РКЖ. Образование, номер 2-2020
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
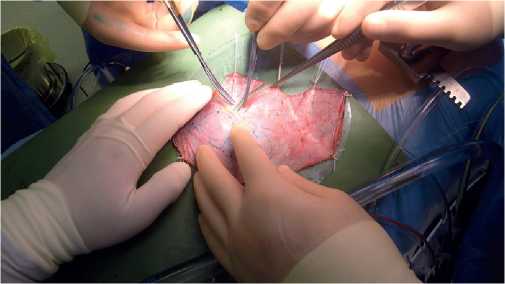
Aim. To analyze the short-term outcomes of Ozaki procedure.
Material and methods. This retro-prospective multicenter study included 724 patients with aortic valve (AV) disease, who underwent AV neo-cuspitization (AVNeo) from 2015 to 2019. The register included 395 (54,5%) men and 329 (45,5%) women. The median age of patients was 63 (57-67) years (minimum age, 10 years; maximum age, 83 years). A total of 496 (68,6%) patients had aortic stenosis, 44 (6%) — aortic regurgitation, 184 (25,4%) — aortic stenosis and regurgitation. Infective endocarditis as a cause of AV disease was diagnosed in 23 (3,2%) patients. NYHA class III-IV heart failure was in 348 (48%) patients. Atrial fibrillation was registered before surgery in 141 (19,5%) patients.
Results. In total, 314 (43,4%) patients underwent a single intervention (AVNeo), while the remaining 410 (56,6%) patients underwent combined operations. Access to the heart was performed through a median sternotomy in 687 (95%) patients, and in 37 (5%) patients through a ministernotomy. The median cardiopulmonary bypass time was 130 (110-130) min, while the myocardial ischemic time — 104 (86-122) min. In-hospital mortality was 1,6%. The maximum and mean pressure gradient after surgery were 10,9 (7,4-14,8) mm Hg and 5,3 (3,5-7,3) mm Hg, respectively. The AV effective orifice area (EOA) and indexed EOA after surgery were 3 (2,5-3,9) cm2 and 1,6 (1,3-2) cm2/m2, respectively. Thirteen (1,8%) patients received a pacemaker. Acute renal failure was recorded in 4 (0,5%) patients, stroke — in 3 (0,4%), and sternal infection — in 10 (1,4%).
Conclusion. The Ozaki procedure is feasible and reproducible, has good shortterm outcomes with excellent hemodynamic parameters. Further research is needed to assess long-term results.
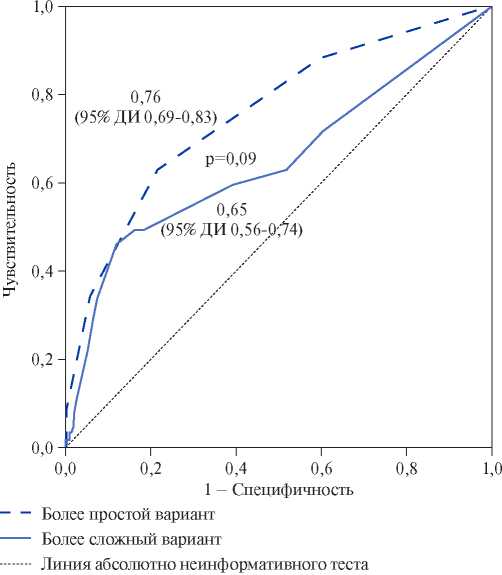
Aim. To create a new prognostic scale for in-hospital mortality risk assessment in patients with pulmonary embolism (PE).
Material and methods. The study was carried out on the basis of Russian register of acute pulmonary embolism SIRENA.
Results. Based on the Russian register of acute pulmonary embolism SIRENA (n=609; women — 50,7%; mean age — 63,0±1,5 years), independent predictors of in-hospital death were determined: left ventricular ejection fraction <40%, immobilization in the last 12 months, creatinine clearance <50 ml/min, syncope as a PE symptom, cyanosis at admission. Each of these factors with a value of 1 became a component of the novel SIRENA score. At the score of 0, 1, 2, 3 and more, in-hospital mortality was 3,1%, 7,0%, 16,7% and 40,0%, respectively. Mortality with a SIRENA score <2 (low risk) was 5,0%, and with a score ≥2 (high risk) — 24,3% (relative risk (RR), 4,87; 95% confidence interval (CI), 2,97-7,98; p<0,001). Predictive sensitivity and specificity for in-hospital mortality were 62,7% and 78,5%, respectively. The area under the ROC curve was 0,76 (95% CI, 0,690,83), which did not differ significantly from sPESI score — 0,73 (95% CI, 0,66-0,80). With a high risk for sPESI and SIRENA, the mortality was 27,1%, which was significantly higher compared to patients with a high risk only for sPESI — 13,9% (RR, 1,94; 95% CI, 1,36-2,82; p<0,001), but did not differ significantly compared with patients at high risk according to SIRENA score — 24,3% (RR, 1,11; 95% CI, 0,75-1,65; p=0,78).
Conclusion. Based on the Russian register of acute pulmonary embolism, the SIRENA score was developed, which has a high accuracy (sensitivity, 62,7%; specificity, 78,5%) in predicting in-hospital mortality.
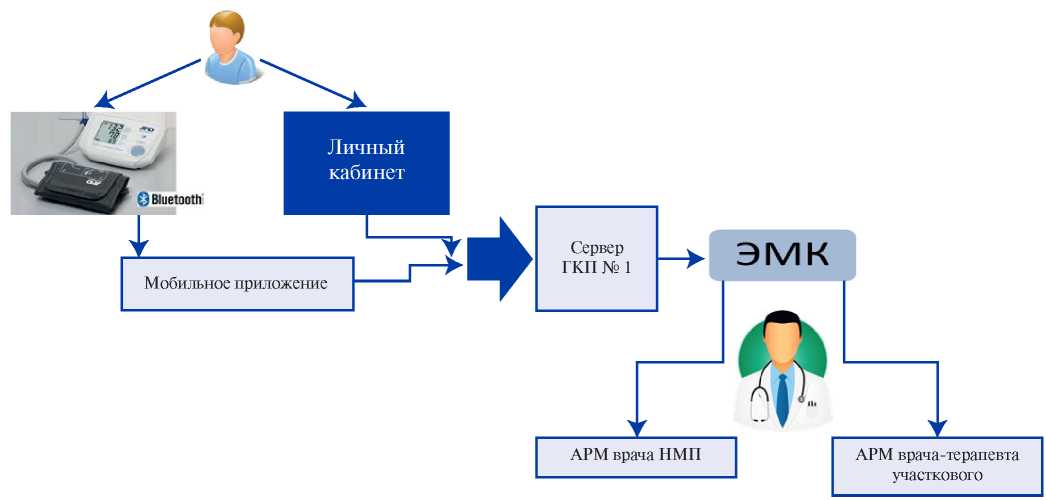
Aim. In a pilot project, to evaluate the effectiveness of remote blood pressure (BP) monitoring in outpatients followed up for hypertension (HTN).
Material and methods. A total of 1,121 patients (707 women and 414 men) with hypertension were included in the pilot project (mean age, 52,0±12,0 years; BP, 151,4±9,1/96,9±10,3 mm Hg). Patients independently measured BP and entered the values into self-management paper diaries (n=886), in digital form to their personal account (n=200), or transmitted data from BP monitor using installed mobile application (n=35). Each of the three groups was assessed at baseline and after 6 months. We assessed achievement of BP targets, medication adherence using the Morisky Green scale, the prevalence of patients with fixed-dose antihypertensive therapy, and the ambulance call rate.
Results. Prior to the study, 15,2% (n=171) of hypertensive patients regularly monitored their BP. After 6 months, the mean systolic BP decreased from 151,4±9,1 to 135,5±10,1 mm Hg (p<0,01), diastolic BP — from 96,9±10,3 to 85,8±6,3 mm Hg (p<0,01). The proportion of patients adhering to treatment (Morisky Green score of 4) increased from 17,9 to 55,4%, the frequency of prescribing dual antihypertensive therapy — from 25,8 to 43,3%, triple therapy — from 11,5 to 22,9%, fixed-dose combinations — from 25,4 to 51,6%. At the same time, the proportion of patients who achieved the target BP values increased from 14,5 to 43,1%, while the ambulance call rate decreased from 19,3 to 16,9%.
Conclusion. The use of remote BP monitoring methods, including BP monitors with automated data transmission, increases the prescription rate of combined antihypertensive therapy and proportion of patients who achieved the target BP, as well as decreases the ambulance call rate.
CML), the accepting inhibitors tyrosine of kinases (TKI) I and the II generations (TKI1 and TKI2 respectively), and development of arterial hypertension.
Material and methods. Examination of 137 patients with CML in the chronic phase (CP) is conducted, the median of age — 47 years. 24 of them were with for the first time the verified diagnosis of CML and earlier did not accept TKI, they have made group of control. Other patients accepted TKI: 39 patients — imatinib 400 mg/day, 36 — dasatinib 100 mg/day, 38 — nilotinib 800 mg/day) more than 6 months. In biochemical analysis of blood indicators of lipidic range were defined. Level detection of ET-1 and VEGF was made by means of enzyme immunoassay. To all patients measurement of the heart rate (HR) and the arterial blood pressure (ABP) on both hands at an interval of 2 minutes from previous was once taken.
Results. In group of patients from CML accepting nilotinib authentically significant increase in levels of systolic and diastolic ABP (р<0,001) in comparison with group of control, with group of the patients accepting imatinib and dasatinib is noted. The most serious changes of lipidic range are noted at the patients accepting nilotinib. In all groups statistically significant increase in level of C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, homocysteine, endothelin-1 and VEGF in comparison with group of control is revealed. The most expressed changes are found in group of the patients accepting nilotinib, values of parameters of C-reactive protein, fibrinogen, homocysteine, endothelin-1 and VEGF are changed authentically (р<0,001) and statistically significantly differ in comparison with group for the first time of the revealed patients with CML and groups of reception of imatinib and dazatinib.
Conclusion. As a result of the conducted research endothelium variation of a function at patients from CML accepting TKI1 and TKI2 is revealed. The above-stated indicators can be used as additional diagnostic criteria for assessment of risk of development of arterial hypertension in patients with CML at reception of TKI.
CLINICAL CASES
We present a case report of a patient with a previously identified cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL), who was admitted due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), confirmed by polymerase chain reaction and computed tomography. Examination and treatment of these patients presents certain difficulties due to the large number of thromboembolic complications caused by a combination of congenital and infectious angiopathies. CADASIL syndrome and COVID-19 were manifested by the progression of neurological symptoms and increasing cognitive impairment. During therapy, there was a positive change with a gradual regression of these disorders.
REVIEW
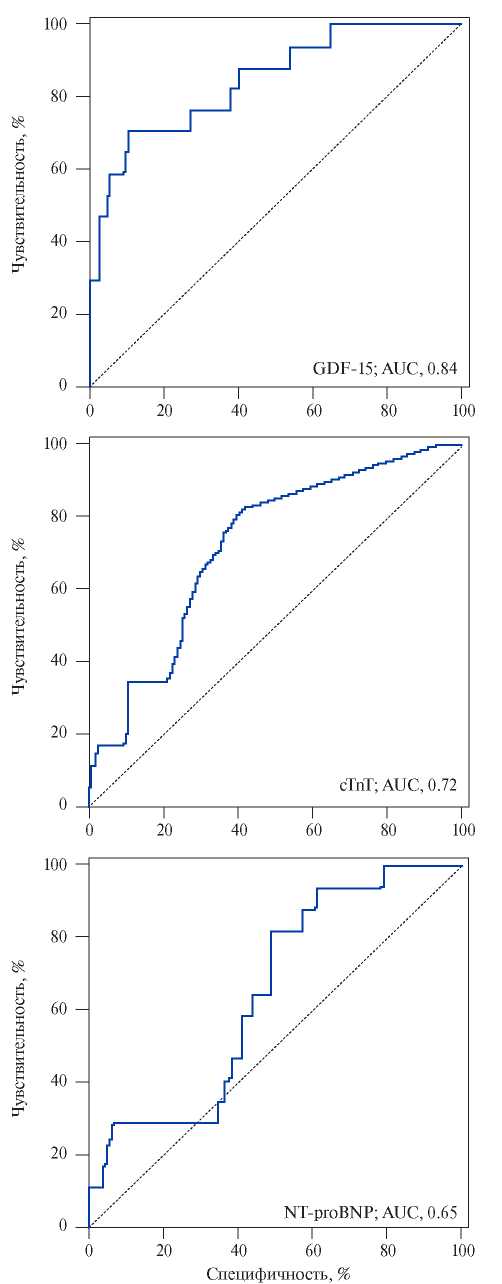
Pulmonary embolism (PE) ranks third in the structure of death causes among all cardiovascular diseases after myocardial infarction and stroke. That is why the timely and earliest possible diagnosis of venous thromboembolism is of particular importance, which will help improve both short-term and long-term patient prognosis. Given the low specificity of current laboratory parameters, such as D-dimer, NT-proBNP, cardiac troponin I, there is an urgent need to search for new biomarkers that can improve the quality of detection and stratification of VTE, including PE. A diagnostic and prognostic test for PE must be accurate, safe, easily accessible and inexpensive, as well as reproducible and non-invasive.
This review presents the currently available literature data on the latest laboratory parameters that characterize right ventricular dysfunction due to PE and provide an evidence base for stratification of the death risk in this category of patients.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, including pre-existing and gestational hypertension, preeclampsia and eclampsia, complicate up to 10% of pregnancies and represent a significant cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. Despite some differences in guidelines, there is consensus that severe hypertension and mild hypertension with organ dysfunction should be managed. However, achieving target values below 160/110 mm Hg remain controversial. The review presents current data on definition, classification, therapy goals and principles used in hypertensive disorders during pregnancy and in the postpartum period in accordance with national and international guidelines.
Natriuretic peptides (NPs) are key diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for patients with heart failure (HF). The main mechanism for increasing serum NP levels, which is characteristic of heart failure, is secretion in response to myocardial wall distention. At the same time, according to Russian and foreign literature, an increase in NPs is reported in a number of many other conditions that are not associated with HF. The study of these causes and mechanisms is necessary to improve the differential diagnosis of HF.
This article discusses the mechanisms of increasing NPs and their diagnostic value in heart failure, as well as a number of other conditions, such as acute coronary syndrome and coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, exercise, kidney failure, taking cardiotoxic drugs (chemotherapy) and sacubitril/valsartan. The article also provides data on identifying NPs in non-invasively obtained biological fluids (urine and oral fluid).
Raised life expectancy of patients with cardiovascular diseases (CVD), due to continuous progress in drug treatment options and widespread use of innovate technologies, increase the burden of CVD on healthcare system. The development of human resources by highly qualified specialists is of fundamental importance. For the rational use of human resources to achieve the targets of federal project on the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, it is necessary not only to analyze the actual situation with medical staffing, but also the potential effects of staff shortages and imbalances on mortality. The review presents evidence of associations between staffing and quality of care and CVD outcomes.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)