EDITORIAL
COVID-19 И БОЛЕЗНИ СИСТЕМЫ КРОВООБРАЩЕНИЯ
- According to the AKTIV registry, about 80% of COVID-19 survivors seek unscheduled medical attention during the year, while about 10% are rehospitalized.
- The most common reasons for seeking unscheduled care are uncontrolled hypertension, decompensated diabetes, destabilization of coronary artery disease.
- The mortality rate of patients after hospital discharge for the year was 3,08%. There were following risk factors for death: age (direct correlation), the levels of hemoglobin (inverse correlation), oxygen saturation (inverse correlation), and aspartate aminotransferase (direct correlation), as well as severe heart failure, prior stroke, cancer, inhospital acute kidney injury.
Aim. To investigate on post-COVID period in patients of the Eurasian region.
Material and methods. A total of 9364 consecutively hospitalized patients were included in ACTIV registry. Enrollment of patients began on June 29, 2020, and was completed on March 30, 2021, corresponding to the first and second waves of the pandemic. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data, computed tomography (CT) results, information about inhospital clinical course and complications of COVID-19 during hospitalization were extracted from electronic health records using a standardized data collection form. The design included follow-up telephone interviews with a standard questionnaire at 3, 6, and 12 months to examine the course of post-COVID period.
Results. According to ACTIV register, 63% of patients after COVID-19 had new adverse symptoms or exacerbations of the existing symptoms lasting for up to 1 year. After hospital discharge, 79,8% of patients sought unscheduled medical attention in the first 3 months, 79,1% at 4-6 months, and 64,8% at 7-12 months. Readmission rate was 11,8% in the first 3 months, 10,9% at 4-6 months, and 10,1% at 7-12 months. The most common reasons for unscheduled treatment in the first 3 months were uncontrolled hypertension, decompensated type 2 diabetes, destabilization of coronary artery disease, gastrointestinal disease, AF episodes, exacerbation of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, decompensated heart failure (HF). The 12-month mortality of COVID-19 survivors after the discharge was 3,08%. Multivariate analysis showed that independent risk factors for fatal outcome were age (direct correlation), the levels of hemoglobin (inverse correlation), oxygen saturation (inverse correlation), and aspartate aminotransferase (direct correlation), as well as class III-IV HF, prior stroke, cancer, inhospital acute kidney injury. Based on these identified risk factors, a nomogram was constructed to determine the 3-month mortality risk after discharge.
Conclusion. Analysis of ACTIV register showed that end of the acute phase of COVID-19 does not imply a complete recovery.
Aim. To study the impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on hospitalization rates, diagnosis, and outcomes of infective endocarditis (IE) with a subanalysis of IE course in combination with COVID-19.
Material and methods. This prospective cohort study included 168 patients with definite or probable IE (DUKE 2015) hospitalized in the V.V. Vinogradov City Clinical Hospital from July 2017 to July 2022. All patients underwent a conventional examination in accordance with current clinical guidelines. We studied clinical, paraclinical and etiological parameters, as well as outcomes.
Two clinical observations of the combination of IE and COVID-19 are presented.
Results. When assessing the local registry of patients with IE, a trend towards an increase in hospitalizations rate of IE in 2021-2022 was shown, with a decrease during the period of long-term lockdowns in Moscow and a subsequent surge after their cancellation. Patients with IE during the COVID-19 pandemic had a more favorable clinical profile, a 2-fold increase in IE diagnosis (due to late hospitalization), frequent detection of Staphylococcus aureus MSSA (32,6%), and frequent surgical treatment (up to 87,6% with a combination of IE and COVID-19), as well as high in-hospital mortality, but without a tendency to increase (30,4%). Clinical observations of IE and COVID-19 combination are presented, which demonstrates the contribution of COVID-19 as the only risk factor for native tricuspid valve IE in a patient without predisposing causes, as well as a factor in the unfavorable prognosis for native aortic valve IE after the addition of COVID-19, which led to lethal outcome.
Conclusion. The present study demonstrates the profile of patients with IE and COVID-19 depending on the epidemiological situation of COVID-19 and the association with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The data obtained make it possible to discuss the potential relationship between COVID-19 and IE. The "endocarditis team" determines the timely implementation of surgery and the absence of an increase in inhospital mortality, regardless of the epidemiological situation.
- During the 12-month follow-up of patients after COVID-19 pneumonia, recovery of right ventricular (RV) function was noted only when assessing longitudinal strain (LS).
- In patients with initial severe lung involvement, LS increases mainly in RV basal segments.
- In patients with initial moderate/mild lung involvement, LS is increased in RV apical segments.
Aim. To study the changes of morphological and functional right ventricular (RV) parameters depending on the severity of coronavirus infection 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia over long-term follow-up.
Material and methods. A total of 200 patients (men, 51,5%, mean age, 51,4±10,9 years) were examined at 2 control visits (3, 12 months after receiving two negative polymerase chain reaction tests). Patients were divided into following groups: group I (n=94) — lung tissue involvement ≥50% according to inhospital chest computed tomography (chest CT), group II (n=106) — lung tissue involvement˂50% according to chest CT.
Results. The groups were comparable in key clinical and functional parameters 3 months after COVID-19 pneumonia. Speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) revealed a significant increase in following global longitudinal strain (LS) parameters: RV free wall endocardial LS (-22,7±3,2% and -24,3±3,8% in group I, p<0,001; -23,2±3,5% and -24,5±3,4% in group II, p><0,001), and RV endocardial LS (-21,0±3,1% and -22,5±3,7% in group I, p><0,001, -21,5±3,2% and -22,6±3,3% in group II, p=0,001 ). Significant increase of segmental endocardial LS was revealed in group I in the basal segments of RV free wall (-26,2±5,1% and -28,1±5,1%, p=0,004) and interventricular septum (IVS) (-16,2 [13,9; 19,5]% and -17,5 [14,6; 21,4]%, p=0,024), IVS middle segment (-20,3±4,1% and -21,5±4,8%, p=0,030), as well as in group II in the apical segments of RV free wall (-21,9±6,7% and -24,4±5,2%, p=0,001) and IVS (-23,7±4,7% and -24,9±4,8%, p=0,014). Conclusion. Recovery of RV function during a 12-month follow-up period in patients with both severe and moderate/mild lung involvement in COVID-19 was detected using the STE method.>˂0,001; -23,2±3,5% and -24,5±3,4% in group II, p˂0,001), and RV endocardial LS (-21,0±3,1% and -22,5±3,7% in group I, p˂0,001, -21,5±3,2% and -22,6±3,3% in group II, p=0,001 ). Significant increase of segmental endocardial LS was revealed in group I in the basal segments of RV free wall (-26,2±5,1% and -28,1±5,1%, p=0,004) and interventricular septum (IVS) (-16,2 [13,9; 19,5]% and -17,5 [14,6; 21,4]%, p=0,024), IVS middle segment (-20,3±4,1% and -21,5±4,8%, p=0,030), as well as in group II in the apical segments of RV free wall (-21,9±6,7% and -24,4±5,2%, p=0,001) and IVS (-23,7±4,7% and -24,9±4,8%, p=0,014).
Conclusion. Recovery of RV function during a 12-month follow-up period in patients with both severe and moderate/mild lung involvement in COVID-19 was detected using the STE method.
What is already known about the subject?
- Patients with established cardiovascular disease or a high risk of cardiovascular events have more severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and higher mortality.
What might this study add?
- Risk factors for heart failure (HF) in patients with COVID-19 have been established. The identified risk factors were ranked according to their significance depending on the odds ratio. In addition, clear quantitative limits (binary points) of decision making for each factor were proposed.
How might this impact on clinical practice?
- The data obtained can be used to create an accessible and cost-effective method for assessing the HF risk in patients with COVID-19 in clinical practice.
Aim. To establish risk factors for heart failure (HF) in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Material and methods. Medical records of 151 patients treated in an infectious disease hospital from November 3, 2020 to February 2, 2021 with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 were retrospectively selected. The collection of clinical, history and laboratory data were carried out by analyzing electronic medical records. We analyzed information on age, sex, body mass index, smoking, and comorbidities. Following laboratory studies were analyzed: complete blood count, biochemical blood tests, coagulation profile, acute phase proteins (C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)), procalcitonin. The diagnosis of HF was confirmed by clinical performance, echocardiography, and elevated levels of the N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). The risk of HF was taken as the endpoint of the study.
Results. The studied sample of patients was divided into two groups depending on HF: the 1st group included 46 patients with HF, the 2nd group — 105 patients without HF. The median age was 66,2 (50-92) years (women, 91 (60,3%)). Laboratory indicators, such as the levels of CRP, LDH, procalcitonin, creatinine, bilirubin, differed significantly from each other, and the median values were higher in patients with HF. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) showed significant intergroup differences: in the group of patients with HF, the median was 4,97% vs 3,62% (p=0,011) in the group of patients without HF. There were following most significant predictors increasing the HF risk: age ≥66 years (odds ratio, 8,038, p<0,001), procalcitonin level, which increases the HF risk in patients by 3,8 times (p><0,001), NLR ≥4,11% (p=0,010), thrombocytopenia ≤220×109/l (p=0,010), history of chronic kidney disease (CKD) (p=0,018). Conclusion. The following predictors of HF were established: age ≥66 years, procalcitonin ≥0,09 ng/ml, NLR ≥4,11%, thrombocytopenia ≤220×109/l, history of CKD, LDH ≥685 U/l and creatinine ≥102 µmol/l, international normalized ratio ≥1,19, QTc interval ≥407,5 ms, bilirubin ≤10,7 µmol/l. It is worth noting that the best accuracy values are demonstrated by the Random Forest algorithm (88,5% on the validation set), but the mathematical model of the neural network turned out to be the most sensitive (90,0% on the validation set). Keywords: novel coronavirus infection, heart failure, prognosis>˂0,001), procalcitonin level, which increases the HF risk in patients by 3,8 times (p˂0,001), NLR ≥4,11% (p=0,010), thrombocytopenia ≤220×109/l (p=0,010), history of chronic kidney disease (CKD) (p=0,018).
Conclusion. The following predictors of HF were established: age ≥66 years, procalcitonin ≥0,09 ng/ml, NLR ≥4,11%, thrombocytopenia ≤220×109/l, history of CKD, LDH ≥685 U/l and creatinine ≥102 µmol/l, international normalized ratio ≥1,19, QTc interval ≥407,5 ms, bilirubin ≤10,7 µmol/l. It is worth noting that the best accuracy values are demonstrated by the Random Forest algorithm (88,5% on the validation set), but the mathematical model of the neural network turned out to be the most sensitive (90,0% on the validation set).
CARDIOSURGERY
The issue of ascending aortic repair with concomitant aortic valve replacement in pa-tients with ascending aortic aneurysm (AscAA) and aortic valve stenosis is still debatable.
Aim. To analyze the dimension changes of the preserved aortic root after simultaneous ascending aorta repair and aortic valve replacement.
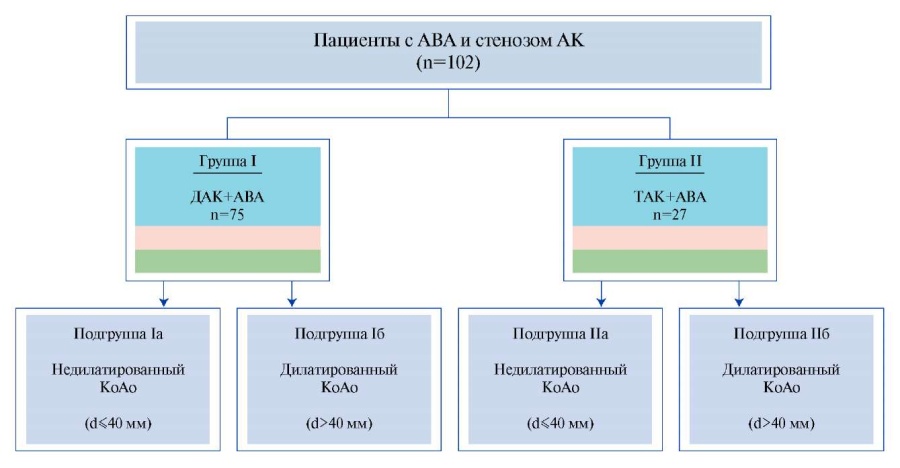
Material and methods. This retrospective study included 102 patients who, from December 2012 to May 2022, underwent simultaneous aortic valve replacement and ascending aorta repair with hemiarch replacement. Patients were divided into 2 following groups based on the aortic valve morphology: group 1 — patients with bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) and AscAA (n=75), group 2 — patients with tricuspid aortic valve (TAV) and AscAA (n=27). Depending on the presence of aortic root dilatation (maximum diameter (d) >40 mm), each of the groups was additionally stratified into 2 more subgroups as follows: patients without aortic root dilatation (d≤40 mm) and patients with its dilatation (d>40 mm). The dynamics of the aortic root diameter was assessed by computed tomography angiography.
Results. The mean follow-up period for patients was 36,2±14,6 months. Survival rate in the BAV+AscAA and TAV+AscAA groups was 96% and 100%, respectively (p=0,380). Freedom from aortic root resurgery was 100% in both study groups. In patients with dilated and non-dilated aortic root of the BAV+AscAA group, an increase in aortic root dimension was noted at a rate of 0,65±0,51 mm/year and 0,32±0,27 mm/year, respectively. In patients of the TAV+AscAA group, a regression in dilated and non-dilated aortic root diameter was observed as follows: 0,93±0,48 mm/year and 0,56±0,43 mm/year, respectively.
Conclusion. In patients with AscAA in combination with BAV stenosis after a singlestep surgical intervention, a weak negative dynamics of non-dilated and dilated aortic root is observed in the mid-term follow-up period. In patients with AscAA and TAV, there is involutive alterations of the aortic root dimension during 3-year follow-up.
- A risk stratification score for complications in patients requiring aortic valve repair has not yet been developed.
- The TAVISCORE program was developed on the basis of an algorithm for determining prognostic coefficients of complications after aortic valve operations.
- The TAVISCORE program is designed to stratify the risk of complications of transcatheter and surgical aortic valve replacement.
Aim. To demonstrate the TAVISCORE program designed to stratify the risk of complications after aortic valve (AV) interventions in patients with reduced ejection fraction.
Material and methods. For the period from 2015-2022 at the Almazov Federal North-West Medical Research Center, 128 interventions on AV were performed for aortic stenosis in patients with reduced ejection fraction as follows: 61 — surgical AV replacement (SAVR), 67 — transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). To create an interactive calculator TAVISCORE (link for free download: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1a3s2MK6Tpk0cIQ_aMB7xe63upEwJsJOh/view?usp=sharing) all patients were combined into one group. For each factor present in the patient, the prognostic coefficient, its contribution to the likelihood of an event in the long-term follow-up period (death, myocardial infarction, stroke), was calculated. The next step, based on the calculations obtained and using the Python 3.10.6 language, was the creation of the TAVISCORE program.
Results. The TAVISCORE was created for the personalized choice of tactics for the treatment of patients with aortic stenosis. It contains 54 risk factors and makes it possible to determine probability of cardiac or non-cardiac events in the long-term follow-up period after SAVR and TAVI. Thus, a tactic with lower probability of a complication can be chosen as optimal in this particular case. Retrospective use of the TAVISCORE after surgery can identify patients at high risk of complications, which will allow them to be selected for more thorough management and more frequent screening.
Conclusion. The TAVISCORE can be used by a multidisciplinary consensus to select the treatment tactics and stratify the risk of complications after different AV replacement variants in patients with a reduced ejection fraction. Further prospective testing of this program is required.
- Russian guidelines and standards do not answer many controversial issues related to carotid endarterectomy.
- Carotid glomus preservation during carotid endarterectomy reduces the number of complications.
- An online risk stratification calculator CarotidScore.ru can be used to select a treatment option for patients with carotid stenosis.
This literature review covers the publications of Russian vascular surgeons in recent years and deals with debatable issues of carotid surgery, including: 1. What is the best technique for carotid endarterectomy (CEA)? 2. Why does restenosis of the internal carotid artery (ICA) develop and how to eliminate it? 3. How to operate on bilateral ICA stenosis? 4. Should carotid glomus be preserved? 5. Is CEA safe in the acute phase of cerebrovascular accident (CVA)? 6. Is CEA safe in elderly patients? 7. How to operate on patients with combined internal carotid and coronary artery involvement? The evidence presented in this publication makes it possible to draw the following conclusions: 1. When choosing a CEA technique, the classical technique with patch angioplasty should be avoided due to the high risk of ICA restenosis. 2. To eliminate ICA restenosis, carotid angioplasty with stenting (CAS) should be used. When performing primary CEA with ICA transposition over the hypoglossal nerve, reCEA can be used 3. In the absence of contraindications, bilateral ICA stenosis can be operated at the same time using CEA. 4. CEA with carotid glomus preservation is the operation of choice in the treatment of patients with hemodynamically significant ICA stenosis due to the elimination of the risks of postoperative hypertension and the formation of hemorrhagic transformation. 5. If there are indications for cerebral revascularization in the most acute period of stroke, CEA should be abandoned in favor of CAS. 6. In old age, CAS is the safest treatment strategy. 7. In the presence of a combined ICA and coronary involvement, the choice of treatment tactics should be carried out only by a multidisciplinary commission, taking into account the risk stratification of adverse cardiovascular events.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY
- The increase in therapeutic options for cancer treatment has determined the need for relapse-free survival.
- Prevention of heart failure in patients with hematologic cancer against the background of various treatment regimens should be a priority.
- The use of thiotriazoline can prevent and slow down cardiovascular disease continuum, leading to the appearance of heart failure.
Aim. To evaluate the effectiveness of morpholinium-methyl-triazolyl-thioacetate (thiotriazoline) as a cardioprotector in patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas who received chemotherapy with the inclusion of anthracyclines.
Material and methods. Fifty patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas were examined on the background of antitumor therapy. The patients were divided into 2 following groups: group 1 (n=27) — standard chemotherapy; group 2 (n=23) — thiotriazoline as a cardioprotector. The quality of life was assessed using the SF-36 questionnaire; the level of troponin I and the natriuretic peptide NT-proBNP was determined; an electrocardiography and echocardiography were performed.
Results. In the course of the study, significant differences (p<0,05) were found in following parameters: the severity of dyspnea and lower limb edema, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, creatine phosphokinase, troponin I level, NT-proBNP, corrected QT interval, end systolic volume, left ventricular ejection fraction, E/A ratio. The results obtained indicate the clinical and paraclinical advantage of thiotriazoline and reflect its cardioprotective effect. Conclusion. The use of thiotriazoline makes it possible to prevent and slow down the cardiovascular disease continuum, leading to the development of heart failure or decompensation that exists in this category of patients. Keywords: cardio-oncology, thiotriazoline, heart failure, anthracyclines, cardiotoxicity>˂0,05) were found in following parameters: the severity of dyspnea and lower limb edema, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, creatine phosphokinase, troponin I level, NT-proBNP, corrected QT interval, end systolic volume, left ventricular ejection fraction, E/A ratio. The results obtained indicate the clinical and paraclinical advantage of thiotriazoline and reflect its cardioprotective effect.
Conclusion. The use of thiotriazoline makes it possible to prevent and slow down the cardiovascular disease continuum, leading to the development of heart failure or decompensation that exists in this category of patients.
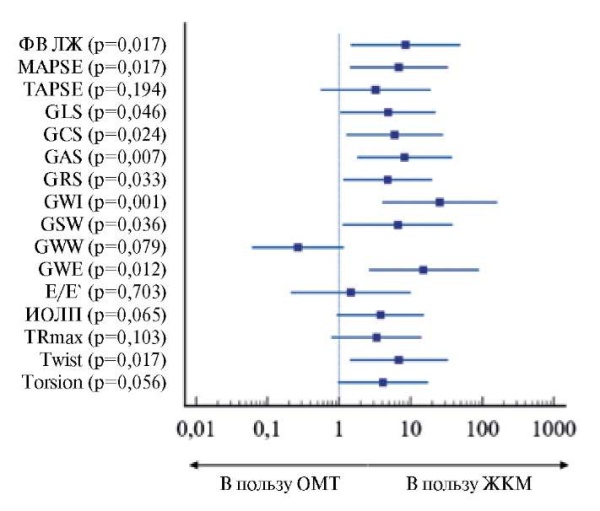
Aim. To assess non-invasive parameters of left ventricular (LV) myocardial work in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (CHrEF) and iron deficiency (ID) after ferric carboxymaltose (FCM) therapy.
Material and methods. There were following inclusion criteria: LV ejection fraction (EF) ≤40%; body >70 kg, receiving best medical therapy (BMT) in recommended doses in accordance with the guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology and the Russian Society of Cardiology. Median age was 67±11,7 years (men, 83%), while median LVEF and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide was 29% and 315 ng/ml, respectively. Patients were randomized by the envelope method. The first group consisted of 19 patients who received therapy with intravenous FCM 1500 mg in 2 injections with an interval of one week between injections in addition to BMT. The control group consisted of 16 patients who received BMT without FCM. All patients underwent a standard echocardiography, and non-invasive LV myocardial work was assessed immediately before inclusion in the study and after 3 months.
Results. In the first group of patients receiving FCM therapy, an increase in LVEF (29,1±10,3 vs 35,4±11,1; p=0,001), mitral annular plane systolic excursion (1,2 (1;1,6 ) vs 1,5 (1,3;1,9), p=0,001), LV global longitudinal strain (-7 (-5;-8) vs -8 (-6;-11), p=0,007) and non-invasive indicators of myocardial work (global work index (826±314 vs 1041±354), p=0,0001; global constructive work (1173±388 vs 1435±405), p=0,0001; global work efficiency (85 (82;87) vs 86 (82;88), p=0,017)). There were no significant changes in the studied parameters in the BMT group.
Conclusion. Patients with HFrEF and ID treated with FCM showed a significant increase in LV systolic function, including non-invasive myocardial work parameters, compared with the control group.
METHODS OF STUDY
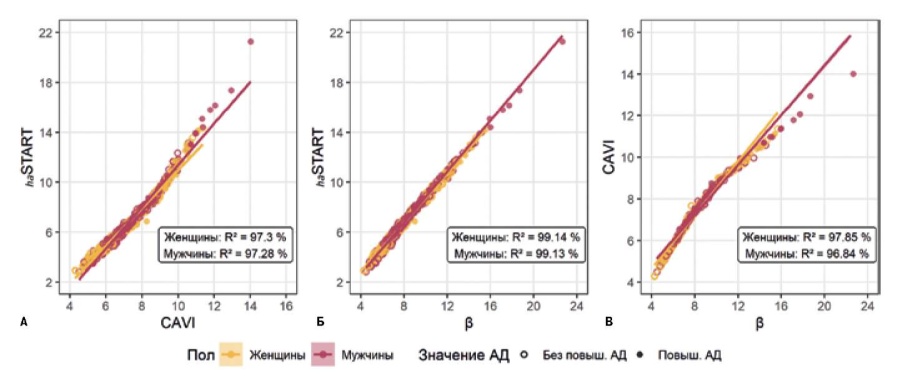
- Novel solution in the assessment of arterial stiffness is START index.
- Comparison of the novel START vascular stiffness index with the CAVI index.
- The START vascular stiffness index significantly correlates with the CAVI index.
Aim. To compare the cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) and the novel START vascular stiffness index and assess their values and correlations with clinical parameters.
Material and methods. This multicenter study included 928 (403 men and 525 women) randomly selected patients, aged 18 to 89 years (mean age, 41±15,8 years). Inclusion criteria were age over 18 years. There were following exclusion criteria: mental disorder, severe somatic diseases and cancer, contraindications for volume sphygmography using the Fukuda Denshi VS-1500 VaSera system, no patient consent, ankle-brachial index <1,0 and >1,3. Further, according to the main parameters obtained using volum sphygmography, a novel START index was calculated. Comparison of index values and analysis of their correlation with clinical indicators, such as age, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, pulse pressure (PP), body mass index and heart rate (HR), were carried out using simple and multiple linear regression, dispersion analysis, calculation of the Pearson coefficient (r), in the software environment R version 4.0.2.
Results. Statistical analysis revealed a high correlation between START and CAVI indices (r=0,986, p<0,001). The values of both indices increase significantly with age (ANOVA p><0,001). Both START and CAVI correlate with all studied clinical parameters. However, in men, there was no relationship of the indices with PP and HR (p>0,05). According to multiple linear regression, the relationship between diastolic blood pressure at the age of 30-60 years and PP at the age of 18-40 years with the START index is more pronounced than with the CAVI index. However, further study of the mathematical model did not reveal a significant difference in the index values for groups with and without high blood pressure.
Conclusion. The START vascular stiffness index significantly correlates with the CAVI index, showing no significant differences from CAVI in quantitative relationships with blood pressure, body mass index, heart rate, and sex in various subgroups of the subjects.
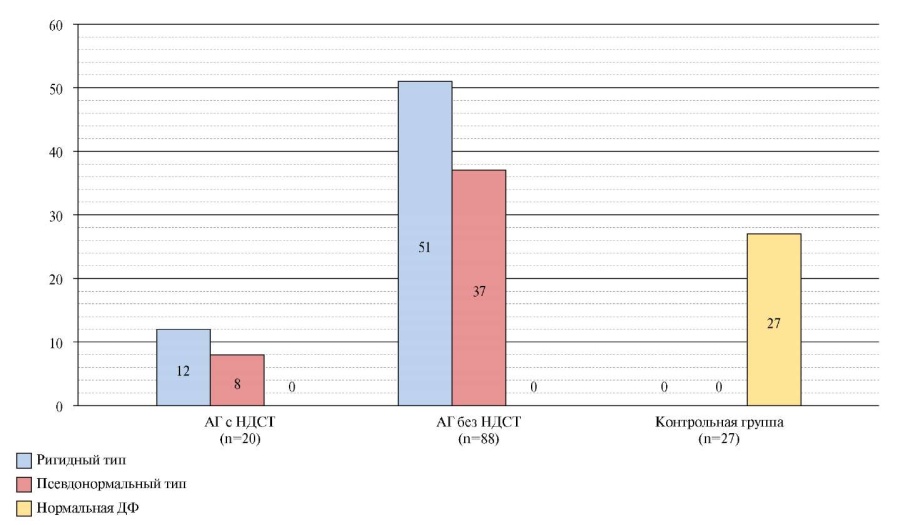
- In late postmenopausal women with undifferentiated connective tissue disease and hypertension, the most common were diastolic function of rigid type.
- Despite the similarity of clinical performance and occurrence of various diastolic dysfunction types, hypertensive patients with undifferentiated connective tissue disease had a more pronounced impairment of left ventricular diastolic function compared to patients with only hypertension.
- The performed analysis indicates a significant contribution of undifferentiated connective tissue disease associated with hypertension to the development of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction.
Aim. To assess myocardial diastolic function (DF) in late postmenopausal women with undifferentiated connective tissue disease (UCTD) and hypertension (HTN).
Material and methods. This cross-sectional study included 135 postmenopausal women, the median age of which was 68 years (65÷70,5 years). The anamnesis was collected using a standardized questionnaire. Verification of UCTD was carried out according to clinical guidelines. All patients underwent standard transthoracic echocardiography. The assessment of left ventricular (LV) DF was carried out according to the transmitral flow. LV diastolic dysfunction (DD) was classified into three types: rigid, pseudonormal, and restrictive. Statistical processing was carried out in the STATISTICA 13.0 environment. The measure of data averaging is the median, the measure of dispersion is 25%÷75%. The significance of differences was assessed using the Mann-Whitney test. Differences were considered significant at p˂0,05.
Results. Group 1 — 20 (14,8%) patients with verified UCTD and HTN, group 2 — 88 (65,2%) patients with HTN without UCTD, control group — 23 (30%) patients without HTN and UCTD. There were no differences in age, duration of postmenopause and body mass index between the groups. In the first group, a significant decrease in the ratio of peak early to late diastolic LV filling velocity was revealed (p˂0,01). A significant increase in left ventricular end-systolic wall stress revealed in group 1. In 108 (100%) patients, LVDD was detected; among the patients of the control group, DD was not detected. In 8 (40%) patients in group 1, a pseudo-normal type of DD was detected, while in 12 out of 20 patients (60%) — rigid type of DD. When assessing DF in patients of group 2, a significant decrease was found in the ratio of peak early to late diastolic LV filling velocity, a significant increase in LV end-diastolic wall stress and end-diastolic pressure. In 2 out of 3 (57,80%) patients of group 2, DD of the rigid type was detected, while pseudonormal type — in 32,2% of patients in this group. Group 2 patients had a significant decrease in the early diastolic mitral annular velocity (p˂0,01).
Conclusion. The analysis of myocardial echocardiographic characteristics indicates a significant contribution of HTN-associated UCTD to the development of LVDD in postmenopausal women.
- The role of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) as a cardiovascular marker in an association with resistant hypertension was considered.
- Increased release of brain natriuretic peptide is a compensatory response aimed at lowering blood pressure and adapting the body; so the use of NT-proBNP may be promising for determining the prognosis of resistant hypertension.
- According to recent clinical trials, the use of dual neprilysin inhibition and sacubitril/valsartan seems promising to reduce the NT-proBNP level and effectively control blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension.
Modern medicine has successfully used the N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) as a biomarker for many cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). According to a number of studies, NT-proBNP may also play a role in the development of resistant hypertension (RH), but the existing work addresses this issue only indirectly. In turn, RH causes serious damage to the economic and social spheres, worsening the quality of life of patients. Thus, the complexity of verification and treatment of RH, the inconsistency of the described associations of NT-proBNP and RH makes this topic more relevant than ever.
CLINICAL GUIDELINES
Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology.
(ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)