ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Aim. In 2021, the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) were published, where a new SCORE2 CVD risk assessment model was introduced. In our work, we compared approaches to determine the indications for initiating lipid-lowering therapy in the Russian population aged 25-64 years according to the guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of lipid metabolism disorders of the Russian National Atherosclerosis Society (2020) and ESC guidelines for CVD prevention (2021).
Material and methods. The ESSE-RF epidemiological study was conducted in 12 Russian regions. All participants signed informed consent and completed approved questionnaires. We performed anthropometric and blood pressure (BP) measurements, as well as fasting blood sampling. In total, 20665 people aged 25-64 years were examined. The analysis included data from 19546 respondents (women, 12325 (63,1%)).
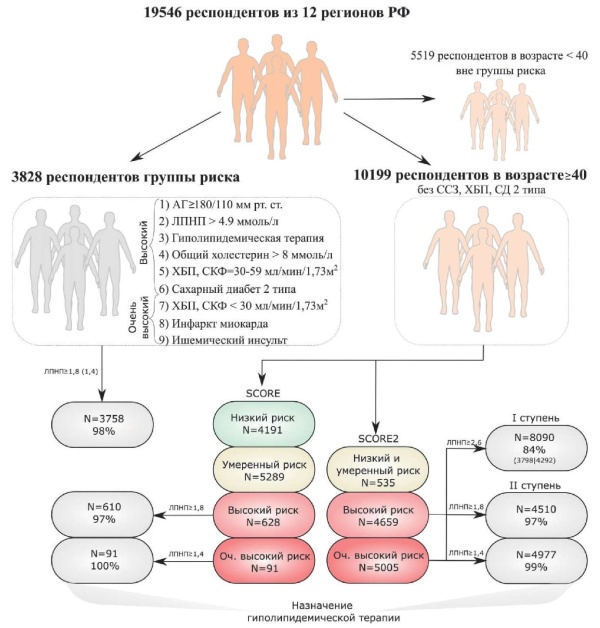
Results. Of the 19546 participants, 3828 (19,6%) were classified as high or very high CV risk based on the 9 criteria: BP ≥180/110 mm Hg, total cholesterol >8,0 mmol/l, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) >4,9 mmol/l, lipid-lowering therapy, chronic kidney disease (CKD) with glomerular filtration rate <60 ml/min/1,73 m2, type 2 diabetes, previous stroke and/or myocardial infarction. Of 3828 people, lipidlowering therapy was indicated in 3758 (98%) (criteria for LDL ≥1,8 mmol/l and LDL ≥1,4 mmol/l, respectively, high and very high risk). In addition, 5519 individuals aged <40 years were excluded from further analysis due to the lower age threshold of models. For 10199 participants aged >40 years without established CVD, diabetes, CKD, cardiovascular risk stratification was performed according to the SCORE and SCORE2. Of them, according to the Russian National Atherosclerosis Society (2020) and ESC 2021 guidelines, lipid-lowering therapy was indicated for 701 and 9487 participants, respectively.
Conclusion. Using the new approach proposed by the ESC in 2021, the number of patients aged 40-64 years without CVD, diabetes and CKD with indications for lipidlowering therapy for primary prevention in Russia increases by 14 times compared with the 2020 Russian National Atherosclerosis Society guidelines.
Aim. To study the association between depression and metabolic cardiovascular risk factors, hypertension (HTN) and its control in a random sample of Tyumen Oblast population of men and women aged 25-64 years.
Material and methods. The study object was a random sample of the population of the Tyumen and the Tyumen Oblast aged 25-64 years, examined as part of the ESSE-RF epidemiological study. The study included 1658 participants. Among them, 30,3% (n=503) were men, while 69,7% (n=1155) — women. Mean age was 48,9±11,4 years. The prevalence of metabolic risk factors (hyperlipidemia, carbohydrate metabolism disorder, obesity), hypertension and the likelihood of its control in men and women with different levels of depressive disorders diagnosed using the HADS scale were assessed.
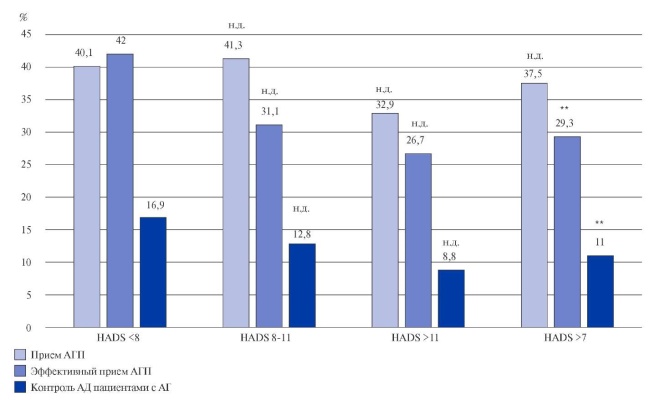
Results. Compared with participants without depression, persons with psychological disorders were significantly more likely to have HTN (55,5% vs 47,6%, p<0,01), elevated levels of total cholesterol (TC) (63,9% vs 54,0%, p<0,01) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL) (66,7% vs 60,3%, p<0,05), carbohydrate metabolism disorders (8,3% vs 5,2% p<0,05), obesity (49,2% vs 37,7%, p<0,01). Significantly more often hypertensive subjects without depression took antihypertensive drugs effectively (odds ratio (OR) — 1,747, 95% confidence interval (CI), 1,001-3,053) and controlled blood pressure (OR — 1,533, 95% CI, 1,05-2,36). There was no association between the use of antihypertensives and the level of depressive disorders. Among women with depression (HADS>7), dyslipidemia (65,5% vs 57,4% for TC, p<0,05; 71,0% vs 62,9% for LDL, p<0,05), carbohydrate metabolism disorders (10,1% vs 5,2%, p<0,01), obesity (53,3% vs 43,2%, p<0,01), HTN (60,6% vs 45,6%, p<0,01) were more common. Men with clinical depression were more likely to have HTN (69,0% vs 47,7%, p<0,05), with a high level of depression — hyperlipidemia (58,9% vs 46,7% for TC, p<0,05; 67,1% vs 53,9% for LDL, p<0,05). Women with elevated depression levels were less likely to take antihypertensive drugs (30% vs 49,4%, p<0,01) and control hypertension (13,8% vs 21,2%, p<0,05).
Conclusion. The data obtained confirm the association of depressive disorders with metabolic risk factors and the likelihood of HTN control, which is especially significant among women.
Aim. To study the prevalence of carbohydrate metabolism disorders in a repre - sentative sample of the working-age population of the Krasnoyarsk Krai aged 25-64 years and to identify the association of these disorders with cardiovascular pathology.
Material and methods. A random representative sample within the all-Russian epidemiological study ESSE-RF included 1603 residents of the Krasnoyarsk Krai aged 25 to 64 years. The gradation of carbohydrate metabolism disorders was carried out on the basis of fasting plasma glucose level in accordance with the criteria of the American Diabetes Association (ADA). Hypertension (HTN) was defined as office BP ≥140/90 mm Hg or an indication of previous use of antihypertensive drugs. The presence of myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, coronary artery disease (CAD) was detected by anamnesis collection. Statistical processing was carried out using IBM SPSS v 22 and Microsoft Excel 2021 programs. When comparing differences by sex, age, level of education, and type of residence, differences was assessed by chi-squared test and considered significant at p≤0,05.
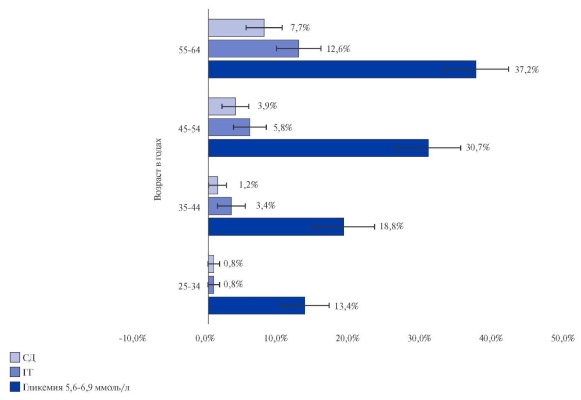
Results. In total representative sample of Krasnoyarsk Krai population, 3,6% of participants indicated prior diabetes, while its prevalence naturally increased with age. The detection rate of fasting glucose of 5,6-6,9 mmol/l among individuals without prior diabetes (impaired fasting glycemia (IFG), as one of the criteria for prediabetes, according to ADA guidelines) was 22,5% of the general population. Fasting hyperglycemia (HG) ≥7,0 mmol/l without prior diabetes was registered in 3,8%. This figure can be roughly considered as the proportion of people with newly diagnosed diabetes. IFG and HG were significantly more common among men, as well as among those with primary and secondary education compared with higher education. In rural residents, all types of carbohydrate metabolism disorders were more common than in urban ones. Compared with the normoglycemic group, the presence of prior diabetes, IFG and GH was associated with a significantly higher prevalence of hypertension, CAD and stroke.
Conclusion. The prevalence of IFG, fasting HG ≥7,0 mmol/l and diagnosed diabetes in a representative sample of the Krasnoyarsk Krai aged 25-64 years exceeds the national average, although it is consistent with the data of a number of other Siberian regions. The prevalence of both carbohydrate metabolism disorders in general and the percentage of possible undiagnosed diabetes increases with age. At the same time, there are more such individuals among those with primary and secondary education, as well as among rural residents. The approximate proportion of undiagnosed diabetes in the study population reaches 50%. Timely detection of carbohydrate metabolism disorders can contribute to the earlier implementation of active preventive measures and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
Aim. To study the contribution of behavioral and social risk factors to the development of metabolically unhealthy obesity (MUO) according to a prospective study in the Russian population.
Material and methods. From the HAPPIE project, 3197 people aged 45-69 years with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m2 were selected, who had all the necessary parameters for obesity phenotype determination. The prospective analysis included the first (2003-2005) and third screenings (2015-2017). A subsample was formed (n=1275; 276 men — 22%, 999 women — 78%). The mean follow-up period was 12,4 years. IDF criteria (2005) were taken for analysis.
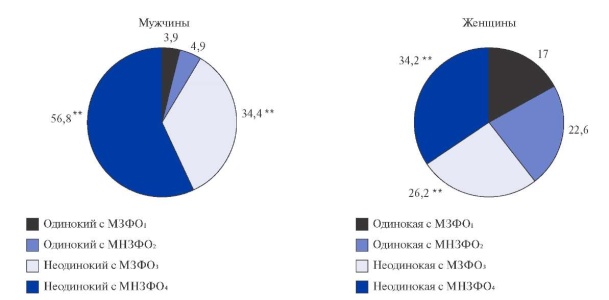
Results. Men with a metabolically healthy obesity (MHO) phenotype most often have a secondary and higher education, while women with MHO — vocational and secondary education. In women, secondary education was most often noted. Among persons with obesity, both men and women are more often not single, while having MUO as follows: 56,8% and 34,2%, respectively. Men and women have a low-intensity activity, regardless of the obesity phenotype. The prevalence of smoking in the present time does not differ in the MHO and MUO groups. Metabolically healthy women consume more alcohol than those with MUO. In men with sedentary lifestyle and fasting hyperglycemia, the risk of MUO over a 12-year follow-up period was significantly higher. In women, the risk of conversion from MHO to MUO is increased when blood pressure (BP) is ≥130/85 mmHg.
Conclusion. In the Russian population, the risk of MUO in men increases with a level of physical activity <3 h/week and a blood glucose level ≥6,1 mmol/l; in women, only BP ≥130/85 mm Hg contributes to the development of MUO.
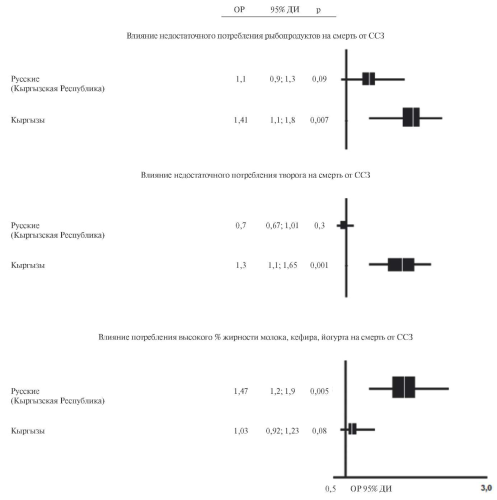
Aim. To assess the 7-year survival rate and the association of risk factors (RFs) with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among rural residents in Russia and the Kyrgyz Republic, as well as to analyze ethnic characteristics (according to the Interepid study).
Material and methods. This study was carried out within the Interepid international project, which included a cross-sectional epidemiological study of the prevalence of major noncommunicable diseases and their risk factors in 2011- 2012, and a prospective stage among rural residents of two countries (Russia, the Kyrgyz Republic). In 2019, the vital status of respondents was reassessed (7 years after the initial examination), and endpoints were collected, including all-cause and cardiovascular deaths.
Results. A significant similarity of rural residents of the analyzed regions in relation to the factors associated with mortality was revealed. Smoking in men, obesity in women, and hypertension in both sexes were associated with an increased death risk. Country differences were found only in relation to low physical activity and dietary habits. Ethnic developments in the population of the Kyrgyz Republic also concerned only the contribution of food habits.
Conclusion. The results obtained are important for planning, implementing and evaluating the effectiveness of public health promotion programs. It is also necessary to develop differentiated treatment and prevention measures in the Russian population and among the indigenous inhabitants of the Kyrgyz Republic, including taking into account the prevalence of CVD risk factors and their impact on life prognosis.
Aim. To determine the dynamics and impact of sleep duration in 2003-2018 on the risk of myocardial infarction (MI) in an open population aged 45-64 years in Novosibirsk.
Material and methods. The study included representative samples of the population aged 45-64 years, obtained as part of the screening IV in 2003-2005 (men, 576; mean age, 54,23±0,2 years; response rate, 61%; women, 1074; mean age, 54,27+0,2 years; response rate, 72%) and screening VI in 2015-2018 (men, n=275; mean age, 49±0,4 years; response, 72%; women, n=390; mean age, 45±0,4 years; response rate, 75%). Screenings were carried out according to the standard protocol of the WHO MONICA-psychosocial Program (MOPSY). The Jenkins Questionnaire was used to assess sleep duration and disturbances.
Results. For the period from 2003-2005 to 2015-2018, we revealed decrease in the number of following people: with 7 hours of sleep at night from 44,9% to 31,9%; with 8 hours of sleep from 28,5% to 24,4%. In addition, the number of participants with ≤5 hours of sleep increased from 4,9% to 9,9%, while those with ≤6 hours — from 16,2% to 27,2%, as well as the number of people sleeping 9 hours a day (from 3,7% to 5,4%). In 2003-2005, among the population in the age group of 55- 64 years, 7-hour sleep was observed more often (45б1%); 6-hour sleep prevailed in the group of people aged 45-54 (18,9%). There were no significant differences between the duration of sleep and the age group according to screening VI in 2015- 2018. Among men, 6-hour sleep were observed more often (38.4%), and among women — 7 hours (37,3%). Those who sleep 7 hours a night were more likely to consider their sleep “good” (35,3%) in 2015-2018. In a population of 45-64 years old, over a 14-year period, the risk of MI was higher as follows: 1. in men with 5-6 hours of sleep than with 7-8 hours of sleep at night by 1,689 times (95% confidence interval (CI), 1,124-2,537 p<0,012); in men aged 45-54 years by 2,416 times (95% CI, 1,311-4,452; p<0,005), respectively; 2. in women with 5-6 hours of sleep by 1,591 times (95% CI, 1,058-2,392; p<0,026) compared with 7-8-hour duration of sleep. In the 45-54 year group, the risk of MI was higher among women with 9-10 hours of sleep a night by 4,44 times (95% CI, 2,726-20,309; p<0,0001) compared with women who had 7-8 hours of sleep at night.
Conclusion. We revealed that over the period of 2003-2018, the duration of night sleep of 7-8 hours among the population aged 45-64 years (without cardiovascular diseases) decreased both among men and women. At the same time, the “good” quality of sleep was more often found in people with 7-hour sleep. It was determined that short sleep duration was associated with MI among men and women, and long sleep duration turned out to be a risk factor for MI for women in the group of 45-54 years.
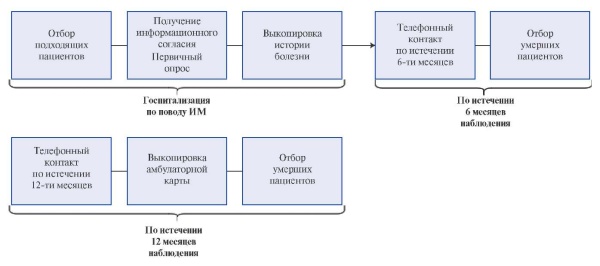
Aim. To evaluate a 1-year outpatient management of patients after myocardial infarction (MI) aged <75 years according to a Russian multicenter study, as well as to assess compliance with recommendations on the frequency of visiting specialists and the performance of diagnostic examinations.
Material and methods. This observational study includes a representative sample of MI patients admitted to 16 clinics in 13 Russian regions. Patients with MI who were alive the next day after hospitalization aged <75 years were included in the study according to a special randomization scheme. When writing this article, the data from questionnaires of 6 and 12 months after hospitalization were analyzed: the number of visits to doctors of various specialties, hospitalizations, the number of diagnostic procedures performed (electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography and surgical interventions (percutaneous coronary intervention, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)). The study included a cohort of 723 patients who participated in the survey both 6 and 12 months after hospitalization (67% — patients discharged from the hospital), of which 562 (77,7%) were men and 161 (22,3%) — women. Statistical processing was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics v.25 software for Windows.
Results. In the first 6 months after MI, 218 (38,8%) men and 62 (38,5%) women visited the cardiologist the recommended number of times. However, 151 (20,9%) people were not monitored by a cardiologist in the first six months. There was a significant increase in the number of people not observed during the second 6 months up to 209 (28,9%) people (p<0,01). Of the 689 interviewed patients, 210 (30,5%) people visited the therapist the recommended number of times in the first six months, while in the second 6 months — 402 (58,4%) patients. It is also reasonable to single out patients who were not monitored by either a cardiologist or a general practitioner into a separate group. In the first 6 months, the total number of unobserved patients was 68 (7,5%), while in the second six months this number increased to 189 (25,9%). The recommended number of ECGs (4 or more times) was performed in 316 (40,4%) patients, while ECG was not performed in 35 (4,5%) patients. Echocardiography 2 or more times was performed in 194 (25,4%) patients. The procedure was not performed in 167 (21,9%) patients. During the first 6 months, 170 (22%) people were hospitalized, while 156 (20,2%) — during the second half of the year. Angioplasty during the first 12 months after discharge from the hospital was performed in 183 (23,1%) patients, CABG — in 41 (5,2%) patients without age and sex differences.
Conclusion. Outpatient management of patients aged <75 years 12 months after MI characterized by low compliance with recommendations on the number of cardiologist consultations and diagnostic procedures, which may adversely affect adherence to the recommended drug treatment and lead to a worse prognosis.
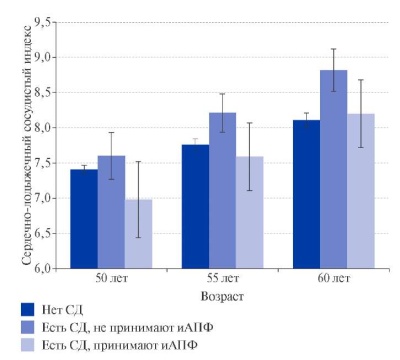
Aim. To examine associations of cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) with classical, behavioral and social risk factors (RFs) of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in adult population.
Material and methods. The study included 1365 people (women, 59%) from a representative sample aged 25-64 years (ESSE-RF), who underwent standard cardiology screening and volume sphygmography (VaSera-1500). All respondents signed an informed consent to participate in the study. The analysis included blocks of classical, social and behavioral risk factors for CVD. A linear model was used to identify associations. An error rate of <5% was considered significant.
Results. Age, sex, systolic blood pressure (SBP), triglycerides were associated with higher CAVI values, and body mass index (BMI) was associated with lower values, respectively. After 45 years, a direct association with heart rate (HR) became increasingly important, while after 50 years — with diabetes and the intake of beta-blockers, while the association between diabetes and CAVI was observed only among individuals not taking angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. A direct association was found with high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) in men, and an inverse association with diuretics in women, respectively. A sedentary work in combination with a history of bronchitis or with positive family history for CVD showed a direct relationship, while a sufficient physical activity (PA) showed an inverse relationship with the studied indicator, but only among people with belowaverage income.
Conclusion. According to the data obtained, in addition to age and sex, the following risk factors made a significant contribution to CAVI parameters in the examined population: BMI, SBP, triglycerides, diabetes, HR, intake of betablockers, diuretics, ACE inhibitors; hsCRP, PA. The unfavorable role of betablockers, high HR, diabetes, sedentary work, chronic lung pathology, hereditary burden, as well as the protective role of ACE inhibitors, diuretics and intense PA in relation to arterial stiffness in the working-age population has been shown. Additional studies are needed to determine the nature of a number of associations. The results obtained may contribute to the study of CAVI role in risk stratification and further development of methodological approaches to CVD prevention.
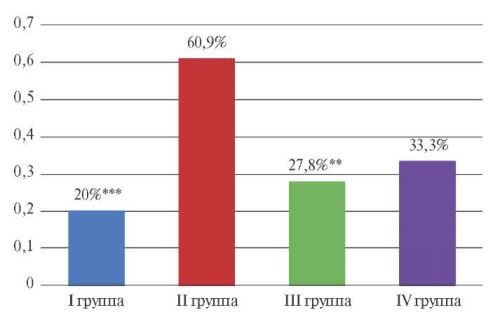
Aim. To evaluate the impact of training primary care physicians about the principles of smoking treatment on the rate of successful quitting among their patients.
Material and methods. Within the regional program on cardiovascular prevention among men aged 45-55 years, a study was made on the effectiveness of an educational seminar for primary care physicians (clustered quasi-experimental study). The main group consisted of 70 physicians (subjects of intervention) who underwent face-to-face training at a 3-hour interactive seminar on the principles of behavioral and drug treatment of smoking patients. In the following year, they consulted 423 smokers (subjects of analysis). The comparison group was represented by 174 doctors trained with extramural program who consulted 654 smokers. The doctors of both groups were provided with methodological and informational support in the form of short guides and brochures for patients. The main outcome studied was smoking cessation in patients one year after physician training. The comparison of outcomes was carried out taking into account the cluster structure of data using hierarchical regression. The initial imbalance of comparison groups in history of smoking, quit attempts, as well as level of alcohol consumption was corrected at the analysis stage.
Results. In total, 12,6% of patients in the observed cohort quit smoking after one year, which was significantly higher than the common successful self-quit rate (3-5%). The likelihood of quitting smoking was strongly influenced by a particular doctor (ICC=0,326). Face-to-face interactive training of physicians significantly increased the probability of successful refusal in patients compared with distance learning (adjusted hazard ratio (HR) =4,8; odds ratio (OR) =5,3, 95% confidence interval (CI), 2,7-10,6, p<0,001). The likelihood of successful withdrawals among patients among primary care physicians was much higher than among health center patients (adjusted HR=4,5; adjusted OR, 5, 95% CI, 1,2-20,6, p=0,027).
Conclusion. Education of primary care physicians in the principles of smoking treatment, combined with the provision of information materials for patients, significantly increases the success rate among motivated smokers. At the same time, a face-to-face interactive seminar is much more effective than distance learning. General practitioners demonstrate the best professional productivity, regardless of the training form.
Aim. To establish the correlations of the soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2 protein (sST2) and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) with some clinical and paraclinical characteristics of patients with heart failure (HF).
Material and methods. The study included 130 patients with HF (men — 54, women — 76, mean age, 64,3±8,3 years) from the regional registry of HF patients in the Voronezh Oblast. All patients underwent echocardiography and general clinical investigations. In addition, the serum levels of sST2 and NT-proBNP were determined and their correlations with other parameters were studied.
Results. The blood level of sST2 in HF patients was 339,8 [266;405] pg/ml. In the study sample of patients with HF, sST2 levels correlated with right atrial (r=0,49) and right ventricular (r=0,32) sizes, left ventricular end-diastolic dimension (r=0,34) and volume (r=0,33), left ventricular early diastolic filling rate (r=-0,35), blood calcium level (r=-0,55) and functional class of exertional angina (r=-0,37).
Conclusion. The data obtained may indicate a pathogenetic relationship between sST2 and systolic and diastolic dysfunction of the left ventricle and right heart.
Aim. To study the interdependence of spousal body mass and influence of spouse overweight on the death risk according to the 27-year cohort prospective study.
Material and methods. We examined a random household sample (n=1546; married couples, 427). Overweight frequency among spouses was studied on the first stage of the study (1988-1991). In 2002-2005 (stage II), the examination was repeated and overweight dynamics were studied. In 2015 (stage III), we analyze mortality rates and significance of overweight and spousal overweight for the mortality risk formation. Overweight was detected in people with body mass index ≥25 kg/m2. Two hundred deaths were recorded during 27-year follow-up. Vital status was established for 97% of observed persons.
Results. Overweight was detected in 61,1% of men who lived with overweight wife and in 45% of men whose wife had normal body mass (p<0,01). Overweight was diagnosed more often in women whose husband also had overweight comparing with women who lived with normal weight husband (76,2% vs 61,7%; p<0,001). The risk of overweight formation among individuals whose spouse’s body mass increased from norm to overweight was in 3,04 times higher than in persons whose spouse had a stable normal body mass and in 2,2 times higher than in participants whose spouse had overweight on study stages I and II. Relative risk of mortality in men who lived with overweight wife was 2,07.
Conclusion. 1) We found the body mass concordance in spouses. 2) The average body mass index in men and women who lived with overweight spouse is higher than in men and women whose spouse had a normal body mass. 3) Interdependence of spousal body mass was revealed in dynamics. 4) Spousal overweight is an independent predictor of premature mortality in men.
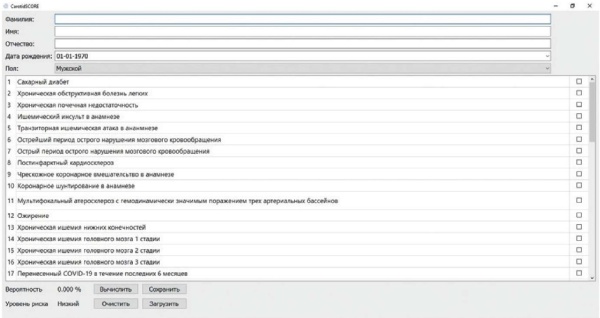
Aim. To demonstrate the first Russian computer program (carotidscore.ru) for risk stratification of postoperative complications of carotid endarterectomy (CE).
Material and methods. The present study is based on the analysis of a multicenter Russian database including 25812 patients after CE operated on from January 1, 2010 to April 1, 2022. The following types of CE were implemented: conventional CE with patch angioplasty — 6814 patients; eversion CE — 18998 patients. Following postoperative complications were assessed during the study: death, stroke, myocardial infarction (MI), composite endpoint (death + stroke + MI).
Results. During inhospital postoperative period, 0,18% of participants died, while 0,14% had MI, 0,35% — stroke. The composite endpoint was recorded in 0,68%. For each factor present in patients, a predictive coefficient was estimated. The predictive coefficient was considered as a numerical parameter reflecting the strength of the effect of each factor on the development of postoperative complications. Based on this equation, predictive coefficients were calculated for each factor present in patients in our study. The total contribution of these factors was reflected as a percentage and denoted the risk of postoperative complications with a minimum of 0% and a maximum of 100%. On the basis of obtained calculations, a CarotidSCORE program was created. Its graphical interface is based on the QT framework. It is possible not only to estimate the risk of a complication, but also to save all data about a patient in JSON format. The CarotidSCORE program contains 47 patient parameters, including clinical, demographic, anamnestic and angiographic characteristics. It makes it possible to choose one of the four CE types, which will provide an accurate stratification of the complication risk for each of them.
Conclusion. CarotidSCORE (carotidscore.ru) may determine the probability of postoperative complications in patients undergoing CE.
OPINION ON THE ISSUE
The article considers the urgent problem of combating cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) in the Nizhny Novgorod region, including the high prevalence of CVDs and the timely identification of risk factors. The changes in mortality from all and individual causes was analyzed. Attention was paid to the negative impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on the health of people suffering from noncommunicable diseases. We also described the necessity to improve healthcare efficiency for CVD patients by improving the complex of managerial and preventive measures.
LITERATURE REVIEW
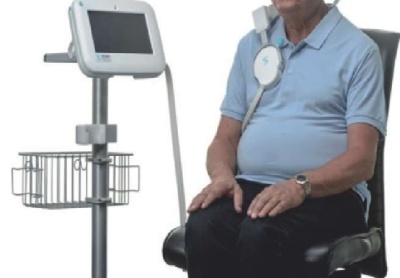
Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is based on multilevel pathological pathways, which include hemodynamic overload and venous stasis. Determination of the volemic status is one of the most important tasks in managing such patients. Despite the availability of modern diagnostic markers (physical examination, chest x-ray, and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) assessment), they do not accurately assess the degree of fluid overload, and therefore there remains a need to find a new, accurate and simple technology for assessing pulmonary congestion. The urgency of this problem has led to the development of a novel non-invasive remote dielectric sensing (ReDS) technology, which is a quantitative method for measuring the total volume of lung fluid by determining the tissue dielectric properties. The use of this technology makes it possible to quickly, non-invasively and quantitatively measure the fluid content in the lungs, makes it possible to optimize the treatment regimen and reduces the number of readmissions. This article presents the results of studies on the efficacy, safety and prospects for using a ReDS technology for the quantitative measurement of total lung fluid in patients with ADHF.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)