in predicting the efficacy of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in patients with left ventricular non-compaction (LVNC) and heart failure (HF).
Material and methods. This observational retrospective study included 26 patients with a morphological signs of LVNC cardiomyopathy according to echocardiography (Chin, Jenni, Stollberger criteria) and MRI (Petersen criterion). All patients underwent CRT implantation. The changes of the left ventricular size and function were assessed using echocardiography. Before the CRT procedure, all patients underwent contrast-enhanced cardiac MRI.
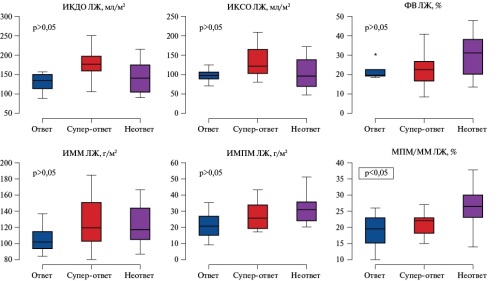
Results. According to a response to CRT, patients were divided into 3 following groups: responders (a decrease in left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic volume (EDV) according to echocardiography from 15 to 30%, a decrease in HF functional class), super-responders (a decrease in LV EDV by more than 30%) and non-responders (failure to meet the response criteria). The study identified factors influencing the CRT results, the most significant of which were the familial LVNC cardiomyopathy, sex and age of patients, as well as following parameters of cardiac morphology: myocardial fibrosis according to MRI, myocardial non-compaction severity, LV volume index.
Conclusion. MRI is a technique that can make a significant contribution to predicting the CRT effectiveness in patients with LVNC and HF. Therefore, it should be performed in all patients before CRT to optimize the selection procedure and exclude patients who are unlikely to benefit from CRT.
What is already known about the subject?
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is one of the most common cardiomyopathies, which has a genetic origin and characterized by left and/or right ventricular hypertrophy.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows us to evaluate the cardiac structure and myocardial fibrosis severity in HCM.
What might this study add?
- The cardiac MRI of patients with HCM were analyzed depending on the genetic testing data.
- In patients with HCM, a positive genetic analysis, regardless of the affected gene, is associated with a greater severity of fibrosis according to MRI, which indicates a less favorable prognosis.
Aim. To analyze the data of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) depending on the results of genetic testing.
Material and methods. The study included 83 patients with a diagnosis of HCM (39 men, 44 women, mean age 50,4±14,9 years) who had no contraindications to MRI. Cardiac MRI was performed on 1,5 T and 3 T MRI systems using a standard protocol. T1 and T2 mapping was performed in 41 patients, and the extracellular volume fraction was estimated. All patients underwent genetic testing with assessment of sarcomeric genes, two non-sarcomeric genes associated with HCM, and genes of syndromic diseases (HCM phenocopies).
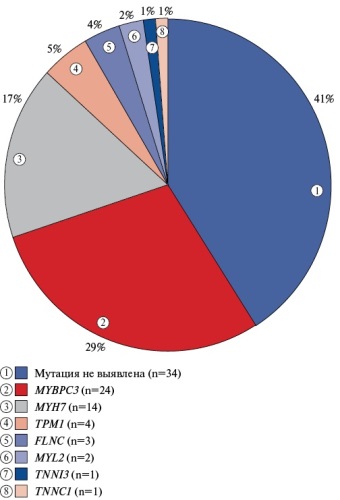
Results. Positive results of genetic testing were obtained in 49 (59%) of 83 patients: MYBPC3 29%, MYH7 17%, TPM1 5%, FLNC 4%, MYL2 2%, TNNC1 1%, TNNI3 1% (genotype-positive group (G+)). Negative results of genetic testing were obtained in 34 (41%) patients (genotype-negative group (G-)). In the G-group, patients were significantly older than in G+ (57,7±12,9 vs 45,3±14,2 years, p<0,05), with a smaller left ventricular (LV) wall thickness (18,9±4,2 vs 21,3±5,9 mm, p<0,05), and a higher LV ejection fraction (70,5±10,7 vs 64,7±10,4%, p<0,05). Comparison of myocardial fibrosis parameters between the groups showed a significantly lower incidence of delayed contrast enhancement in the G-group, and in its presence, the fibrosis severity, which was assessed as the fibrosis percentage from the total LV mass, was significantly lower than in the G+ group (71% vs 92%; 5,0±8,0% vs 11,4±9,0%, respectively, p<0,05). When analyzing G+ patients depending on the identified mutations, no significant difference in the severity of fibrosis was found between the groups.
Conclusion. In patients with HCM, a positive genetic analysis, regardless of the affected gene, is associated with a greater severity of fibrosis according to MRI data, which indicates a less favorable prognosis.
- Non-ischemic myocardial contrast pattern is accompanied by an increase in the left atrial volume, which in turn is a predictor of continued left ventricular remodeling in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy in the postoperative period.
Aim. To evaluate the heart morphological features and the significance of the non-ischemic myocardial contrast pattern in medium-term prognosis of continued left ventricular (LV) remodeling after surgery in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Material and methods. The results of paramagnetic contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were analyzed in 31 patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy with an average age of 58,4±7,6 years before complex surgical treatment. The heart morphological features and non-ischemic contrast pattern in the myocardial segments remote from the infarction area according to contrast-enhanced MRI were assessed.
Results. Patients with a non-ischemic contrast pattern had higher left atrial volume index (p=0,02), LV end-systolic index (p=0,03), and right ventricular sizes (p=0,01). A relationship was found between the left atrial volume index and cardiac remodeling in the postoperative period (p<0,005, correlation coefficient r=0,53).
Conclusion. Non-ischemic myocardial contrast pattern is accompanied by an increase in the left atrial volume, which in turn is a predictor of continued LV remodeling in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy in the postoperative period.
- Genetic studies on cardiomyopathies reveal significant associations between certain single nucleotide polymorphisms and the disease risk.
- The AG/GG allelic variant of the SCN5Agene (rs1805124), 6a/6a allelic variant of the MMP3gene (rs35068180) and the patient's age have prognostic significance in the development of DCM, while the AG/GG allelic variant of the CTLA4 gene (rs231775), AA and AG allelic variants of the SCN5A gene (rs1805124) have prognostic significance in the development of ischemic myocardial dilation.
- However, additional studies are needed to confirm these associations and fully understand their mechanisms, including large cohort studies and meta-analyses.
Aim. To develop a prognostic model for the development of primary and secondary cardiomyopathy based on genetic predictors.
Material and methods. The study included 221 patients with cardiomyopathy. The mean age of the participants was 55,30±9,69 years, with the age range from 20 to 77 years. Two following groups of patients were determined: the first group (n=111) with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and the second group (n=110) with ischemic myocardial dilation. DNA was extracted from the venous blood of all participants using phenol-chloroform extraction for subsequent genotyping using polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis.
Results. The performed multivariate analysis using the stepwise selection method showed a significant effect of the following predictors at the third step: AG/GG allelic variant of the SCN5A gene (rs1805124), 6a/6a allelic variant of the MMP3 gene (rs35068180) and the patient's age.
The performed multivariate analysis using the stepwise selection showed a significant effect of the following predictors: AG/GG allelic variant of the CTLA4 gene (rs231775), AA and AG allelic variants of the SCN5A gene (rs1805124).
Conclusion. Genetic studies on cardiomyopathies reveal significant associations between certain single nucleotide polymorphisms and the risk of disease development. The study results showed that the AG/GG allelic variant of the SCN5A gene (rs1805124), 6a/6a allelic variant of the MMP3 gene (rs35068180) and the patient's age have prognostic significance in the development of DCM. In addition, AG/GG allelic variant of the CTLA4 gene (rs231775), AA and AG allelic variants of the SCN5A gene (rs1805124) have prognostic significance in the development of ischemic myocardial dilation.
- Machine learning methods improve the accuracy of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy diagnosis, which will ensure a personalized approach to choosing patient management tactics.
- Further addition of datasets with information on concomitant diseases and treatment methods will significantly improve the performance of the proposed models.
Aim. To develop predictive models for differential diagnostics of hypertrophic phenotype in patients with concomitant diseases, as well as to validate through independent assessment.
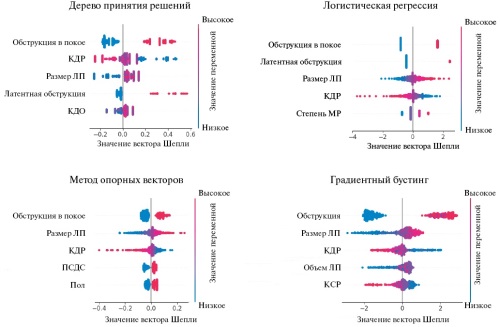
Material and methods. The study included an analysis of 1169 medical records from the medical information system of patients with severe myocardial hypertrophy and a preliminary diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) (I42.1, I42.2). The patients were divided into 3 following groups: patients with a probable HCM, patients with moderate myocardial hypertrophy (>15 mm) due to a known disease, and patients with severe myocardial hypertrophy that cannot be explained by left ventricular pressure overload ("gray zone"). The original dataset contains 74 parameters. Machine learning models of the following classes were created and optimized: logistic regression, support vector machine, decision tree, and gradient boosting decision trees.
Results. All models have sufficient accuracy in detecting HCM, but the accuracy of ruling out the diagnosis is quite low. The use of a machine learning model using logistic regression reduced the HCM misdiagnosis risk in the group of questionable diagnosis to 31%.
Conclusion. Four predictive models for differential diagnosis of severe left ventricular myocardial hypertrophy were developed to improve the HCM diagnosis. Blinding validation showed that logistic regression is the most optimal model for clinical practice.
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can lead to subacute/chronic post-COVID myocarditis, the clinical manifestations of which develop on average 8 months (from 1 month to 3 years) after acute COVID-19.
- Diagnostic approaches, in addition to standard examination, include the assessment of anticardiac antibody titers, biopsy using virological and immunohistochemical diagnostic methods.
- The efficacy and safety of immunosuppressive therapy with glucocorticoids and/or hydroxychloroquine has been proven.
Aim. To study the mechanisms and clinical variants of subacute and chronic myocarditis after SARS-CoV-2 infection using morphological and virological studies and to develop approaches to its treatment.
Material and methods. The study included 89 patients with documented coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The diagnosis of post-COVID myocarditis was established based on myocardial biopsy and/or cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data in combination with anamnesis, increased titers of anticardiac antibodies, and other criteria. The average time of presentation after infection was 8,0 [4; 17,5] months, while the average follow-up period was 7,0 [6,0; 13,5] months. Electrocardiography, Holter monitoring, echocardiography, cardiac MRI (n=60), determination of anticardiac antibody levels, myocardial biopsy (n=38), and autopsy (n=1) were performed.
Results. All patients showed an association between the onset or exacerbation of cardiac symptoms and COVID-19. The clinical variants of post-COVID myocarditis were identified: arrhythmic (n=24) with newly developed arrhythmias with normal myocardial contractility; decompensated (n=65) with newly diagnosed heart failure, including a variant developed with primary (genetic) cardiomyopathies and amyloidosis (n=10). The profile of arrhythmias in the arrhythmic variant varied from potentially life-threatening rhythm and conduction disorders (sustained ventricular tachycardia, grade II-III atrioventricular block) to infrequent supraventricular premature beats. In the decompensated variant, lymphocytic myocarditis was most often morphologically detected, while eosinophilic and giant cell myocarditis, associated with a worse prognosis, were rarer. Simultaneous development of nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis, infective endocarditis with the development of valvular heart defects was noted. In 10 cases, myocarditis was combined with primary cardiomyopathies, AL amyloidosis. Treatment included the administration of antiarrhythmic, cardiotropic, immunosuppressive therapy (glucocorticoids 16-32 mg/day in 68,5% of patients, hydroxychloroquine 200-400 mg/day in 33,7%). In the arrhythmic type, complete arrhythmia suppression was achieved in 25% of cases, while partial in 58,3%. In one case, a pacemaker was implanted. In patients with a decompensated myocarditis, corticosteroids were effective regardless of the viral genome/proteins in the myocardium.
Conclusion. COVID-19 can induce subacute and chronic myocarditis with the development of isolated arrhythmias or severe heart failure.
- Young patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), including those with indications for implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, have a higher incidence of overweight/obesity and hypertension han in the Russian population.
- Diagnosis of HCM established in childhood and adolescence is an informative marker of the disease clinical course and an indication for genetic testing and family screening.
- The reverse curvature hypertrophy of the interventricular septum is additional valuable information that, along with the pediatric age of HCM diagnosis, should be taken into account when referring for genetic testing and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging.
Aim. To study the clinical, morphological and genetic characteristics of young patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) with indications for primary and secondary prevention of sudden cardiac death (SCD).
Material and methods. The study included 44 young patients with HCM who were examined in accordance with national clinical guidelines for HCM (2020). The AHA HCM SCD Calculator was used to calculate the risk of SCD. The genetic study was performed using a target panel of 108 genes associated with cardiomyopathies.
Results. In the study cohort, young patients in 72,7% of cases (n=32) had from 1 to 3 cardiometabolic risk factors (on average 1,53±0,8).
The age of 18 patients with indications for implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) ranged from 18 to 44 years (28,8±2,2). The age at diagnosis was 18,5±7,4 years, while the asymptomatic period lasted 6,4±0,9 years. The estimated risk of SCD ranged from 3,11 to 20,71% (6,15 [4,67; 7,32]). In 83,3% of cases (n=15), familial HCM was diagnosed, while 50% (n=9) had a positive family history of SCD. In the subgroup of patients with indications for ICD, genetic variants with pathogenic significance (class IV and V) encoding the production of sarcomere proteins were detected in 6 of 9 probands (66,7%).
In patients with indications for ICD (n=18), compared to patients without it (n=26), the diagnosis of HCM was more often established in childhood and adolescence (61,1% vs 23%, p=0,01). In patients with indications for ICD, the reverse curvature hypertrophy of the interventricular septum was significantly more often diagnosed (72,2% vs 38,5%, p=0,028). Among patients with indications for ICD, the proportion of people with low physical activity was 50% (n=9), of which 55,6% (n=5) were diagnosed with overweight/class 1 obesity.
Conclusion. Childhood and adolescence at the time of diagnosis of HCM and reverse curvature hypertrophy of the interventricular septum are significantly more common in young patients with indications for ICD.
CARDIOSURGERY
- Among hypertensive patients with descending thoracic aortic aneurysm/abdominal aortic aneurysm referred for endovascular treatment, the comorbidity index is high — coronary artery disease, chronic kidney disease, and type 2 diabetes are common.
- In almost half of the patients, hypertension is not adequately controlled.
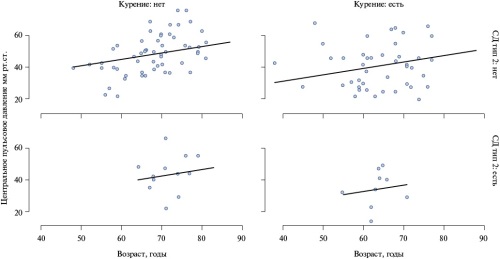
- The increase in central systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure is mainly due to an increase in the direct pulse wave regardless of the aneurysm location, while the reflected wave (augmentation pressure and augmentation index) effect varies and is more pronounced in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- With an increase in the aneurysm diameter, a decrease in the carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity is observed, while the central diastolic blood pressure increases. These phenomena should be taken into account when developing treatment tactics for such patients.
Aim. To analyze perioperative characteristics, including central hemodynamic parameters, of patients with hypertension (HTN) and descending thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) or abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) who were referred for endovascular aortic repair ([T]EVAR).
Material and methods. Local registry data were used. The study included 126 patients (103 men, 67±9 years). In addition to the basic examination, noninvasive measurement of central blood pressure (BP) and carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV) was performed. Quality of life (QOL) was assessed using the EQ-5D-3L questionnaire.
Results. The most common comorbidities were coronary artery disease (68%), obesity (39%), chronic kidney disease (26%), and type 2 diabetes (18%). Patients with AAA were significantly older and had a higher comorbidity burden, but had a better QOL than patients with TAA (59% vs 71%, p<0,05. High medication adherence was noted in 31% of patients receiving an average of 2 antihypertensive drugs and 59% of them had controlled HTN. Carotid-femoral PWV was higher (10,9 vs 9,6 m/s, p=0,006) and augmentation index (AIx) was lower in TAA (21% vs 29%, p<0,001). Large aneurysm size was associated with lower cfPWV and increased central diastolic BP (p=0,01 and p=0,03, respectively). Increased central pulse pressure (CPP) was positively associated with left ventricular mass index (r=0,21, p=0,037). A decrease in CPP and AIx was observed after [T]EVAR.
Conclusion. Patients with HTN and TAA/AAA referred for [T]EVAR have a high comorbidity burden and high QOL. Although the vast majority of patients receive a combination of only two drugs, insufficient adherence to therapy has been revealed. An increase in aneurysm diameter is associated with a decrease in cfPWV and increased central diastolic BP, indicating a potential impact of aneurysm on central hemodynamics in patients receiving antihypertensive therapy.
CORONARY HEART DISEASE, MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
- Dynamic single-photon emission computed tomography allows identification of decrease in global stress myocardial blood flow and myocardial flow reserve in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease.
- Global myocardial flow reserve can be considered as one of the selection criteria for myocardial revascularization in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease.
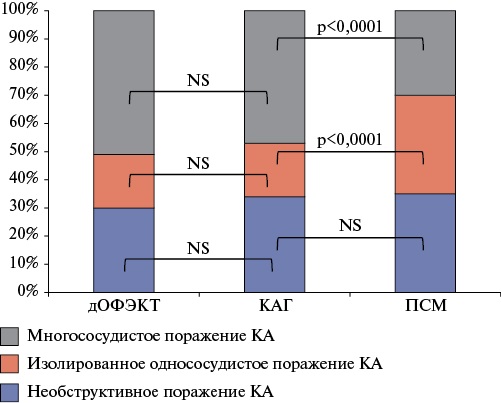
Aim. To study the relationship between the coronary atherosclerosis involvement area and ischemia severity in terms of the consistency of dynamic single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and myocardial perfusion scintigraphy (MPS) data with coronary angiography in patients with multivessel coronary artery (CAD) disease.
Material and methods. The study included 327 patients with suspected or confirmed coronary artery disease (CAD), who previously underwent dynamic SPECT, MPS and invasive or computed tomography coronary angiography. Based on the data on coronary artery (CA) involvement, patients were selected: 1) with multivessel CAD (n=171), 2) with single-vessel CAD (n=71) and 3) non-obstructive CAD (n=85). Based on the MPS data, the presence and impaired perfusion area at rest and during the stress test, as well as the degree of their discrepancy were assessed: summed stress score (SSS), summed rest score (SRS) and summed difference score (SDS). The values of myocardial blood flow (MF) and MF reserve (MFR) were assessed using dynamic myocardial SPECT.
Results. Standard MPS indices did not differ between the groups with non-obstructive, single-vessel and multivessel CAD as follows: 2,0 (0,0; 4,0) vs 5,0 (2,0; 7,0) vs 5,0 (3,0; 9,0) — SSS; 0,0 (0,0; 1,0) vs 3,0 (0,0; 5,0) vs 2,0 (0,0; 4,0) — SRS; 2,0 (0,0; 3,0) vs 3,0 (1,0; 6,0) vs 2,0 (0,0; 5,0) — SDS, respectively. The transient ischemic dilation did not differ between the study groups.
Dynamic SPECT revealed a decrease (p<0,01) in global stress MF and MFR in patients with multivessel CAD compared to groups with non-obstructive and isolated single-vessel atherosclerosis: 1,07 (0,69; 1,49) vs 1,46 (1,08; 1,88) vs 1,48 (0,93; 1,89); 1,64 (1,16; 2,33) vs 2,28 (1,52; 2,93) vs 2,36 (1,58; 3,07), respectively.
Net Reclassification analysis showed that MFR allows for correct reclassification of a significant proportion of patients with CAD compared to MPS (NRI=0,31, p=0,001).
Conclusion. Dynamic myocardial SPECT is an adequate tool for assessing the ischemia volume in patients with extensive coronary involvement, and global MFR can be considered as one of the selection criteria for myocardial revascularization. The results obtained in this study require further study.
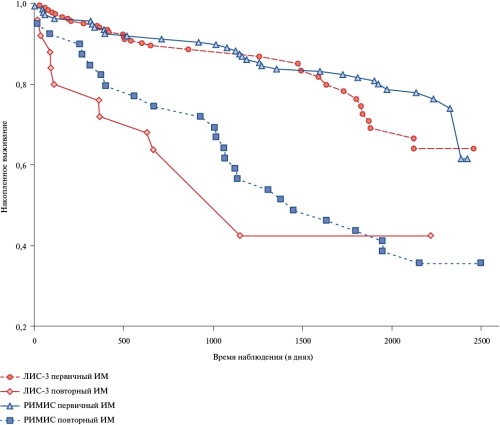
- The long-term survival of patients after primary and recurrent myocardial infarction in the Russian registries LIS-3 and RIMIS were compared.
- The long-term prognosis of patients after recurrent myocardial infarction is several times worse than the prognosis of patients after primary myocardial infarction.
- Current treatment methods of acute myocardial infarction, including percutaneous coronary intervention, do not solve the problem of high residual risk of death after the event, and this applies to the greatest extent to patients with recurrent myocardial infarction.
- The obtained results indicate the need to develop adequate secondary prevention measures after primary myocardial infarction.
Aim. To compare the long-term survival of patients after primary and recurrent myocardial infarction (MI) in the LIS-3 and RIMIS registries.
Material and methods. The retrospective RIMIS registry included patients with acute transmural MI admitted to the emergency cardiology department of one of the Moscow vascular centers in 2017. A total of 214 patients were included, of which 23 people died in hospital and 191 people were included in the prospective registry part. Long-term vital status was assessed on average 6 years after discharge from hospital and was determined in 178 patients. The response rate was 93,19%. The prospective registry LIS-3 included all patients admitted to the Lyubertsy Regional Hospital with a diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome, of which 78 patients were discharged after confirmed MI in the first 9 months of 2014, and 164 patients were discharged after confirmed MI in the first 9 months of 2018. A total of 242 patients were included. Long-term vital status was determined in 207 patients. The response rate 85,5%. The median follow-up was 872 days. Comparative analysis of patient cohorts from the RIMIS and LIS-3 registries did not reveal any significant differences in the main demographic, anamnestic, and clinical parameters. The frequency of percutaneous coronary intervention in the acute stage of MI was higher in the RIMIS registry than in the LIS-3 registry (96,9 and 62,3%, respectively).
Results. During the follow-up period, 31,4% of patients died in the RIMIS registry, and 20,8% of patients in the LIS-3 registry. Kaplan-Meier curves did not reveal any significant differences in patient survival in both registries. At the same time, in both registries, the long-term survival of patients after recurrent MI was significantly worse than that of patients who had a primary MI.
Conclusion. Patients who had an acute MI, despite modern treatment in the acute stage, have a high residual risk of death. This is especially true for patients who had a recurrent MI.
- The cognitive status of most patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) referred for myocardial revascularization surgery is more pronounced than in conditionally healthy patients undergoing routine medical examination.
- The following parameters were studied: cognitive error — "catastrophizing", attribution parameter — "stability of failures", personal anxiety, lower ability to recover from stress — "resilience".
- The cognitive status of the majority of patients with CAD in the study group is more pronounced than in patients with cerebral ischemia, according to the cognitive error indicator — "exaggeration of danger".
Aim. To analyze the cognitive status (thinking style and nature of stress experience) in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) who underwent myocardial revascularization.
Material and methods. The study involved 150 patients with the average age of 54 years. The study sample included three following groups of respondents: patients with CAD who underwent myocardial revascularization 1,5 months before the study (n=50); patients with cerebral ischemia (n=50); conditionally healthy respondents who underwent routine medical examination (n=50). The following were used: the Cognitive Mistakes Questionnaire by A. Freeman, R. DeWolf (in the Russian adaptation by A.E. Bobrov, E.V. Fayzrakhmanova); the Questionnaire of Styles of Explanation of Successes and Failures by T.O. Gordeeva, O.A. Sychev, E.N. Osin, V.A. Titova Gransham; the Brief Resilience Scale by B. Smith, et al. (in the Russian adaptation by V.I. Markova, L.A. Alexandrova, A.A. Zolotareva); the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory by C. D. Spielberger (in the Russian adaptation by Yu.L. Khanin). To assess the significance of differences in cognitive status and the nature of stress experience between the above-mentioned groups, Student's t-test (t) was used. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS Statistics ver. 27.0.1.
Results. Patients with CAD who underwent myocardial revascularization differ from conditionally healthy patients who underwent routine medical examination, in higher expression of following cognitive status indicators: "catastrophizing" (t=-6,718 at p<0,01), "stability of failures" (t=-3,092 at p<0,01), high expression of personal anxiety (t=-5,238 at p<0,01) and low expression of resilience (t=3,163 at p<0,01). In addition, CAD patients differ from patients with cerebral ischemia in higher expression of the cognitive status parameter "exaggeration of danger" (t=-6,292 at p<0,01).
Conclusion. In patients with CAD, the indicators of cognitive status and ability to recover after revascularization may indicate chronic traumatization caused by disease and surgery as the trigger event. The data obtained may be important for the development of prevention and rehabilitation programs.
- New data were obtained on the relationship between the ceramide profile of local fat depots and such an important risk factor for cardiovascular diseases as smoking.
- Associations were found between ceramide (CER) levels in cardiac adipose tissue (epicardial and perivascular) and smoking, manifested by an increase in the concentration of CER d18:1/16:0, 18:0, 24:1, 22:0. In the subcutaneous adipose tissue of smoking patients, an increased content of CER d18:1/14:0, 17:0 was found.
Aim. To describe ceramide profile of subcutaneous, epicardial, perivascular adipose tissue (SAT, EAT, PVAT, respectively) in patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVD) depending on smoking.
Material and methods. Ceramide (CER) profile in the SAT, EAT, PVAT of patients with CVD (30 patients with coronary artery disease and 30 patients with degenerative non-rheumatic acquired heart defects) was determined using a high-resolution chromatography mass spectrometry (Agilent 1200 series (Agilent Technologies, Germany)) with a maXis impact mass spectrometer (Bruker, Germany)). Biopsies of SAT, EAT, PVAT were obtained during surgery. Statistical analysis was performed in GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software).
Results. Associations of CER levels in visceral adipose tissue and smoking were found, manifested by an increase in the concentration of CER d18:1/16:0, 18:0, 24:1, 22:0. In the SAT of smoking patients, an increased content of Cer d18:1/14:0, 17:0 was found.
Conclusion. The ceramide profile of local fat depots differed in smoking and non-smoking patients with CVD. The obtained results indicate the modulation of CER synthesis during smoking and the accumulation of CER mainly in the EAT and PVAT in CVD. Taking into account the wide range of metabolic effects, the use of CER as biomarkers and targets for personalized therapy is promising for identifying high-risk individuals and improving therapeutic and diagnostic strategies for CVD.
STRESS IN THE POPULATION
What is already known about the subject?
- Prior studies on the relationship between hypertension and stress coping strategies included mainly middle-aged and elderly patients with established behavioral stereotypes, and they demonstrated contradictory results.
What might this study add?
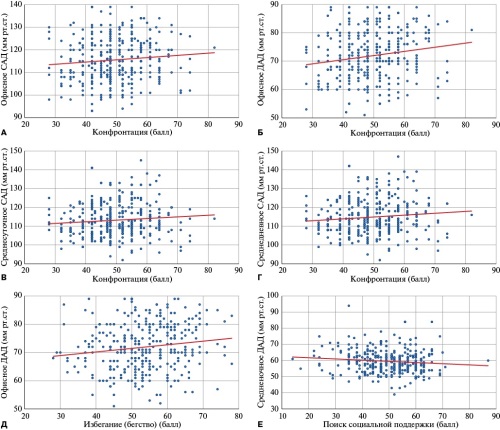
- In young people, the level of clinical and ambulatory blood pressure directly depends on the frequency of using such stress coping strategies as confrontation and avoidance (escape) and vice versa — on coping by seeking social support.
How might this impact on clinical practice?
- Early prevention programs for hypertension, along with traditional recommendations for lifestyle correction, may additionally include stress coping training.
Aim. To study the relationship between office and ambulatory blood pressure (BP) and various stress coping strategies in healthy young adults.
Material and methods. The design of the cross-sectional study included individuals of health status groups I or II aged 20 to 29 years with office BP <140/90 mm Hg. All individuals included in the study underwent office BP measurement and 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM). To determine the frequency of coping strategies, a Ways of Coping Questionnaire was used. For statistical analysis, the Stattech program, version 4.0.6 (Russia) was used.
Results. The study included 347 participants, including 101 (29,1%) males; the median age was 22 (21-23) years. Linear dependencies were established between office BP and various ABPM parameters with three stress coping strategies: confrontation, avoidance, and seeking social support. The frequency of confrontation correlated with the greatest number of parameters, both assessed in office BP and ABPM. A direct dependence was noted between confrontation and office systolic blood pressure (SBP) (ρ=0,109; p=0,042) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (ρ=0,174; p=0,001), as well as average 24-hour SBP (ρ=0,120; p=0,025) and average day-time SBP (ρ=0,128; p=0,017). The avoidance frequency also directly correlated with the level of office DBP (ρ=0,158; p=0,003). With an increase in avoidance use by 1 point, clinical DBP increases by 0,13 mm Hg. At the same time, an inverse linear relationship was established between the strategy of seeking social support and night-time DBP (ρ=-0,112; p=0,036). With an increase in the frequency of seeking social support by 1 point, a decrease in the average night-time DBP by 0,07 mm Hg is expected.
Conclusion. In young people, the level of office and outpatient BP linearly depends on the frequencies of using three models of coping behavior: confrontation, avoidance, and seeking social support.
GUIDELINES FOR THE PRACTITIONER
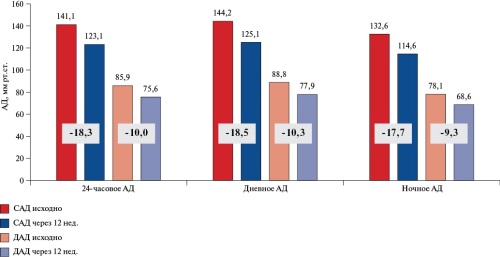
- The FORPE is the first study to present the non-immunogenic staphylokinase administration experience in patients with massive pulmonary embolism with hemodynamic instability. Non-immunogenic staphylokinase is as effective as alteplase and has a high safety profile. The use of non-immunogenic staphylokinase was not accompanied by major bleeding and hemorrhagic stroke.
- For the first time, the results of computed tomography pulmonary angiography showed a significant reduction in thrombotic masses and a decrease of right ventricular dysfunction after thrombolysis with non-immunogenic staphylokinase.
- The unique mechanism of action of non-immunogenic staphylokinase allows using in a single dose of 15 mg, regardless of the patient's body weight. Rapid (10-15 s) single bolus administration of non-immunogenic staphylokinase is convenient for use in emergency medicine.
Aim. To assess the safety and efficacy of a single intravenous bolus of non-immunogenic staphylokinase compared with alteplase in patients with massive pulmonary embolism and hemodynamic instability. Non-immunogenic staphylokinase is a modified recombinant staphylokinase with low immunogenicity, high thrombolytic activity and fibrin selectivity.
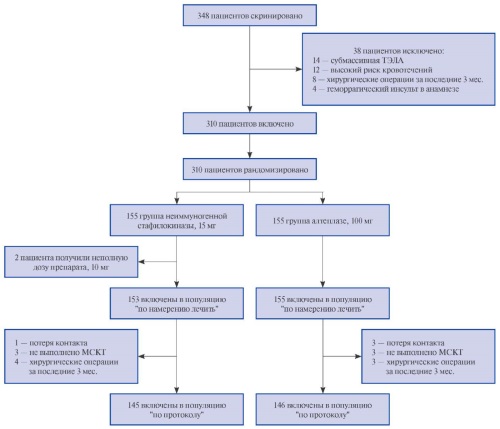
Material and methods. This multicenter, open-label, randomized, comparative clinical trial FORPE in two parallel groups was conducted in 23 clinical centers in Russia. A total of 310 patients aged 18 years and older with hemodynamic instability and computed tomography pulmonary angiography verified massive pulmonary embolism and right ventricular dysfunction were included. The patients were randomly assigned in either non-immunogenic staphylokinase (15 mg) or alteplase (100 mg) group. Both medicines were administered intravenously. An independent biostatistician created a randomization sequence using computer-generated random numbers. Randomization was performed using the envelopes. The study was open-label, and emergency unit staff, investigators, and patients were informed about the assigned drug. The primary efficacy endpoint was 7-day all-cause death after randomization. The non-inferiority margin was set at 10% for the difference in 7-day all-cause mortality after randomization between the compared groups. Non-inferiority was tested using the Welch t-test for the primary efficacy endpoint. Secondary efficacy endpoints were analyzed in both the intention-to-treat and per-protocol populations.
Results. Of 348 patients screened between December 25, 2020, and July 31, 2023, 310 (89%) were included in the study. Of the total number, 155 (50%) patients were randomized to the non-immunogenic staphylokinase group and 155 (50%) to the alteplase group. In the non-immunogenic staphylokinase group, the primary efficacy endpoint, 7-day all-cause death, was 2% in the intent-to-treat population and 2% in the per-protocol population, whereas in the alteplase group it was 3% (odds ratio (OR) 0,75, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0,11-4,49; p=1,00) and 3% (OR 0,75, 95% CI 0,11-4,52; p=1,00), respectively. The difference in the primary efficacy endpoint was 0,6% (95% CI -2,8 to -4,0) in the intent-to-treat population and 0,6% (95% CI -2,9 to -4,2) in the per-protocol population. Thus, the lower limit of the 95% CI did not cross the non-inferiority margin (p<0,001). There were no cases of hemorrhagic stroke in the non-immunogenic staphylokinase group, whereas there were three cases (2%) of hemorrhagic stroke in the alteplase group (p=0,25). Serious adverse events were experienced by 11 patients (7%) in the non-immunogenic staphylokinase group compared with 12 patients (8%) in the alteplase group (p=1,00).
Conclusion. Non-immunogenic staphylokinase is at least as effective as alteplase in the treatment of patients with massive pulmonary embolism with hemodynamic instability and has a higher safety profile. Future observational studies of non-immunogenic staphylokinase are needed to continue assessing its safety and efficacy. Given the high safety and efficacy of non-immunogenic staphylokinase, its use should be studied in patients with moderate-to-high risk pulmonary embolism.
LITERATURE REVIEW
- Growing interest in nocturnal hypertension and non-dipping pattern of blood pressure (BP) is due to their high prevalence and confirmed association with adverse outcomes even when target office and mean 24-hour BP have been achieved.
- Nocturnal hypertension is probably a more significant prognostic marker compared to non-dipping pattern, due to the low reproducibility of the latter.
- Diagnostic capabilities in identifying disturbances in the 24-hour BP profile are characterized by the increasing indications for 24-hour BP monitoring and the development of home BP monitors with the function of night measurements.
- The main approach to the treatment of nocturnal hypertension is the use of long-acting antihypertensive agents and the search and treatment of the leading cause of nocturnal BP disorders in an individual patient.
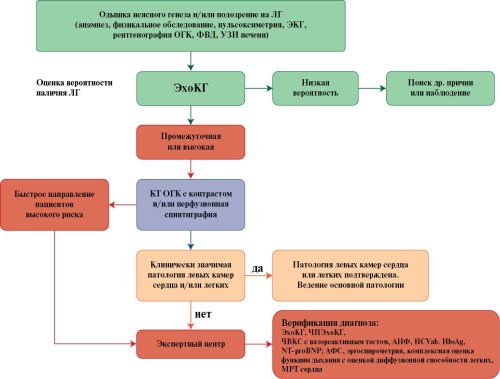
Impaired 24-hour blood pressure (BP) profile is receiving increasing attention due to improved detection capabilities, increased incidence, and confirmed associations with cardiovascular risk. However, there are gaps or conflicting data in knowledge about nocturnal hypertension (HTN) and non-dipping. The review focuses on current problems associated with elevated nocturnal BP with an emphasis on diagnostic capabilities, prognostic significance of changes and treatment options.
EXPERT CONSENSUS
Russian Society of Cardiology, National Atherosclerosis Society, Russian Society of Cardiosomatic Rehabilitation and Secondary Prevention, Russian Association of Endocrinologists
CLINICAL GUIDELINES
The Russian Society of Cardiology (RSC)
With the participation of: the Russian Association of Cardiovascular Surgeons, Eurasian Association of Cardiology (EAC), The Russian Medical Society on Arterial Hypertension (RMSAH), Russian Respiratory Society (RRS), the Association of Anesthesiologists and Intensive Care Specialists, the Russian Society of Radiologists and Radiologists (RSRR), the Association of Rheumatologists of Russia.
Endorsed by the Research and Practical Council of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (12.09.2024).
Russian Society of Cardiology (RSC)
With the participation: National Society of Myocardial Diseases and Heart Failure, Society of Heart Failure Specialists, Russian Scientific Medical Society of Internal Medicine
Endorsed by the Research and Practical Council of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (12.09.2024)
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)