РКЖ. Образование, номер 1-2020
The review includes data over the past 20 years on the mechanisms of the influence of hypertension and related interdependent conditions, such as insulin resistance, chronic inflammation and oxidative stress on the vascular ageing. The review also discusses modern concepts of the interaction of biological and vascular aging, as well as possible ways of their reversal. The central indicators of biological aging in this review are telomere length and telomerase activity. The article discusses antihypertensive therapy as a possible way to slow down both vascular and biological aging, and describes the results of modern studies on the effect of various antihypertensives, including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, sartans and others, on the telomeres.
The review describes the role of electrocardiography in the diagnosis of the most common nonischemic myocardial diseases associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac death, especially in youth sports.
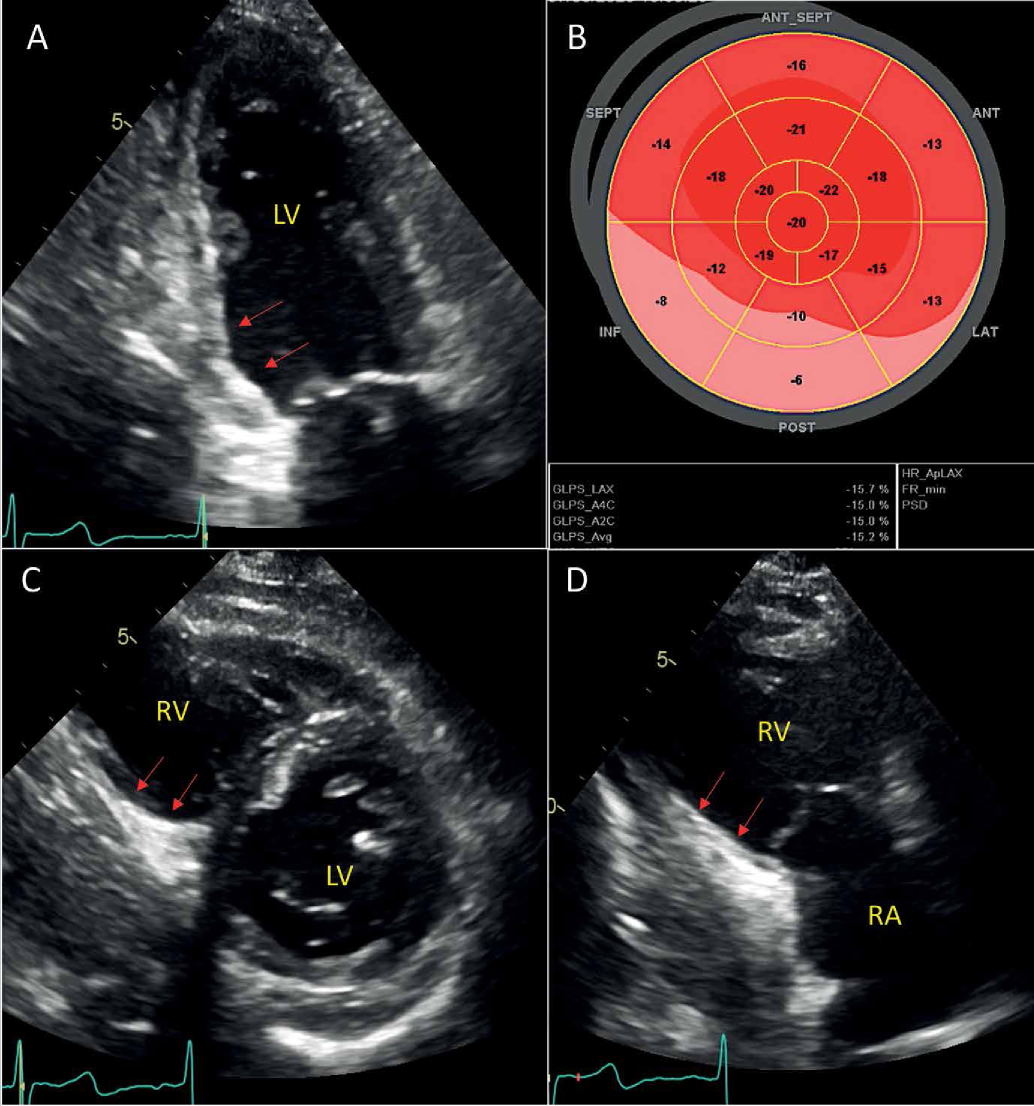
Right ventricular (RV) performance is an important predictor of adverse events and mortality in patients with cardiovascular diseases. Echocardiography is the first-choice imaging modality for the assessment of RV systolic function, however conventional two-dimensional echocardiographic parameters have important limitations and under specific conditions poorly correlate with the gold-standard imaging modality, cardiac magnetic resonance. Recent advances in novel echocardiography techniques, including three-dimensional echocardiography and two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography opened new era in RV imaging enabling more accurate and reproducible assessment of RV performance thus providing deeper insight into the pathophysiology of this intriguing cardiac chamber. In this comprehensive review authors summarize the state-of-the-art echocardiographic approach to the assessment of the RV systolic function with specific emphasis on modern techniques, their advantages, limitations and pitfalls in the various clinical settings.
Preoperative examination of patients undergoing high-risk elective non-cardiac surgery requires identifying factors associated with both the type of surgery and comorbidity profile of each patient. Determination of clinically significant echocardiographic changes, even without severe symptoms, can contribute to a change in management or revision of scheduled date and surgery tactics. The aspects of defining echocardiographic criteria for potential postoperative cardiovascular complications, especially in asymptomatic patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction, are an important clinical problem. The diastolic stress test, a relatively new type of exercise testing, is currently an additional diagnostic tool to detect heart failure in patients without reduced ejection fraction. The prospects of using this method before non-cardiac surgery in patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction is discussed in this article.
The review article summarizes the results of studies on the pathogenesis, as well as the clinical and prognostic role of coronary artery calcification (CAC) in coronary artery disease. The modern views of cardiologists, surgeons and general practitioners on the comorbidities manifested by CCA are presented. The modern ideas on the relationship between atherogenesis, CCA and bone resorption are described; groups of informative biological markers reflecting the severity of process are identified. Modern diagnostic methods for the detection and study of CCA are highlighted, their advantages and limitations are indicated. The effect of atherosclerosis treatment on coronary calcification and osteopenia are discussed. Further prospects and lines of research in this area are presented.
The aim of this review was to study the evidence base for the efficacy and safety of the P2Y12 receptor blocker ticagrelor in combination with acetylsalicylic acid in patients with stable coronary artery disease and high and moderate risk of adverse cardiovascular events. Currently, the mortality rate of this category of patients remains high. Long-term dual antithrombotic therapy allows to improve the prognosis. Ticagrelor at a low dose (60 mg 2 times a day) in combination with acetylsalicylic acid in randomized clinical trials and an actual clinical practice has shown a beneficial effect on prognosis in stable coronary artery disease.
Testing for inherited thrombophilia in patients with venous thromboembolism is one of the most common genetic testing options prescribed by clinicians. Despite the large evidence base for the relationship of hereditary hemostasis disorders with the risk of venous thrombosis, most patients should not be tested. Performing tests in the acute phase of thrombosis or during anticoagulant therapy leads to erroneous results. The choice of anticoagulant therapy regimen and its duration are not specified by the presence of hereditary thrombophilia. The test results can be useful for increasing medication adherence of patient, determining the cause of thrombosis, especially at a young age or in atypical localization.
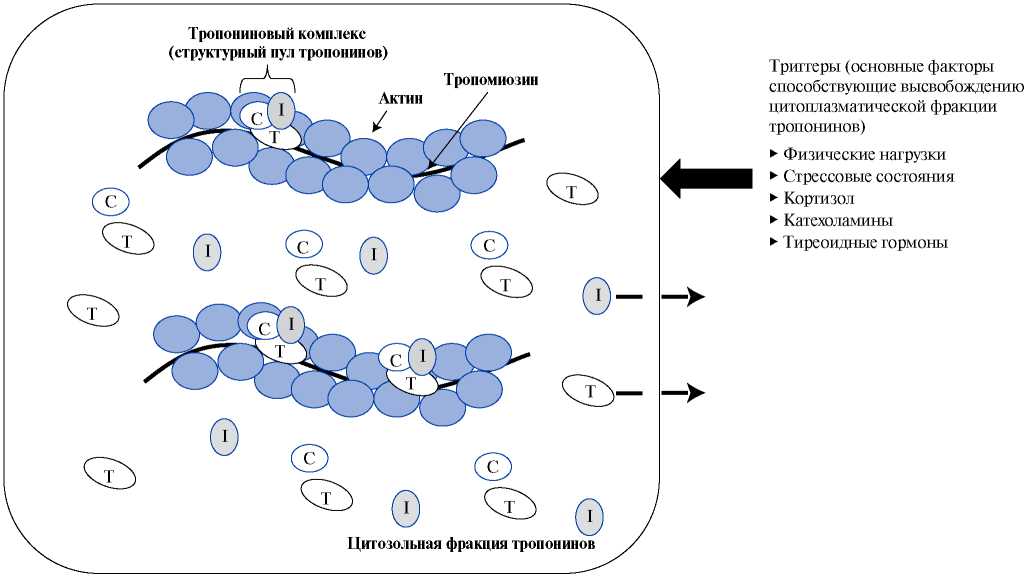
Modern laboratory methods for determining biomarkers of cardiovascular diseases are highly sensitive and can detect almost single molecules in human biological fluids, significantly speeding up and improving the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. However, in this case, there is a decrease in specificity and it is necessary to take into account a number of additional factors that may affect the result of the study. Recent studies have shown that circadian rhythms (CR) are among these factors.
This review article is devoted to the discussion of recently discovered CR of cardiac troponins (CT). A number of articles reported that, both in healthy people and in patients with a number of chronic diseases, CT concentrations change during the day. Given that modern algorithms for diagnosing myocardial infarction (MI) are based on serial studies (0-1 h and 0-3 h) of blood serum, and the values of CT in the blood serum for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI) for this period of time are only a few ng/l, the CT CR can to some extent affect the accuracy of MI diagnosis. Thus, natural physiological changes in the concentration of CT during the day can be mistakenly interpreted as diagnostically significant deviations and lead to an erroneous interpretation of laboratory test results.
Comorbidity is a common feature of a modern patient. The combination of atrial fibrillation (AF) and various types of coronary artery disease is widespread in actual clinical practice. In such cases, additional pathophysiological mechanisms appear that worsen the clinical course and patient’s prognosis. The management of AF patients who have undergone acute coronary syndrome and/or percutaneous coronary intervention is a challenging problem, which can be solved by large-scale clinical trials. The AUGUSTUS randomized trial with a two-by-two factorial design proved that full-dose apixaban is superior in safety to the vitamin K antagonist warfarin, while not inferior in effectiveness. This pattern has been preserved in several important subanalysis on stent thrombosis, hospitalization rates, and conservative management of acute coronary syndrome. The obtained results are included in the novel European Society of Cardiology guidelines on AF.
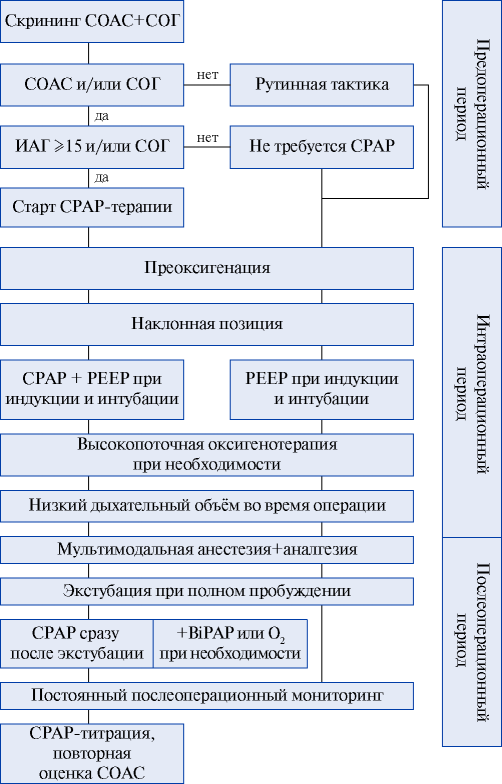
The article presents a non-systematic review of studies on breathing-related sleep disorders in patients with morbid obesity, and on the use of non-invasive ventilation in the pre-, peri-, and postoperative period of bariatric surgery, with an assessment of cardiovascular effects.
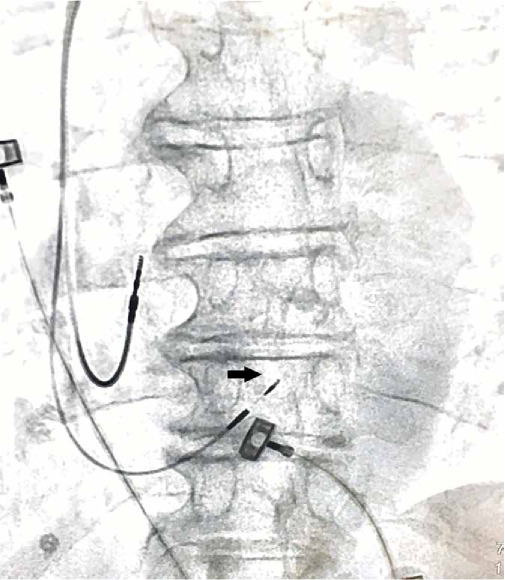
His bundle pacing (HBP) implements physiological impulse propagation along the cardiac conduction system and can serve as an analogue of both right ventricular and biventricular pacing. This review highlights clinical anatomy issues related to HBP; the technique of lead implantation in the His position is considered. We also describe the electrophysiological basis of HBP, possibilities of lead extraction, indications for implantation, and prospects for further development of the technique. HBP is a promising direction in cardiology, which in the future may fundamentally change the algorithms for managing patients with heart failure and conduction disorders.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)