ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ КАРДИОЛОГИЧЕСКОЙ ПОМОЩИ. ОРИГИНАЛЬНЫЕ СТАТЬИ
Despite widespread knowledge in the management of patients with lipid metabolism disorders, their application in clinical practice is insufficient. Identification of barriers to the implementation of key principles of clinical guidelines in routine practice is the first step of the implementation study.
Aim. To assess the organization and quality of care for patients with dyslipidemia in order to identify barriers to the implementation of the main principles of clinical guidelines in practice.
Material and methods. An implementation study was planned, the initial stage of which was to conduct an anonymous online questionnaire among health care representatives of various levels in all Russian subjects.
Results. The study involved 788 physicians, 124 heads of medical organizations and 48 chief freelance specialists from 84 Russian subjects. A wide range of barriers was identified: low availability of lipoprotein (a) testing (66,6% of physicians), coronary calcium index (79,4% of physicians, 71,8% of heads of a medical organizations, 79,2% of chief freelance specialists) and CT angiography (70,0% of physicians, 71,0% of heads of a medical organizations, 85,4% of chief freelance specialists). Lack of funds to manage lipid service (55,6% of heads of a medical organizations, 35,4% of chief freelance specialists). The key barrier to regular lipid-lowering therapy and achieving target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels is lack of perceived need for treatment in patients (58,1% of physicians, 80,0% of heads of a medical organizations, 87,5% of chief freelance specialists), for PCSK9-targeted therapy — high cost (44,1% of physicians, 34,7% of heads of a medical organizations, 23,0% of chief freelance specialists). The possible fixed-dose combination therapy for dyslipidemia was positively perceived (59,7% of physicians, 42,0% of heads of a medical organizations, 35,4% of chief freelance specialists). Inclusion of innovative therapy in medicine assistance program will improve the situation in achieving target LDL-C levels (85,6% of physicians, 91,1% of heads of a medical organizations, 95,8% of chief freelance specialists).
Conclusion. A wide range of barriers to the implementation of clinical guidelines on lipid metabolism disorders into practice have been identified. Based on the results obtained, the second stage of the implementation study will identify strategies aimed at eliminating the identified barriers.
- An analysis of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) cases, which developed before the ambulance arrival, followed by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), was performed.
- Bystander-performed CPR increases the success rate of CPR by ambulance team. However, bystanders try to provide assistance in no more than 27% of cases, which causes a high mortality rate.
- To reduce mortality from OHCA, the attention should be focused on the development, implementation and regulatory support of measures aimed at involving the population in providing first aid.
Aim. To study the regional epidemiological characteristics of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), the process and effectiveness of care for OHCA, and identify priority areas for improving the care provision.
Material and methods. An analysis of the data from the "Crimean registry of cases of OHCA and cardiopulmonary resuscitation" was performed. The study used data from 2020 to 2022. The analytical sample consisted of all OHCA cases developed before the ambulance arrival, followed by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
Results. Of the 356 OHCA cases occurred before the ambulance arrival, followed by CPR (2020 — 141, 2021 — 103, 2022 — 112), in 65,2% of cases (n=232) cardiac arrest developed in men, in 64,0% (n=228) — in city residents, 70,2% (n=250) — in private houses or apartments. The mean age was 59 years (median 62 years). The cause of 89,6% of OHCA cases (n=319) was disease, 3,9% (n=14) — drowning, 2,8% (n=10) — trauma, 2,0% (n=7) — asphyxia, 1,1% (n=4) — toxicity, 0,6% (n=2) — electrical injury. In addition, 7,3% (n=26) of patients survived. Bystanders attempted CPR before ambulance arrived in 27,2% (n=97) of cases. In cases where CPR was performed by bystanders, ambulance specialists were 2,5 times more likely to register a potentially shockable rhythm on the primary electrocardiogram (19,6% and 7,7%, respectively; p=0,001), 2,2 times more often performed defibrillation (22,7% and 10,4%, respectively; p=0,003). When defibrillation was performed, the proportion of survivors was 3,9 times higher than without defibrillation (20,4% and 5,2%, respectively; p=0,001).
Conclusion. Conducting CPR by OHCA bystanders increases the success rate of CPR performed by ambulance team. However, bystanders rarely provide first aid, which causes a high mortality rate. To reduce mortality in OHCA, the attention should be focused on the development, implementation and regulatory support of measures aimed at involving the population in providing first aid. This should include regular population training in CPR, widespread popularization of first aid, remote provision of CPR instructions by emergency dispatchers to untrained OHCA bystanders and ensuring the availability of automated external defibrillators.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY. ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Aim. To evaluate the contribution ticagrelor compared with clopidogrel therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and patients with myocardial infarction (MI) to achieving the State Program "Health Development" target "decrease of cardiovascular mortality" in the country as a whole and Russian regions in 2023-2025.
Material and methods. In the first year of therapy, all patients over 18 years of age with a confirmed diagnosis of ACS who were indicated for dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) were considered as the target population. In the second and third years, therapy was continued by patients at high risk of coronary events after MI. The number of deaths that could be additionally prevented within 1 year after diagnosis using DAPT with ticagrelor compared with DAPT with clopidogrel was calculated based on the PLATO trial. For post-MI patients, the number of deaths that could be prevented in the second and third years of therapy using DAPT with ticagrelor+acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) compared with ASA monotherapy was calculated based on the PEGASUS trial. The proportion of the target "decrease of cardiovascular mortality of the population" in 2023-2025 that can be achieved by using DAPT with ticagrelor instead of clopidogrel or ASA monotherapy was calculated.
Results. The use of ticagrelor as part of DAPT for patients with ACS will make it possible (compared to DAPT with clopidogrel or ASA) to contribute to achieving "decrease of cardiovascular mortality" target in the Russian Federation:
in 2023 — 8,0% due to expected prevention of 4443 cardiovascular deaths,
in 2024 — 30,3% due to expected prevention of 4753 cardiovascular deaths,
in 2025, 5366 cardiovascular deaths can be
Conclusion. The use of ticagrelor as part of DAPT for patients with ACS will contribute to achieving "decrease of cardiovascular mortality" target in the Russian Federation.
Therapy with a fixed-dose combination of amlodipine/indapamide/perindopril in patients with uncontrolled hypertension, obesity and stable coronary artery disease:
- promotes stable control and achievement of target blood pressure levels;
- improves cardiac structural parameters in the form of a decrease in the left ventricular mass index and a decrease in the left atrium volume index;
- is characterized by metabolic neutrality in relation to carbohydrate, lipid and purine metabolism;
- reduces the manifestations of chronic inflammation and the concentration of serum leptin and subcutaneous adipose tissue;
- along with a decrease in the adipocyte size of subcutaneous fatty tissue, it increases the sensitivity of tissues to leptin.
Aim. In an open-label clinical trial, to evaluate the effectiveness and impact on metabolic parameters of triple antihypertensive combination therapy with amlodipine, indapamide and perindopril arginine (perindopril A) in patients with hypertension (HTN) and stable coronary artery disease (CAD) in combination with abdominal obesity (AO), who have not had an adequate response to dual antihypertensive therapy for at least 4 weeks.
Material and methods. The study included 68 adult patients aged 42 to 64 years (51 (47; 60) years) with AO, stable CAD and uncontrolled HTN, despite treatment with two drugs: an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor and a thiazide and thiazide-like diuretic. In the study, patients, in accordance with the general characteristics of the drug, after prescribing a free triple-dose combination of amlodipine, indapamide, perindopril in appropriate dosages, received one of the following combination of amlodipine/indapamide/perindopril for 24 weeks: group 1 (n=34) — 10/2,5/10 mg and group 2 (n=34) — 5/1,25/5 mg, one tablet daily. The analysis of the primary endpoint was to assess the change in mean systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) in the sitting position from baseline to 24 weeks. Secondary efficacy endpoints included the proportion of patients achieving target mean SBP and DBP values for this category in the sitting position of 120-130 mm Hg and 70-79 mm Hg, respectively, at 12, 16, 20 and 24 weeks. Safety was assessed throughout the study. The effect on metabolic parameters was assessed at 24 weeks of the study.
Results. Sixty-seven (98,5%) patients completed the study. The mean decrease in blood pressure from the initial level (group 1159/96 mm Hg; group 2161/95 mm Hg) to 24 weeks (group 1 126/76 mm Hg; group 2 132/84 mm Hg) was significant (p<0,0001 for all). The proportion of patients who reached the target mean values of SBP (120-130 mm Hg) and DBP (70-79 mm Hg) in the sitting position by 24 weeks was 80,16% and 79,28% in group 1, respectively; in group 2 — 65,32% and 70,06%, respectively. No serious adverse events were recorded. Its administration, regardless of the doses of individual components in combination, was accompanied not only by metabolic neutrality in relation to carbohydrate, lipid and purine metabolism, a decrease in chronic inflammation, but was also associated with a decrease in serum leptin concentration and subcutaneous adipose tissue, an increase in tissue sensitivity to leptin, as well as a decrease in the size of adipocytes in subcutaneous fat.
Conclusion. Triple fixed-dose of amlodipine/indapamide/perindopril in two different dosages is effective, safe and well tolerated in patients with HTN and stable CAD in combination with AO.
КЛИНИКА И ФАРМАКОТЕРАПИЯ. МНЕНИЕ ПО ПРОБЛЕМЕ
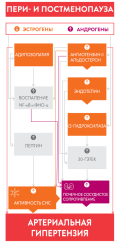
An important role in the development and evolution of hypertension in females is applied to sex hormones. Estrogen deficiency and hyperandrogenism, characteristic of periand postmenopause, are links in the pathogenesis of hypertension in this period of a woman's life and are accompanied by an increase in sympathetic nervous system activity, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activation, salt sensitivity, abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome, left ventricle hypertrophy, left atrial dilatation with a high risk of atrial fibrillation, stroke and heart failure development. The paper discusses antihypertensive therapy during periand postmenopause, effectiveness and tolerability of different drug classes. Special attention is paid to the mechanism of action of selective I1-imidazoline receptor agonist moxonidine, which in women during this period both effectively reduces high blood pressure and has a beneficial metabolic effect, what is documents in studies of monotherapy, combined antihypertensive therapy with major classes and in combination with menopausal hormone therapy. The paper presents the joint expert opinion concerning above mentioned issues.
- Adherence to treatment in patients with heart failure (HF) is not optimal and requires improvement.
- High adherence to treatment in patients with HF can reduce mortality and improve their quality of life, without significantly increasing financial costs.
- The problem of adherence of patients with different HF phenotypes depending on LVEF is not well represented in the literature.
The problem of rational management of patients with heart failure (HF) remains extremely relevant due to its increasing incidence and poor prognosis. Based on current guidelines, therapy for patients with HF involves systematic and long-term use of many medications, and their effectiveness largely depends on the quality of the patient’s compliance. Pharmacotherapy of older patients with HF is complicated by metabolism and the coexistence of many diseases associated with polypharmacy, which significantly reduces the response to therapy. Insufficient adherence to treatment has been proven to reduce the quality of life of patients. Currently, three HF phenotypes have been identified, depending on the left ventricular ejection fraction. However, the number of studies examining the characteristics of patient adherence in different phenotypes is limited, which requires further research. The article is an analytical review devoted to various aspects of adherence to treatment in patients with HF. The terms and concepts associated with compliance, the history of its research, the main modern approaches to pharmacotherapy of HF for different phenotypes are briefly covered. The results of a number of large clinical studies are presented, including the assessment of adherence in patients with HF and its relationship with prognosis.
- The combination of beta-blockers and non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers should not be used in routine practice.
- Their use is possible in patients with stable angina or myocardial infarction with insufficient anti-ischemic effectiveness and the impossibility of revascularization and/or uncontrolled tachycardia when treated with beta-blockers in maximum tolerated doses.
- This combination is applicable to control the ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation after excluding the true cause of high-frequency atrial fibrillation.
One of the most effective medications used for various cardiac diseases and syndromes to improve symptoms and, in some cases, prognosis, are betablockers (BBs) and calcium channel blockers (CCBs). The combination of BBs and dihydropyridine CCBs has a synergistic clinical effect and is well tolerated. The clinical effects of a combination of beta blockers and non-dihydropyridine CCBs (verapamil, diltiazem) are also synergistic. However, this combination increases the incidence of side effects and complications of drug therapy.
The article discusses the controversial issues of such a combination and substantiates the main conclusion that the discussed combination is not applicable in routine practice. This position should be clearly reflected in all Russian cardiology guidelines. However, the article discusses the possible combined use of BBs with nondihydropyridine CCBs in isolated cases, excluding contraindications, taking into account almost daily monitoring of tolerability, individual characteristics of the patient and by decision of a medical team.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY. LITERATURE REVIEW
- Previous studies have proven that myocardial fibrosis is manageable and reversible only with timely therapeutic intervention, making its early detection and evaluation crucial.
- Novel therapeutic strategies for inhibiting fibrosis at cardiorenal continuum will slow the progression of heart failure and increase the life expectancy of patients.
Heart failure (HF) is an urgent public health problem worldwide. A fundamental role in HF progression is played by fibrosis, which causes structural myocardial and vascular changes. In this regard, it seems relevant to search for pathogenetically justified HF therapy, aimed at slowing the myocardial fibrosis progression. The results of EMPA-REG OUTCOME study showed that glucose-lowering drugs, namely sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, have a positive effect on HF course, reducing cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization rate of patients for decompensated HF. Large-scale studies showed the antifibrotic properties of SGLT2 inhibitors. The review article presents the results of experimental studies on the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in animals. A number of mechanisms for the implementation of the antifibrotic properties of SGLT2 inhibitors affecting the cardiovascular system have been described. It seems relevant to further study SGLT2 inhibitors in clinical trials in order to identify and correct the pathogenetic mechanisms of myocardial fibrosis.
КЛИНИКА И ФАРМАКОТЕРАПИЯ. КЛИНИЧЕСКИЙ СЛУЧАЙ
Patients after heart transplantation (HT) are at very high risk for cardiovascular disease. Protocols for the management of heart recipients include the initiation of lipid-lowering therapy (LLT), regardless of sex, age and origin of heart failure. Given drug interactions and the risk of post-transplant complications, the LLT possibilities are limited in the transplanted population. The paper presents first Russian experience of using siRNA LLT for the treatment of dyslipidemia in solid organ transplant recipients.
ПРОГНОЗИРОВАНИЕ И ДИАГНОСТИКА. ОРИГИНАЛЬНЫЕ СТАТЬИ
- A novel approach to assessing left ventricular (LV) systolic function using global longitudinal strain and afterload compensates for the shortcomings of routine ejection fraction (EF) determination.
- The sensitivity and specificity of myocardial function parameters in predicting mildly reduced and reduced EF after myocardial infarction (MI) has been established.
- The use of these indicators in the acute period of myocardial infarction to determine the risk of reduced LV global contractile function and a personalized approach to cardiac rehabilitation is of clinical value.
Aim. To study the diagnostic value of myocardial function parameters to assess their predictive ability in relation to left ventricular (LV) global contractility in patients after myocardial infarction (MI).
Material and methods. The final analysis included 97 patients with MI aged 55,9±8,6 years. We performed standard two-dimensional echocardiography and speckle tracking echocardiography with analysis of following myocardial function parameters: global work index (GlobalWI, mm Hg %); global constructive work (GlobalCW, mm Hg %); global wasted work (GlobalWW, mm Hg %); global work efficiency (GlobalWE). The probability of ejection fraction (EF) reduction was analyzed using ROC curves using three criteria. The function parameters with the maximum sum of sensitivity and specificity were selected as the cut-off point.
Results. On days 7-9 after MI, depending on the EF, patients were divided into 3 groups: "REF" — patients with EF <40%); "MREF" — with EF from 40 to 49%, and "PEF" — patients with EF ³50%. By the 24th week, GlobalWI increased by 23% in the PEF group and by 33% in the MREF group. In the REF group, there was a gradual decrease in GlobalWI until the end of the study. In the PEF group, GlobalCW increased by 21% by week 24. By the end of follow-up, an increase in GlobalWW of 15% was observed in the REF group. GlobalWI, GlobalCW and GlobalWW were found to have the highest sensitivity values (60%) for reduced EF, ranging from 4049% at 24 weeks from the index event. GlobalWW had the highest specificity value (80%). With regard to a decrease in EF <40% by week 24, the GlobalWW had the highest sensitivity (50%) and specificity (70%).
Conclusion. Parameters of myocardial function have diagnostic and prognostic value for assessing LV systolic function after MI. Already in the acute period, myocardial function parameters can be used to determine the risk of decreased LV global contractility.
- After the end of chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer receiving doxorubicin, genotype 6A/6A, allelic variant 6A rs35068180 of the MMP-3 gene, genotype AA and allelic variant A rs2232228 of the HAS3 gene can be considered as predictors of early cardiotoxicity.
Aim. To evaluate the relationship of polymorphic variants rs2232228 of the HAS3 gene, rs8187710 of the ABCC2 gene, rs35068180 of the MMP-3 gene with cardiotoxicity after the end of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer.
Material and methods. The study included 100 patients (women, mean age 52,5±9,4 years) diagnosed with breast cancer who received anthracycline antibiotics (doxorubicin, total dose 240 mg/m2 or 360 mg/m2). Echocardiography was performed before and after the end of chemotherapy. Polymorphic status of selected targets was determined using the real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results. After the end of chemotherapy, based on the changes of left ventricular ejection fraction and global longitudinal strain, cardiotoxicity (CT) was detected in 20 patients. There were following significant differences between subgroups: rs8187710 of the ABCC2 gene — not identified; rs2232228 of the HAS3 gene — genotype AA, odds ratio (OR) 3,37 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1,14; 9,97) and allelic variant A, OR 2,17 (95% CI 0,98; 4,80) are significantly more common (p<0,05) in the cardiotoxicity+ subgroup; rs35068180 of the MMP-3 gene — genotype 6A/6A, OR 2,53 (95% CI 0,93; 6,88) and allelic variant 6A, OR 2,19 (95% CI 1,08; 4,44) are significantly more often (p<0,05) in the cardiotoxicity+ subgroup.
Conclusion. Genotype 6A/6A, allelic variant 6A rs35068180 of the MMP-3 gene, genotype AA and allelic variant A rs2232228 of the HAS3 gene can be considered as predictors of early cardiotoxicity after the end of chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer receiving doxorubicin.
- One of the factors of premature and progressive course of atherosclerosis is familial hypercholesterolemia (FH).
- The most significant predictors of carrying pathogenic LDLR mutations are the levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), family history of coronary artery disease (CAD), as well as previous coronary bypass surgery; pathogenic APOB mutations — LDL-C, family history of cerebrovascular accident or CAD, arcus senilis.
- Diagnostic criteria for potential FH vary among different patient groups. Their diagnostic significance depends on sex, and in women, on reproductive status.
Aim. To analyze the clinical characteristics of carriers of pathogenic LDLR and АРОВ mutations, as well as the prognostic value of Dutch Lipid Clinic Network Score (DLCNS) as applied to carriage of АРОВ or LDLR.
Material and methods. The study included 1233 outpatient lipid clinic patients. Biomaterial samples from 421 patients with the hereditary dyslipidemia were studied using Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) to identify carriage of familial hypercholesterolemia (FH)-associated genes (LDLR, АРОВ, PCSK9, LDLRAP1), as well as polymorphism of the APOE gene. Statistical processing was performed using descriptive statistics methods.
Results. According to the data obtained, the most significant predictors of pathogenic LDLR mutations are the levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), family history of coronary artery disease (CAD), and previous coronary artery bypass grafting. The level of LDL-C, family history of cerebrovascular accident or CAD, and arcus senilis were more significant for verifying the carriage of pathogenic АРОВ mutations. Using screening potential carriers of FH using the DLCN or Simon-Broome diagnostic criteria, the probability of FH may be underestimated due to the discrepancy between the scale criteria and the prognostic contribution of clinical or anamnestic data. These scales do not take into account the estrogen status of potential female carriers of FH.
Conclusion. Thus, diagnostic criteria for identifying potential FH vary among different patient groups. Their diagnostic significance depends on sex, and in women, on reproductive status. Only part of DLCN and Simon-Broome criteria can be applied to assess the FH likelihood, and to a greater extent for carriage of LDLR, but not АРОВ.
ПРОГНОЗИРОВАНИЕ И ДИАГНОСТИКА. ОБЗОР ЛИТЕРАТУРЫ
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) has socio-economic significance due to late diagnosis and financial costs of its treatment.
- OSA is associated with a high risk of cardiovascular mortality, as well as a range of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases.
- In Russia, there are no clear guidelines that would allow clinicians to refrain from implanting a pacemaker in the effective treatment of OSA.
In recent decades, there has been increased interest in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), especially in patients with a combination of OSA and sleep bradyarrhythmias. Worldwide, the diagnosis of OSA is steadily increasing. Increasingly, clinicians have begun to use CPAP therapy to treat sleep-related bradyarrhythmias. But in world practice there are no unambiguous guidelines for the management of this group of patients.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)