ACUTE AND CHRONIC HEART FAILURE. ORIGINAL ARTICLES
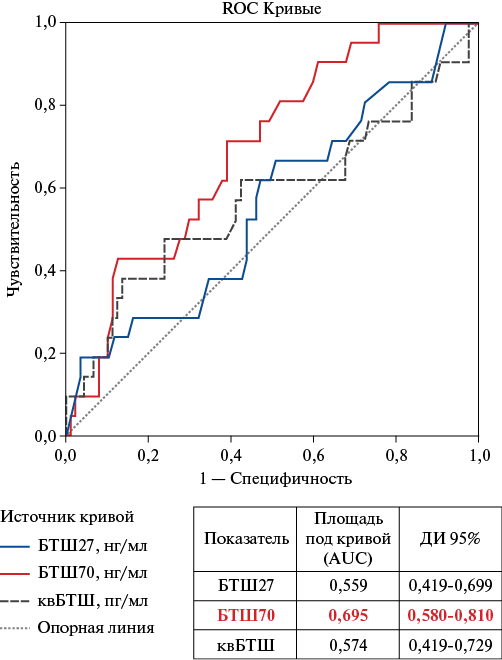
- Determination of serum heat shock protein (HSP) levels is used for biochemical assessment of cellular stress activity.
- Elevated concentrations of HSP70 and cardiovascular HSP are associated with worse prognosis in patients who have suffered acute decompensated HFpEF.
Aim. To analyze the relationship between the concentrations of circulating heat shock proteins (HSP): HSP27, HSP70 and cardiovascular HSP (cvHSP) with the course of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and the outcomes of acute decompensated HFpEF (ADHFpEF).
Material and methods. A total of 120 patients with a confirmed diagnosis of HFpEF aged 50 to 90 years and acute decompensated HFpEF at the time of blood sampling, as well as 20 patients with HFpEF without clinical manifestations of ADHFpEF were examined. Before treatment, blood was collected from patients and serum was obtained with subsequent storage at -80 0C for biomarker testing by the enzyme immunoassay (AssayPro, USA and Cloud-Clone, USCN) on a Thermo Multiscan FC microplate photometer (USA). Fatal outcomes were monitored in patients in the interval from 6 months to 1,5 years.
Results. The median serum levels of HSP27, HSP70 and cvHSP are significantly higher in patients with decompensated than with compensated HFpEF. Elevated baseline levels of HSP70 (>3,5 ng/ml) and cvHSP (>1321 pg/ml) in patients with ADHFpEF are associated with an unfavorable survival prognosis. For HSP27, no significant differences were found in the survival analysis.
Conclusion. An association was found between serum concentrations of HSP70 and cvHSP with an unfavorable survival prognosis in patients with ADHFpEF, which allows them to be considered as potential prognostic markers of this disease.
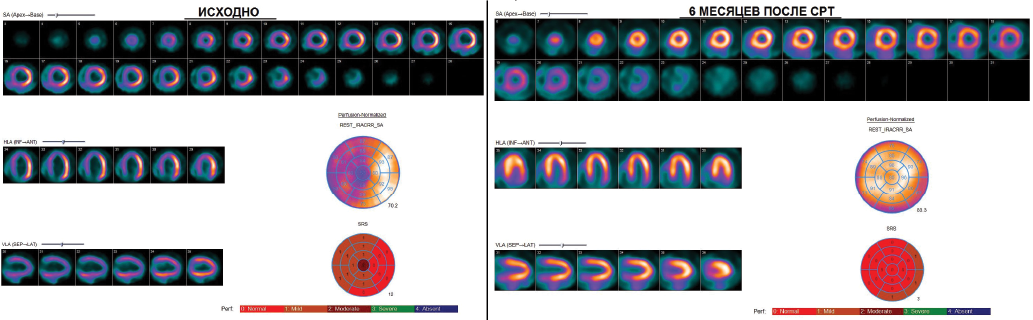
- 99mTc-MIBI washout rate from the left ventricular (LV) myocardium did not demonstrate predictive value in determining a positive response after cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) in patients with heart failure of non-ischemic origin.
- CRT has a positive effect not only on LV myocardial contractility, but also on myocardial perfusion, which is manifested by a decrease in perfusion defect size, washout rate, and mechanical desynchrony.
Aim. To study the significance of 99mTc-MIBI washout rate as a scintigraphic marker of mitochondrial dysfunction in predicting the effectiveness of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), and to evaluate the long-term effect of CRT on 99mTc-MIBI clearance and myocardial perfusion.
Material and methods. The study included 30 patients with heart failure of non-ischemic origin and indications for CRT. Before CRT, patients underwent 99mTc-MIBI myocardial perfusion scintigraphy (MPS) at rest. To assess the 99mTcMIBI washout rate, scanning was performed twice (after 1 hour and 3 hours). In addition, we assessed the severity of perfusion defects, contractility and mechanical desynchrony of the left ventricle (LV). All patients were rehospitalized after six months to assess the effectiveness of treatment and to perform MPS to assess the changes of scintigraphic parameters. According to echocardiography data, patients were divided into responders and non-responders. The criterion for a positive response to CRT was a decrease in LV end-systolic volume by 15% or more and/or an increase in LV ejection fraction by 10% or more.
Results. Of all patients included in the study group, 23 (77%) were CRT responders. In this group of patients, the initial LV contractility indices were higher, and mechanical cardiac desynchrony was less pronounced compared to nonresponders. There were no significant differences in the 99mTc-MIBI washout rate and the severity of LV perfusion defect between responders and non-responders. Only in the responder group a significant decrease in the perfusion defect size was noted 6 months after CRT from 6 (3-9) points to 3 (3-4) points (p=0,0001), in contrast to non-responders (from 5 (4-8) to 6 (4-7), p=0,55). 99mTc-MIBI clearance decreased in both groups.
Conclusion. Baseline 99mTc-MIBI washout rates did not demonstrate predictive value in determining CRT responders. This intervention has a positive effect on LV perfusion and contractility.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY
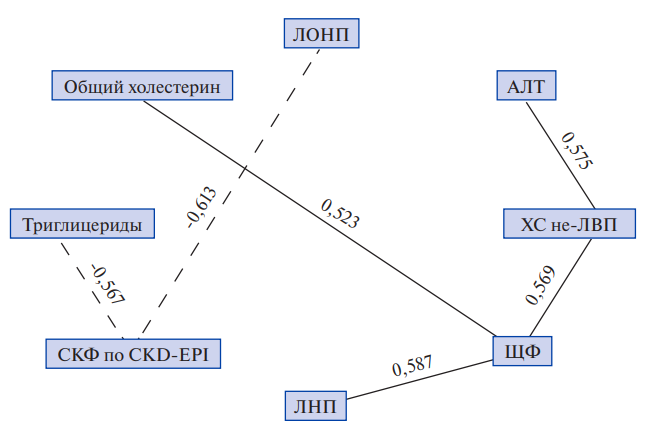
- Patients with acute leukemia at the end of chemotherapy and after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplanta-tion experience changes in lipid profile, characterized by an increase in total cholesterol due to an increase in low-density lipoproteins and a decrease in high-density lipoproteins, as well as an increase in triglyceride levels. This is probably due to the pathogenetic therapy being carried out, including cytostatic agents and its effect on liver func-tion.
Aim. To study changes in lipid profile in patients with acute leukemia who received pathogenetic therapy.
Material and methods. The study included 13 patients diagnosed with acute leukemia who underwent pathogenetic therapy, including multiagent chemotherapy and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. The median age was 40 years. All patients in the study group underwent an assessment of lipid profile, as well as an assessment of liver and kidney function at the time of diagnosis, the end of chemotherapy courses, and after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Results. Total cholesterol, triglyceride, very low-density lipoprotein and lowdensity lipoprotein values in the study groups significantly change over time at different stages of treatment. Total cholesterol values have a higher risk of increasing in patients with acute leukemia at the end of chemotherapy and after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation compared to the disease onset. Patients with acute leukemia significantly more often have an increase in total cholesterol and triglyceride levels by the end of chemotherapy and after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Discussion. Increased cardiovascular risk in patients with acute leukemia receiving pathogenetic therapy, including allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, is associated with high antitumor therapy toxicity, and is also a consequence of the neoplastic process. Hypolipidemia at the onset of acute leukemia is primarily associated with their increased consumption by neoplastic cells. Impaired liver function and decreased glomerular filtration rate during treatment of acute leukemia are largely associated with highly toxic regimens of antitumor therapy.
Conclusion. In patients with acute leukemia at different stages of pathogenetic treatment, including polychemotherapy and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, the development of lipid metabolism disorders is the pathogenetic basis for the formation of cardiovascular complications.
Aim. To assess cost-effectiveness of using sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors as a part of therapy for cardiovascular death prevention and achieving the Reduction of Cardiovascular Mortality indicator of the Healthcare Development state program in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and resistant hypertension (RH).
Material and methods. The target population is Russian comorbid patients with CKD and RH. The population size of 263303 people was determined based on Russian statistical data, literary sources and assumptions adopted in the study. To predict cardiovascular death, parametric modeling was used based on published clinical trial data. We calculated the drug costs required to prevent one cardiovascular death, as well as to achieve a target indicator for reducing cardiovascular mortality by one percent when using SGLT2 inhibitors in Russia as a whole and separately in each region.
Results. The costs of CKD therapy in working-age patients with RH, who are indicated for therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors (n=263303) in 2025 were RUB 7,6 billion. The use of standard therapy with SGLT2 inhibitors in the target group of patients will prevent 2273 cardiovascular death cases in the first year, which will ensure the achievement of the Reduction of Cardiovascular Mortality indicator of the Healthcare Development state program by 9,9%.
Conclusion. The ratio of additional costs to life years gained was RUB 2,49 million, which does not exceed 3 times the gross domestic product per capita (RUB 3,51 million) and indicates the economic feasibility of SGLT2 inhibitor therapy for CKD in patients with RH.
ПРОБЛЕМНАЯ СТАТЬЯ
In elderly and senile patients, a combination of hypertension and atherogenic dyslipidemia is often encountered, which, both separately and in combination ("lipitension"), are associated with a high risk of cardiovascular events. In clinical practice, it is not just the age itself that is important, but the presence of geriatric syndromes in patients. In particular, frailty is characterized by a high risk of adverse outcomes and death, as well as loss of autonomy. This article presents current data on the efficacy and safety of antihypertensive and lipidlowering therapy in elderly patients. It also discusses the thesis that fixed-dose combination of amlodipine, perindopril and atorvastatin can increase adherence to therapy and ensure a balance between the efficacy and safety of treatment in elderly comorbid patients with a number of geriatric syndromes. The treatment of such patients is traditionally associated with polypharmacy and uncontrolled use of medications.
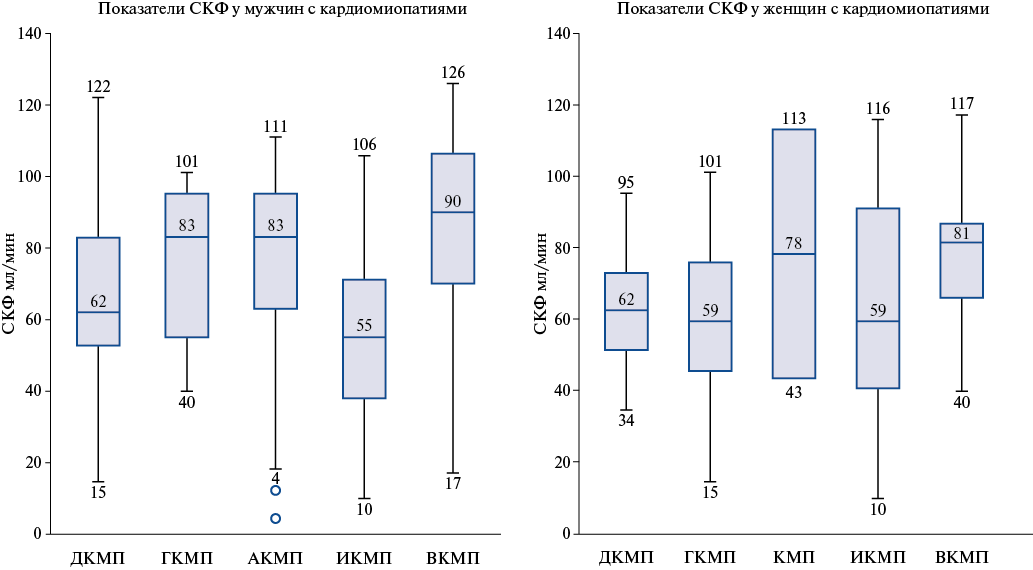
- Myocardial damage in cardiomyopathy is associated with reduced glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- The GFR value closely correlates with the left ventricular contractility in men with dilated and ischemic cardiomyopathy, and in women with ischemic cardiomyopathy it is associated with right ventricular size.
- Different types of myocardial remodeling in cardiomyopathy in men and women with reduced GFR were revealed.
Aim. To identify cardiorenal relationships and related characteristics in individuals with various cardiomyopathies.
Material and methods. An analysis of 267 patients with cardiomyopathy (CMP) was conducted, of which 204 (76,4%) were men. There were dilated CMP (DCM), hypertrophic CMP (HCM), alcoholic (ACM), ischemic CMP (ICM) and inflammatory CMP (InCM). We assessed the relationships between glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and CMP forms and following echocardiography parameters: ejection fraction (EF), left ventricular (LV) end-systolic (ESD) and end-diastolic dimensions (EDD), left ventricular wall thickness (LVWT), right ventricle (RV), left and right atria.
Results. Among individuals with CMP, a significant decrease in GFR was found in DCM, ICM, and HCM. In men, there was a positive relationship between GFR and EF and a negative relationship between GFR and ESD in DCM (r=0,317, p=0,012 and r=-0,269, p=0,036) and ICM (r=0,359, p=0,017 and r=-0,660, p=0,007). In women, no relationships between GFR and EF were found. In women with DCM, a strong positive relationship between GFR and LVWT (r=0,894, p=0,041) was found. In women with ICM, a negative relationship between GFR and RV (r=-0,650, p=0,003) and ESD (r=-0,829, p=0,042) was found. In women with DCM and ICM, only the RV parameter was included in the regression equations with the dependent variable GFR, while in men, all echocardiography parameters were included. In the general HCM group, there was a negative correlation between GFR and LVWT (r=-0,571, p=0,021). In the HCM group, a negative relationship between GFR and EDD was recorded in young men (r=-0,520, p=0,027) and in young women (r=-0,750, p=0,05).
Conclusion. In individuals with DCM, ICM, and HCM, a decrease in GFR is observed compared to ACM and InCM at the corresponding age. In men with DCM and ICM, a positive correlation of GFR with EF is recorded, and in women with ICM, a negative relationship of GFR with RV. Therefore, sex-specific relationships between GFR and echocardiography parameters in men and women reflect one or another adaptive model of cardiovascular remodeling in CMP. Left ventricular remodeling in CMP with thickening or thinning is associated with a decrease in GFR in both men and women.
ПРОГНОЗИРОВАНИЕ И РЕАБИЛИТАЦИЯ В КАРДИОЛОГИИ И КАРДИОХИРУРГИИ
- About one third of heart conduction disorders in transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) occur before bioprosthetic valve implantation.
- The most common heart conduction disorder after TAVI is new-onset complete left bundle branch block, which in most cases is persistent and remains until the patient is discharged from the hospital.
- Intraoperative Holter monitoring in TAVI can be an important tool for assessing and predicting various heart conduction disorders, as well as determining the optimal postoperative patient management strategy.
Aim. To evaluate the timing and relationship of heart conduction disorders with various surgical steps of transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) using intraoperative Holter monitoring.
Material and methods. This prospective observational study included 60 patients with high risk of atrioventricular (AV) conduction abnormalities who underwent TAVI for severe aortic stenosis. Intraoperative heart rhythm assessment was performed using continuous Holter monitoring. After the procedure, cardiac rhythm recording was continued for the next 24 h. The target time intervals of the main surgical steps were then compared with conduction disorders (transient and/or persistent) identified (first-degree AV block, complete AV block, right and left bundle branch blocks).
Results. Newly diagnosed conduction disorders were noted in 85,3% of patients. In 31,2% of patients, conduction disorders were noted before bioprosthetic valve implantation (positioning of guidewire, balloon valvuloplasty), in 23,4% — at the stage of bioprosthetic valve implantation, and in 31,5% — immediately after the balloon postdilation. The transient course was most characteristic of complete AV block, the resolution of which in the postoperative period was noted in 62,5% of cases. First-degree AV block and left bundle branch block persisted before discharge from the hospital in 71,4% and 65% of cases, respectively. Among transient cardiac conduction disturbances, first-degree AV block had the longest duration, the median time to resolution of which was 420 min.
Conclusion. About a third of heart conduction disorders in TAVI occur before bioprosthetic valve implantation. The most common heart conduction disorder after TAVI is new-onset complete left bundle branch block, which in most cases is persistent and remains until the patient is discharged from the hospital. Intraoperative heart rhythm monitoring after TAVI can be an important tool for assessing and predicting various heart conduction disorders, as well as determining the optimal postoperative patient management strategy.
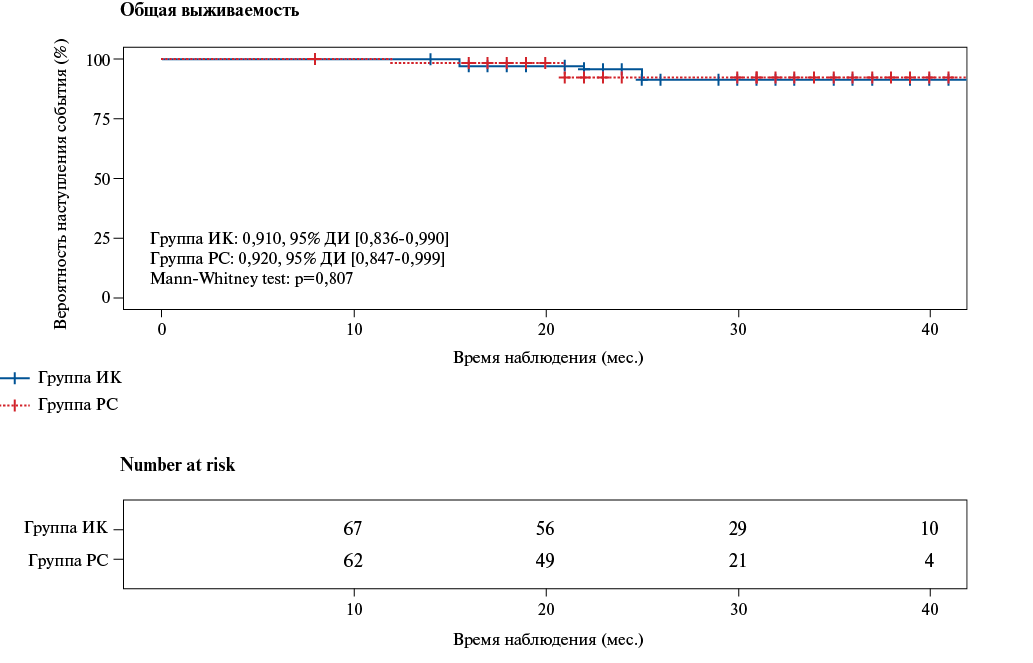
- Within 26-month follow-up period, no significant differences in overall survival and freedom from major adverse cardiovascular events were found in patients operated in on- and off-pump conditions.
- A history of atrial fibrillation, type 2 diabetes, left ventricular ejection fraction <50%, significant extracranial stenosis (>60%) are predictors of a higher mid-term death probability.
Aim. To analyze inhospital and mid-term outcomes of offand on-pump complete bilateral internal thoracic artery (BITA) grafting in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease (CAD).
Material and methods. The article analyzed the immediate and mid-term (26 months) outcomes of BITA grafting in 178 patients with multivessel CAD. In 99 patients, there was on-pump conditions, and in 79 cases — off-pump. After nearest neighbor propensity score matching, without preliminary screening of unsuitable patients in the groups, 148 patients were selected, of which 2 groups with same sample size (n=74) were generated (off-pump and on-pump). The groups were comparable in terms of sex (p=0,483), age (p=0,061), body mass index (p=0,977), comorbidities, the number of hemodynamically significant coronary lesions (p=0,508), but there were significantly more patients with local ascending aortic calcification and significant extracranial artery stenosis (>60%) in the off-pump group (p=0,015 and p=0,039).
Results. The groups were comparable in the number of revascularized target coronary arteries (p=0,762), the incidence of inhospital complications. The mean follow-up period was 26 months. The long-term survival rate of patients was 93,7% in the ff-pump group and 93% in the on-pump group (p=0,807). Freedom from cardiovascular mortality was 100% in both groups, while freedom from adverse cardiovascular events was 98,4% in the off-pump group and 94% in the on-pump group (p=0,198).
Conclusion. Off-pump BITA grafting is an effective and safe method of surgical treatment of CAD, which allows for complete myocardial revascularization in patients with multivessel CAD and does not increase the complication rate during the inhospital period. In the period of up to 26 months, BITA grafting, regardless of the surgery conditions, was associated with high survival rate, complete freedom from cardiovascular mortality and high freedom from cardiovascular events.
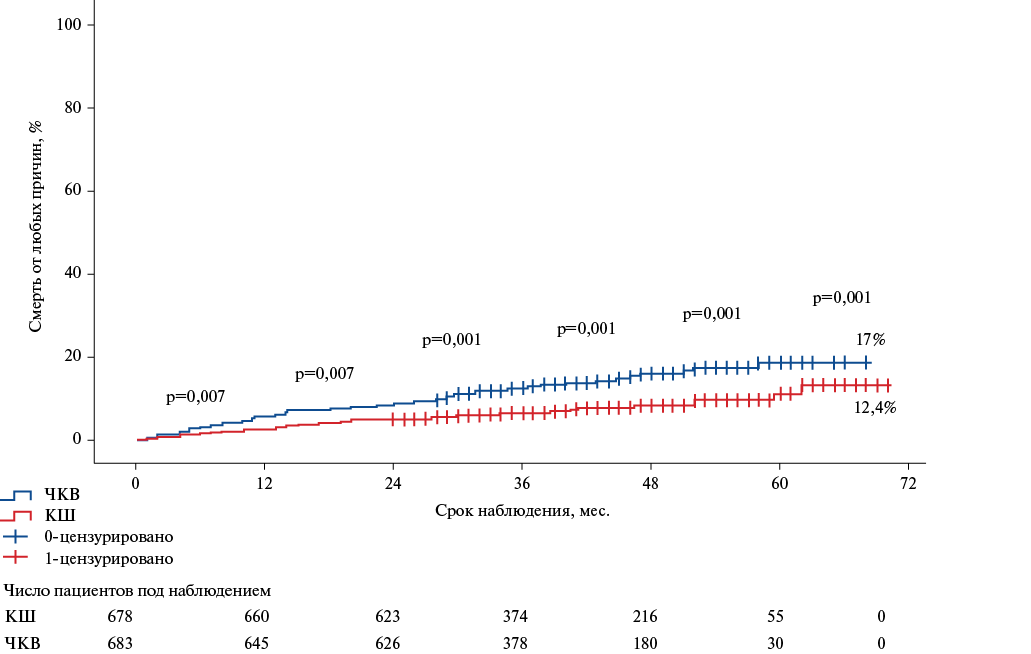
- Comparison of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with stable coronary artery disease indicate their comparable inhospital and 30-day postoperative mortality and a significant advantage of CABG over PCI in reducing the long-term all-cause mortality, primarily in patients with complex coronary artery involvement regardless of diabetes and patients with non-reduced myocardial contractility (left ventricular ejection fraction >40%).
- In single-vessel coronary artery disease, long-term all-cause mortality after CABG and PCI did not differ, which, when choosing the intervention tactics, speaks in favor of PCI as a less invasive revascularization method.
Aim. To assess the long-term all-cause mortality after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) in patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) under various clinical and anatomical scenarios.
Material and methods. This single-center cohort retrospective study assessed the outcomes of CABG and PCI with implantation of second-generation drugeluting stents in 4177 patients with stable CAD. Inhospital, 30-day and remote 5-year all-cause mortality (mean follow-up period — 38 months) was assessed. Also, the influence of the initial severity of CAD, the presence/absence of diabetes, myocardial contractility on remote all-cause mortality after myocardial revascularization was assessed.
Results. Inhospital and 30-day risks of death in patients who underwent PCI and CABG, after comparing the initial clinical characteristics, did not differ significantly. In the long-term follow-up period, PCI compared with CABG was associated with an increased all-cause mortality in the main groups (PCI vs CABG: odds ratio (OR) 1,84, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1,30-2,62, p<0,001), as well as in the following subgroups: (1) in patients with multivessel CAD (OR 1,77, 95% CI 1,19-2,64, p=0,005), (2) in patients with left main CAD >50% (OR 5,04, 95% CI 1,72-14,76, p=0,003), but not in patients with single-vessel disease (OR 2,084, 95% CI 0,9964,361, p=0,051). Diabetes in the main study groups did not affect the difference in mortality as follows: CABG had an advantage over PCI regardless of diabetes. However, CABG in patients with multivessel disease and diabetes, in contrast to patients without diabetes, led to a significant decrease in all-cause death risk (OR 2,29, 95% CI 1,173-4,47, p=0,015). Also, PCI compared with CABG was accompanied by an increase in the 5-year death risk in patients with an not reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) >40% (OR 1,74, 95% CI 1,205-2,536, p=0,003), but not in patients with LVEF <40% (95% CI 1,314-4,709, p=0,809).
Conclusion. The obtained data indicate a significant reduction in the 5-year risk of all-cause mortality in patients undergoing CABG compared to patients after PCI. Potential long-term benefit from CABG compared to PCI may be obtained in patients with complex coronary artery involvement (left main coronary artery stenosis >50%, lesion of two or more coronary arteries), with concomitant diabetes in multivessel disease, and patients with non-reduced LVEF (>40%).
- Inflammation plays a leading role in triggering and maintaining the main mechanisms determining coronary conduit damage after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), which is the basis for graft dysfunction.
- Analysis of changes in inflammatory response humoral markers after surgery showed that patients with bypass dysfunction (D+) had significantly higher levels of C-reactive protein, fractalkine, IL-1β, neopterin at all testing time points (before surgery, 24 hours and 7 days after CABG).
- In the future, therapeutic approaches aimed at CX3CL1/CX3CR1/ IL-1β/neopterin block may become a new strategy for the prevention and treatment of adverse cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease, including after CABG.
Aim. To assess the influence of systemic inflammatory response activation on the incidence of coronary conduit dysfunction and the risk of cardiovascular events after coronary artery bypass grafting, as well as to identify the most significant humoral markers.
Material and methods. The study included 84 patients with stable coronary artery disease who underwent examination and isolated coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). Humoral inflammation markers were assessed before surgery, 24 hours and 7 days after CABG. Control coronary bypass angiography was performed intraoperatively and 1 year after CABG. An analysis of clinical and paraclinical data was performed in two following groups: Group 1 — patients (n=10) diagnosed with bypass graft dysfunction (D+) during control bypass angiography 1 year after surgery; Group 2 — patients (n=74) without bypass graft dysfunction (D-) according to control bypass angiography 1 year after CABG.
Results. Coronary conduit dysfunction was detected in 10 (12%) patients 1 year after CABG, which was caused by venous bypass graft thrombotic occlusion in 7 (70%) cases, and hemodynamically significant bypass graft stenosis in 3 (30%) cases. The following adverse cardiovascular events were registered in these patients: cardiovascular death — 2 patients; recurrent angina — 8 (80%) patients; acute myocardial infarction — 4 (40%) patients; hospitalization due to decompensated heart failure — 2 (20%) patients; repeated myocardial revascularization — 8 (80%) patients; life-threatening arrhythmias (ventricular tachycardia) — 3 (30%) patients. These patients had significantly higher levels of hs-C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), fractalkine, IL-1β, neopterin at all testing time points (before surgery, 24 hours and 7 days after CABG), indicating a more pronounced activation of inflammatory mechanisms.
Conclusion. The study confirmed the leading role of inflammation in triggering and maintaining the main mechanisms determining coronary conduit damage after CABG, which is the basis for bypass graft dysfunction. This allows us to consider inflammation as an independent cause of vascular damage, and the established significant inflammatory biomarkers (hs-CRP, fractalkine, IL-1β, neopterin) as predictors of bypass graft dysfunction and infavorable outcomes of myocardial revascularization.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease (CAD) intolerant to coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a safe procedure with a low complication rate.
- The outcomes of PCI in patients with left main CAD intolerant to CABG are comparable with the general cohort of patients with multivessel CAD intolerant to CABG who underwent PCI.
- When choosing a management strategy for patients not tolerant to CABG (endovascular or conservative treatment), the specialists should rely not only on clinical data, but also on the coronary anatomical features.
Aim. To evaluate immediate angiographic and clinical outcomes of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with stable and multivessel coronary artery disease (CAD), intolerant to coronary artery bypass grafting.
Material and methods. This retrospective study included 307 patients with multivessel CAD who underwent myocardial revascularization using PCI between 2013 and 2022. Mortality, complications, and clinical parameters after the procedure were assessed in the early postoperative period.
Results. Revascularization was successful in 94,9% of patients, The mean surgery duration was 59,0±28,9 min. The incidence of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events was 3,1%. Complete revascularization was achieved in 54 (17,6%) patients. There were following independent predictors of incomplete myocardial revascularization according to multivariate regression analysis: high EuroSCORE II (odds ratio (OR) 0,83, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0,68-1,0; p=0,047), SYNTAX (OR 0,93, 95% CI: 0,89-0,97; p=0,001), and J-CTO (OR 0,68, 95% CI: 0,49-0,94; p=0,0018) scores.
Conclusion. PCI in patients with multivessel CAD and intolerance to coronary artery bypass grafting is a safe procedure with low inhospital mortality and postoperative complications. PCI in this cohort of patients is associated with a high rate of procedural success. Additional studies, including randomized trials, are needed to assess the long-term prognosis in this cohort of patients.
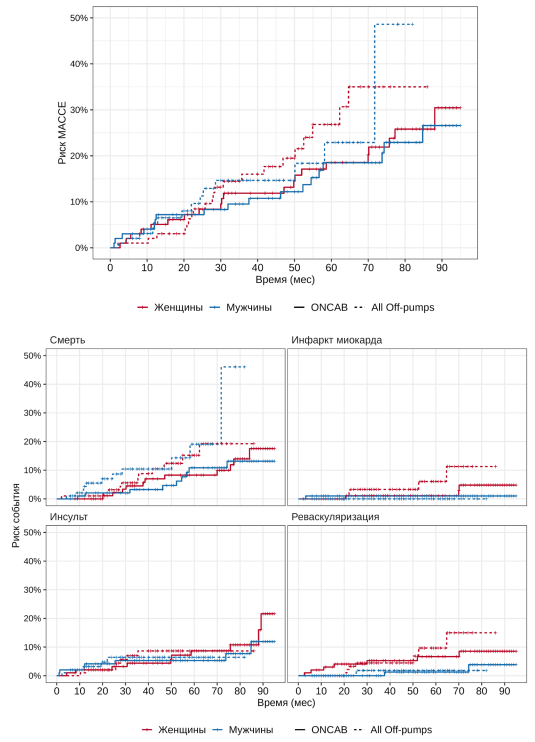
- Findings of CROWN-SAGA study enrolling 200 women and 200 men who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting with a median follow-up of 50 months showed that long-term outcomes were less favorable in female patients.
- This study broadens perspective on the significance of sex-gender variables with respect to outcomes across wide spectrum of surgical techniques, identifying prognostic factors for each sex.
- Results emphasize the importance of differential sex-gender approach towards selection of an optimal surgical technique that improves patient outcomes following myocardial revascularization.
Aim. To conduct an in-depth comparative analysis of the impact of preoperative profile and range of surgical techniques in coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery on shortand long-term outcomes in women and men.
Material and methods. This retrospective and prospective single-center CROWNSAGA study (NCT06749171) includes a sample of 400 patients (200 women and 200 men) who underwent CABG in the period from January 2016 to July 2023 at the Sukhanov Federal Center for Cardiovascular Surgery (Perm). The patients included in the study were divided into groups by sex followed by propensity score matching (PSM) analysis, as well as into stratum of surgical techniques — on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (ONCAB), off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (OPCAB), no-touch aorta technique (NTA), minimally invasive multiple coronary artery bypass grafting (MICSCAB). Furthermore, the impact of multiple arterial grafting (MAG), total arterial revascularization (TAR), composite and sequential grafting on outcomes was analyzed for each sex. The primary endpoint was a composite of allcause mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) and repeat revascularization (major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, MACCE) during the long-term follow-up. The secondary endpoint was allcause mortality during the long-term follow-up.
Results. Median follow-up duration was 50 (1st (Q1) and 3rd (Q3) quartiles: 30; 72) months: 54,5 (33; 75,8) in women and 46 (22; 71) in men. Women had less favorable preoperative profile compared to men. Short-term in-hospital outcomes were comparable between women and men in terms of mortality (2,5% vs 3,5%) and MACCE (1% vs 1,5%). Over long-term follow-up, the incidence of MACCE was 21,2% in women and 16,2% in men (hazard ratio (HR) =1,15 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0,72; 1,82], p=0,557) and the incidence of death was 11,1% in women and 10,2% in men (HR =0,94 [95% CI: 0,51; 1,72], p=0,83). Female cohort had higher risks of MI (HR =6,66 [95% CI: 0,83; 53,28], p=0,038), revascularization (HR =4,11 [95% CI: 1,18; 14,32], p=0,016) and stroke (HR =1,24 [95% CI: 0,59; 2,6], p=0,567). In the all off-pumps strata (OPCAB, NTA, MICSCAB) compared with ONCAB, risk of adverse long-term outcomes was higher among all patients in regard to both MACCE (HR =1,54 [95% CI: 0,95; 2,49], p=0,08) and death (HR =2,17 [95% CI: 1,14; 4,14], p=0,016). No significant difference was observed in longterm MACCE and death rates between women or men when comparing ONCAB, OPCAB, MICSCAB and NTA stratum, except for a significant lower risk of death in men with ONCAB compared to OPCAB (HR =0,28 [95% CI: 0,09; 0,91], p=0,03). The use of graft imaging revealed an increased risk of graft occlusion in women, whereas following off-pump CABG the risk of any occlusion was significantly higher in both sexes compared to ONCAB. Predictor of long-term MACCE and death for women was use of composite grafts, while for men — ejection fraction (EF) £40%, age >70 years, and off-pump CABG. At last follow-up, the persistence of health complaints was significantly higher among female patients versus male patients.
Conclusion. Women overall have less favorable outcomes following surgical myocardial revascularization compared with men. The impact of different surgical bypass techniques on postoperative outcomes varies between women and men. A differential sex-gender approach should be employed in the selection of the optimal surgical technique for CABG, with the objective of improving patient outcomes following myocardial revascularization.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)