ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Aim. To assess the changes in cardiology diagnostics scope in the Russian Federation during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.
Material and methods. In an online survey organized by the Division of Human Health of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), including questions about changes in the workflow of diagnostic laboratories and the scope of cardiac diagnostics from March 2019 (pre-pandemic) to April 2020 (first wave of the pandemic) and April 2021 (recovery stage), 15 Russian medical centers from 5 cities took part.
Results. The decrease in the diagnostics scope by April 2020 by 59,3% compared to March 2019, by April 2021, stopped and was replaced by growth (+7,1%, the recovery rate, 112,1%). The greatest increase was in routine examinations, such as echocardiography (+11,6%), stress echocardiography (+18,7%), stress single photon emission computed tomography (+9,7%), and to a lesser extent resting computed tomography angiography (+7,0%) and magnetic resonance imaging (+6,6%). The performance of stress electrocardiography, stress magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography for the diagnosis of endocarditis in April 2021 compared to March 2019 decreased by 10,3%, 63,2% and 62,5%, respectively.
Conclusion. Due to the resumption of patient admissions for cardiac examinations during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, with the anti-epidemic measures taken and certain changes in the workflow, there has been a recovery in the diagnostics scope in most of the included centers.
Aim. To study the lipid profile in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) depending on the outcome of its acute phase according to the AKTIV international registry.
Material and methods. The AKTIV registry included men and women over 18 years of age with a diagnosis of COVID-19, who were treated in a hospital. A total of 9364 patients were included in the registry, of which 623 patients were analyzed for levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglycerides on days 1-2 of hospitalization. The level of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) was calculated using the Friedewald equation.
Results. We found that a decrease in LDL-C level was significantly associated with an unfavorable prognosis for hospitalized patients with COVID-19. This pattern persisted in both univariate and multivariate analyses. LDL-C levels in the final multivariate model had a significant relationship with the prognosis (an increase in the death risk by 1,7 times with a decrease per 1 mmol/l). In addition, we found that the survival of patients with an indicator level of <2,45 mmol/l is significantly worse than in patients with an LDL-C level ≥2,45 mmol/l. All patients with high LDL-C ((≥4,9 mmol/l) survived, while among patients with low LDL-C (<2,45 mmol/l. All patients with high LDL-C ((≥4,9 mmol/l) survived, while among patients with low LDL-C (<1,4 mmol/l), mortality was 13,04%, which was significantly higher than in patients with LDL-C ≥1,4 mmol/l (6,32%, p=0,047).
Conclusion. A decrease in LDL-C in the acute period is significantly associated with an unfavorable prognosis for hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Determination of LDL-C can be included in the examination program for patients with COVID-19. However, the predictive value of this parameter requires further study in prospective clinical studies.
Aim. To study the associations of changes in lipid metabolism parameters and the severity of a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Material and methods. This cross-sectional study included 270 patients aged 26-84 years (mean age, 53,09±13,22 years) who had COVID-19 within prior two months, which were divided into 3 groups: mild (1, n=128), moderate (2, n=128) and severe (3, n=14) COVID-19. Patients were assessed for body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), hip circumference (HC), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), total cholesterol, triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). In addition, atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) was calculated. Statistical processing was performed using the SPSS software package (version 13.0).
Results. Patients with severe COVID-19 had significantly higher levels of TG and AIP compared with patients with moderate and mild course. BMI and WC were significantly higher in patients in groups 2 and 3 compared with patients in group 1. In women, BMI and AIP levels were significantly higher in the severe COVID-19 group compared to groups 1 and 2. HDL-C levels were lower in patients with severe COVID-19 compared to those with moderate disease. WHR was higher among men in group 3 compared with group 1.
Conclusion. Patients with severe COVID-19 have higher BMI, WC, AIP, TG levels, and lower HD-C levels. The relative odds for severe COVID-19 are associated with increased WC, AIP, TG, and lower HDL-C.
Aim. To study the prevalence of hypotension (HoTN) with an unfavorable prognosis in populations of the Russian Federation and the United States of America in a thirty-year perspective.
Material and methods. We used data from Russian population-based studies performed in 1975-1982 at the now-familiar National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine, and the study Epidemiology of Cardiovascular Diseases and their Risk Factors in Regions of Russian Federation (ESSE-RF) in 2012-2014. A comparison was made with data from studies of US population of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES): NHANES II (1976-1980) and Continuous NHANES (2007-2012). Age, sex, systolic and diastolic blood pressure were analyzed. The proportion of persons with HoTN (prevalence) was calculated in men and women of five age groups using the original HoTN criterion.
Results. We used the previously developed criterion of HoTN with an unfavorable prognosis: for Russian populations, the mean dynamic pressure is <76 and <72 mm Hg, respectively. The prevalence of HoTN in modern populations was 0,1±0,5% in Russia and 6,0±8,7% in the USA (confidence interval for significance level P=0,95). For 30 years, the prevalence of HoTN in Russia according to this criterion has not changed, while in the USA it has increased both in men (on average 3 times) and in women (2,5 times).
Conclusion. The prevalence of unfavorable HoTN in the US adult population is many times higher than in Russia over the entire analyzed period of time, while over 30 years in the US it has increased by 2,5-3 times.
Aim. To analyze the functionality and characteristics of quit smoking applications available to Russian-speaking users using validated scales for its evaluation.
Material and methods. Applications were searched in the App Store and Google Play, and a specialized MARS scale was used to evaluate applications. A total of 598 applications were found, of which 54 applications met the inclusion criteria and were included in the study.
Results. It was found that 54% of applications use short- and medium-term goals as methods and techniques to increase the likelihood of quitting tobacco, while 31% of applications use various educational materials in order to form a negative attitude towards smoking. In addition, 22% of applications use cognitive and behavioral techniques of cognitive behavioral therapy. A negative moderate correlation was established between the application user rating and MARS score (r=-0,32).
Conclusion. The Russian-language anti-smoking mobile applications included in this study demonstrated satisfactory quality on average. A significant number of applications use proven effective cognitive behavioral therapy techniques. At the same time, mobile applications in healthcare has shortcomings, especially in terms of compliance with guidelines, and needs to be further improved.
Aim. To evaluate medium-term survival without irreversible and fatal cardiovascular events in individuals with a high spatial QRS-T angle (sQRS-Ta) from a regional Russian sample.
Material and methods. We analyzed 1394 electrocardiographic records from a random regional sample of men (30%) and women aged 25-64, which were included in the ESSE-RF1 study. Women were on average 5 years older than men, but there was no difference in mean age in the 45-64 groups. The follow-up period lasted 7 year; 26 irreversible events (cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction or stroke) and 63 composite endpoints (CEs) (irreversible event or heart failure progression or revascularization) were identified. Irreversible events and composite endpoint in men were noted more often than in women as follows: 3,7% vs 1,1% (p=0,003) and 6,9% vs 3,6% (p=0,01), respectively. sQRS-Ta was estimated as the angle between the integral QRS and T vectors in the orthogonal leads. Survival was assessed by Kaplan-Meier curves using a log-rank test. Differences were considered significant at p≤0,05.
Results. Sex groups did not differ in mean sQRS-Ta. sQRS-Ta ≥90o was considered to be increased. The divergence of survival curves by the end of follow-up period in men with increased sQRS-Ta relative to men with sQRS-Ta <900 was greater than in women as follows: 0,88 vs 0,96 for CE (p=0,0026) and 0,93 vs 0,96 for irreversible events (p=0,009); in women — 0,94 vs 0,98 for CE only (p=0,0016). Initial event and CE in men with increased sQRS-Ta occurred earlier than those with normal sQRS-Ta and then in women with increased sQRS-Ta. There were no differences in the frequency of sQRS-Ta increase among 45-64-year-old men and women, but irreversible events in men with increased sQRS-Ta occurred 5 times more often than in women. According to two-stage logistic regression, the probability of irreversible event in men is 4,35 times higher than in women (p=0,0002). After adjusting for sex, in individuals with increased sQRS-Ta, it is 2,75 times higher than in individuals with sQRS-Ta <90o (p=0,015).
Conclusion. In men with increased sQRS-Ta (≥90o), survival without irreversible and fatal cardiovascular events was worse, and life expectancy was shorter than in men with normal sQRS-Ta or women with increased sQRS-Ta. The prognosis of irreversible events was significantly affected by male sex and sQRS-Ta increase.
Aim. To evaluate the mid-term outcomes of surgical myocardial revascularization in combination with coronary endarterectomy in patients with diffuse coronary artery disease (CAD).
Material and methods. In this cohort, non-randomized, retrospective, longitudinal study, we compared the mid-term outcomes of surgical myocardial revascularization in combination with coronary artery endarterectomy in patients with diffuse CAD with the outcomes of surgical myocardial revascularization without endarterectomy in patients without diffuse CAD. The study group included 93 patients, while the control group — 99 patients. Mid-term mortality, morbidity, and angiographic outcomes of surgical revascularization were assessed.
Results. The mean follow-up period was 46,7±18,5 months. Mid-term mortality was 5,5% (n=5) in the coronary endarterectomy group and 3,1% (n=3) in the isolated coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) group (p=0,486). Angina recurrence was noted in 14,3% (n=13) of patients in the endarterectomy group and in 14,4% (n=14) of cases in the isolated CABG group (p=0,977). Coronary artery stenting was required in the mid-term period in 4,4% (n=4) of patients in the endarterectomy group and 4,1% (n=4) (p=1000) in the isolated CABG group. A stroke in the mid-term period occurred in 1 (1,1%) patient of the study group and 3 (3,1%) patients in the control group (p=0,334). Graft patency in the anterior interventricular artery was 90,9%, while in the circumflex artery — 100% and in the right coronary artery — 80,4%. There were no significant differences in the patency level between the study and control groups. Quality of life did not differ significantly between groups in the mid-term period.
Conclusion. Coronary endarterectomy is not associated with an increase in mortality and morbidity in the mid-term period, and is accompanied by satisfactory angiographic patency rates. There was no negative effect of coronary endarterectomy on the quality of life in the mid-term period.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY
Hypertension (HTN) remains one of the most important risk factors for cardiovascular events. Modification of additional risk factors, along with a blood pressure decrease, significantly affects the risk of cardiovascular events. Hyperuricemia is one of the new factors that has a high prevalence in the population and affects the risk for cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients. In the treatment with fixed-dose combinations in patients with hypertension and hyperuricemia, metabolic neutrality is of particular importance. When prescribing diuretics, the practitioner faces additional difficulties. These drugs are highly synergistic when added to other major antihypertensives’ classes, but, in some cases, may worsen the metabolic profile. The use of the thiazide-like diuretic indapamide largely avoids a negative effect on the metabolic profile, making it the preferred choice for patients with hyperuricemia.
With a high prevalence in the Russian population and insufficient effectiveness of treatment, hypertension remains a poorly controlled cardiovascular risk factor, including due to the low compliance of patients. Noncompliance is due to a large number of factors, some of which were studied in post-hoc analysis of the Russian observational STIL’ and TRICOLOR studies. It demonstrated that fixed-dose combinations of antihypertensive drugs can make a significant contribution to solving such a complex problem as low compliance.
Aim. We aimed to compare post-interventional angiographic outcomes of ticagrelor versus clopidogrel according to glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
Material and methods. The study included a total of 532 patients, with 334 receiving ticagrelor (62,8%) and 198 clopidogrel (37,2%). Diabetic status of the patients was assessed with HbA1c. TIMI flow grade and TIMI frame count were calculated and compared between two groups.
Results. TIMI flow grade 3 was higher and TFC was lower after percutaneous coronary intervention of the infarct-related artery in patients treated with ticagrelor compared to clopidogrel (89,2% vs. 73,7%; p< 0,001, 20 vs. 24; p< 0,001). There was a positive correlation between the increases in HbA1c and TFC levels in the whole group (r=0,225; p=0,004). In subgroup analysis, higher HbA1c levels did not affect TFC in patients using ticagrelor (r=-0,060; p=0,326 for patients with noreflow, r=-0,133; p=0,321 for patients with TIMI-3 flow). While level of HbA1c did not affect TFC in patients with TIMI-3 flow, the presence of post-procedural no-reflow caused worsening of TFC in patients using clopidogrel as HbA1c levels increased (r=0,374; p=0,005).
Conclusion. Ticagrelor was found to be better in terms of angiographic parameters regardless of diabetes.
EXPERT CONSENSUS
Cardiovascular diseases are widespread and are the leading death cause in most countries, despite the creation and improvement of strategies to reduce cardiovascular risk. A significant role in the development and evolution of cardiovascular diseases belongs to sympathetic nervous system hyperactivity, and therefore the methods of effecting it are relevant for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular pathology. The article discusses modern approaches to interventional and conservative regulation of the autonomic nervous system and neuromodulation in the prevention and treatment of hypertension, heart failure, tachyarrhythmias, as well as reflects a conjoint expert judgment on these issues.
CLINICAL AND INVESTIGATIVE MEDICINE
The possibility of heart inflammation (both myocardial and endocardial) months after a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has not been practically studied, especially since approaches to the treatment of myocarditis in combination with various endocarditis forms have not been developed.
Aim. To study the prevalence and mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2-associated endocardial injury in patients with morphologically verified post-COVID-19 myocarditis, as well as to develop approaches to comprehensive therapy.
Material and methods. The study included 18 patients with severe morphologically verified post-COVID-19 myocarditis (men, 9; 51,1±9,4 years; 35 to 66 years). Patients with prior verified myocarditis/myocardial infarction, rheumatic heart disease, and systemic immune diseases were excluded. The average time after COVID-19 was 6,5 [3.5; 10] months The diagnosis of myocarditis was confirmed by endomyocardial biopsy (including immunohistochemical examination with antibodies to CD3, CD20, CD45, CD68, and to SARS-CoV-2 antigens; polymerase chain reaction for SARS-CoV-2 RNA, DNA of cardiotropic viruses). The blood level of anticardiac antibodies was determined by indirect immunofluorescence. In addition, echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging (n=8), cardiac multislice tomography (n=1), and coronary angiography (n=14) were performed.
Results. Biopsy revealed active (n=12) and borderline (n=3) lymphocytic myocarditis, eosinophilic (n=2) and giant cell (n=1) myocarditis. In 4 patients, nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE) with parietal and intravascular thrombosis was diagnosed, and in one patient — infective endocarditis (IE) of the bicuspid aortic valve. Myocardial persistence of SARS-CoV-2 was detected in 72% of cases (in 3 patients — with NBTE; in 1 — with IE; in 9 — without endocarditis). Titers of anticardiac antibodies increased by 3-4 times in 94% of patients. Patients with endocarditis were characterized by larger heart chambers, lower ejection fraction (27,5±6,6 vs 36,0±13,4%), more severe pulmonary hypertension, and valvular regurgitation. Intraventricular thrombosis according to echocardiography/magnetic resonance imaging and cardiac embolism was not observed. Treatment in all patients included methylprednisolone at an average dose of 24 mg a day. In 10 patients, the result was monitored for at least 3 months as follows: the ejection fraction was 46,0±12,7% and 44,3±7,3% in patients with and without endocarditis, respectively.
Conclusion. Endocarditis in patients with post-COVID-19 myocarditis was detected in 28% (1 patient — IE; 4 — NBTE). The key mechanisms of post-COVID-19 myocarditis and NBTE are long-term (up to 18 months) myocardial persistence of SARS-Cov-2 and the development of an autoimmune reaction. Endocarditis was diagnosed in more severe patients, including those with giant cell and eosinophilic myocarditis. The effectiveness of steroid therapy in combination with anticoagulants in patients with NBTE requires further study. In case of IE, steroids can also be used in the treatment of myocarditis (in combination with antibiotics and immunoglobulin).
SUPPORTING A PRACTITIONER
Ethical norms are traditionally inseparable from medical work as such and are an unconditional part of the general idea of medicine and doctorhood. However, the structure of medical ethics is ambiguous and complex. It includes the ways in which ethically loaded decisions are made, the categories of ethically loaded decisions themselves and the good/bad dichotomy, as well as cultural context that defines these categories. The psychological component also plays a role: mental state of a patient, a doctor, as well as verbal and nonverbal communication. Finally, the legal framework is imperatively introduced into the doctor-patient relationship, setting norms regardless of the nuances of interpersonal interaction. This article discusses the most important and explicit components of an ethical relationship in helping, and also proposes as a universal solution the ethics of virtue neither as an instrumental, but an essential approach.
Aim. To identify the most significant aspects and features of the right of cardiovascular patients to health care, as well as to assess its guarantee and characterize most common legal precedents with violations.
Material and methods. In preparing the article, documents of international law, Constitution of the Russian Federation, primary and secondary federal legislation in Russia, as well as judicial practice materials were used. For their analysis, dialectical, system structural, technical legal, comparative legal research methods were used.
Results. We established that in the Russian Federation there is a very extensive legal framework for regulating the right to health protection and health care. At the same time, the relevant legal acts establish both general (addressed to all individuals) and special (relevant only to cardiovascular patients) guarantees for cardiovascular health care. The scope and content of the legal regulation of guarantees of the right to cardiology healthcare should be generally considered sufficient for the protection of this right. However, judicial practice testifies to the facts of violation of the personal rights in the cardiac care provision.
Conclusion. The most resonant and often reported violations of personal right to health protection in a cardiology are the ones of persons with acute coronary syndrome because of their very dangerous consequences.
CLINICAL CASE
In the presented case report, 27-year-old female patient consulted a dermatologist and a lipidologist due to the appearance of small red spots on the skin. At the stage of examination in the lipid center, the patient was diagnosed with diabetes. During additional examination in the department of endocrinology, the following diagnosis was made: "Newlu-diagnosed type 1 diabetes. Target glycated hemoglobin level 6,5%. Secondary dyslipidemia. Skin xanthomatosis". After the start of therapy, laboratory parameters improved and the number of eruptive xanthomas decreased. Eruptive xanthomatosis in clinical practice is rare, and requires apprehensive attitude of doctors of various specialties. Timely detection of lipid metabolism disorders allows patients to recommend not only rational measures to prevent the development and progression of atherosclerosis, but also to diagnose the causes of secondary dyslipidemia.
REVIEW
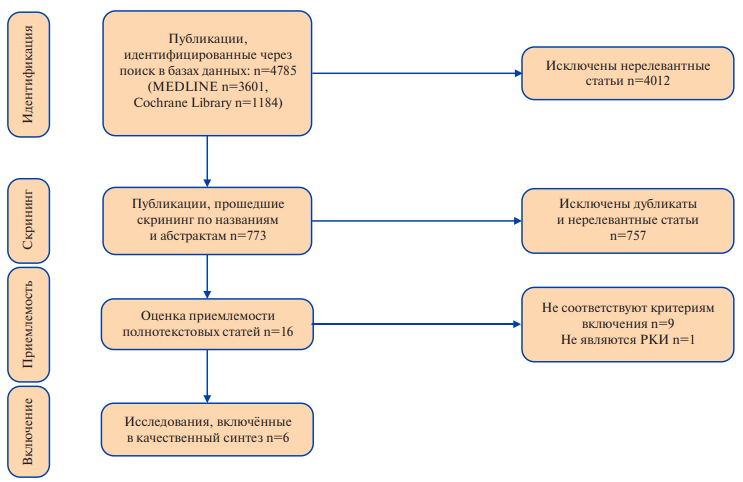
Aim. To collect and analyze currently available clinical studies on the effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) for lowering blood pressure in individuals with normal, high normal blood pressure and hypertension.
Material and methods. The systematic review was prepared according to the PRISMA algorithm with minor modifications. The search algorithm included articles in Russian and English, indexed in the Pubmed/MEDLINE and Cochrane Library databases. The study included studies on the impact of mindfulness interventions on blood pressure levels in individuals aged ≥18 years with an established diagnosis of hypertension, with normal (120-129/80-84 mm Hg) and high normal office blood pressure (130-139/85-89 mm Hg).
Results. A total of 4785 publications were identified and included in the study, of which, after a multistage sampling, including screening of articles, 6 studies were included in a qualitative systematic review.
Conclusion. Qualitative synthesis of the results of clinical studies revealed that the evidence currently available indicates a possible positive effect of mindfulness interventions on blood pressure levels in individuals with normal, high normal blood pressure and hypertension. However, further studies with larger samples and measurement of more primary and secondary endpoints are required.
Gut dysbiosis contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. Firmicutes contain a trimethylamine-producing gene cluster. The aim was to analyze potential role of trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), gut microbiota metabolite, in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and novel therapeutic approaches to reduce TMAO. Some researchers consider TMAO not a mediator but a marker of cardiovascular disease because they have not confirmed associations between elevated TMAO levels, dyslipidemia, C-reactive protein, endotoxin, and cardiovascular mortality. But most studies recognize TMAO as an independent risk factor for serious cardiovascular events. TMAO inhibits reverse cholesterol transport, enhances foam cell formation and platelet hyperreactivity. The adverse effects of TMAO were positively correlated with gut enterotype III. Therapeutic effects on TMAO in atherosclerosis (probiotics, polyphenols, including resveratrol, berberine, trimethylamine lyase inhibitors, phospholipase D inhibitors, reducing the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio, enriching potentially beneficial genera Akkermansia, Lactobacillus, Bacteroides, Roseburia) are attractive for a preventive strategy.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)