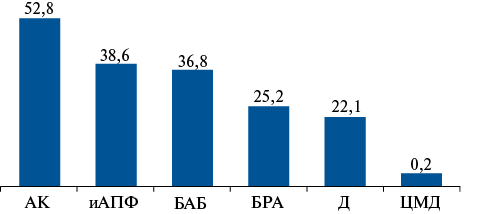ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Aim. To study the pharmacoepidemiological aspects and efficiency of hypertension (HTN) control at the level of primary health care in the Kyrgyz Republic (and their compliance with modern clinical guidelines.
Material and methods. Within the project "Analysis and evaluation of factors determining the control of management of patients with hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases in the Kyrgyz Republic", supported by the Ministry of Health of the Kyrgyz Republic and the Swiss project "Effective management and prevention of non-communicable diseases in Kyrgyzstan", we studied compliance of antihypertensives' prescription with modern clinical guidelines and the effectiveness of HTN control at the level of primary health care in the Kyrgyz Republic. We analyzed the medical records of patients registered with a diagnosis of HTN for 2022. Family doctor groups (FDGs) were used as the Primary Sampling Unit (PSU), which were sampled using probability sampling proportional to the size of the general population. Medical records of patients from FDGs were used as the Secondary Sampling Unit. We selected 40 medical records of patients from each FDG. A total of 3675 medical records of patients with hypertension were studied throughout the Kyrgyz Republic.
Results. The age of patients from the selected 3675 medical records ranged from 19 to 93 years (mean age, 62±9 years). Most of the examined individuals were women (2567 respondents, or 69,9%), while men were represented by 1108 respondents (30,1%). According to the study of medical records, the proportion of individuals with HTN covered by treatment was 86,6% (including 90,3% of women and 84,6% of men, p<0,001), of which 43,8% of patients received monotherapy, 39,4% received dual therapy, 14,4% received triple therapy, and 2,4% of respondents received 4 or more antihypertensive drugs. On average, out of the total number of people receiving antihypertensive drugs, there were 1,76 drugs per patient with hypertension, and this parameter was slightly higher in women (1,83) than in men (1,66). The proportion of effectively treated patients in general among people with HTN was 42,1% (43,5% in women and 35,5% in men, p<0,0001). Hypertension control in the study cohort was 42,1%, and this parameter was also higher in women than in men (44% versus 37,8%, respectively, p<0,001).
Conclusion. The study revealed a high proportion of patients covered by treatment using modern antihypertensive drugs and an increase in the effectiveness of treatment and control of HTN over the past decade in the Kyrgyz Republic.
SUPPORTING A PRACTITIONER
- Since 2000, among patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS), patients with ST-segment elevation (STE) and non-STE (NSTE) ACS have been distinguished.
- The era of mechanical reperfusion creates the preconditions for novel concept — occlusive and non-occlusive myocardial infarction.
- When developing clinical guidelines for ACS when determining indications for emergency coronary revascularization, along with the principle of STE and NSTE, the principle of occlusive and non-occlusive myocardial infarction should be used.
Since patients with occlusive coronary artery thrombosis benefit more from emergency reperfusion, after the widespread introduction of thrombolytic therapy, the concept of Q-wave and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction was replaced by the concept of ST-segment elevation (STE) and non-STE (NSTE) acute coronary syndrome (ACS). But at present, due to the spread of mechanical reperfusion, this concept does not seem to be fully perfect. The electrocardiographic (ECG) diagnostic method allows, among patients with NSTE-ACS, to identify a group of patients with occlusive and/or prognostically unfavorable hemodynamically significant coronary lesions, as well as to provide them with timely percutaneous coronary intervention as early as possible and to improve outcomes. This article rationales changing approaches to the management of patients with NSTE-ACS and analyzes in detail the currently known ECG criteria for occlusive and/or prognostically unfavorable coronary lesions.
CLINICAL CASES
- Stenting of critical coarctation of the aorta (CoA) helps stabilize the child and safely perform radical surgery for congenital heart disease within 2-3 weeks.
- Case report of successful step-by-step surgery of critical CoA in a newborn with multiple organ failure with CoA stenting and subsequent radical surgery was demonstrated.
Introduction. Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) is a congenital severe narrowing of the aortic isthmus, which in turn is often accompanied by impaired organ perfusion or even cardiogenic shock. In newborns with critical CoA in the case of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) closure, the clinical condition of patients with this congenital heart defect (CHD) sharply worsens and leads to multiple organ failure. In this group of children, mortality ranges from 30 to 50% of infant mortality from CHD. This case demonstrates the positive effect of palliative stenting of a narrowed section of the aorta, which made it possible to safely perform radical surgery for CHD.
Case description. Nine-year-old male patient with body weight of 3,5 kg and body length of 53 cm was admitted to the clinic with a diagnosis of CHD: Critical CoA. Secundum atrial septal defect. PDA. Multiple organ failure. Taking into account the severe comorbidity status in the form of multiple organ failure, the high risk of necrotizing enterocolitis, case conference decided to perform a step-by-step CHD treatment as follows: palliative endovascular stenting of critical CoA, followed by radical surgery after stabilization of the patient's condition. The plan was successfully implemented.
Conclusion. Сritical CoA stenting can be used as a bridge to radical surgery of the defect in newborns with multiple organ failure. This palliative intervention helps to stabilize the child for up to 3 weeks and more safely perform radical surgery of CoA.
- Patients with deteriorating renal function should be maintained on greatest possible nephroprotective therapy.
Chronic kidney disease is one of the most important diseases in comorbid patients with cardiovascular disease. To reduce the risk of cardiovascular and renal complications, such patients should receive renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, statins and sodiumglucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors. However, deterioration of kidney function is still common in these patients, especially in the presence of risk factors. This case illustrates the decline in renal function in a patient with obesity, uncontrolled hypertension, type 2 diabetes and atrial fibrillation. The management strategy for such patients is given.
- Renal artery atherosclerosis occurs in 1-5% of patients with hypertension, reaching 7% in individuals over 65 years of age.
- Considering the limitations of drug treatment and the high prevalence of uncontrolled hypertension, experts discuss methods of endovascular treatment, such as angioplasty and stenting.
- In borderline renal artery stenosis, no significant revascularization effect has been demonstrated, so an alternative way to achieve target blood pressure is possible — renal denervation.
Introduction. Renovascular hypertension is one of the most severe types of hypertension in terms of the choice of treatment strategy. Recent studies have not provided a clear answer to the question of which treatment approach (conservative or surgical) is most appropriate for these patients.
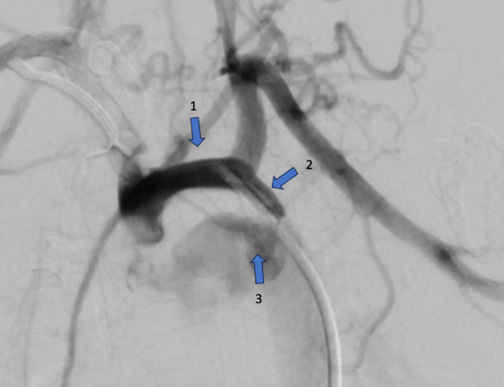
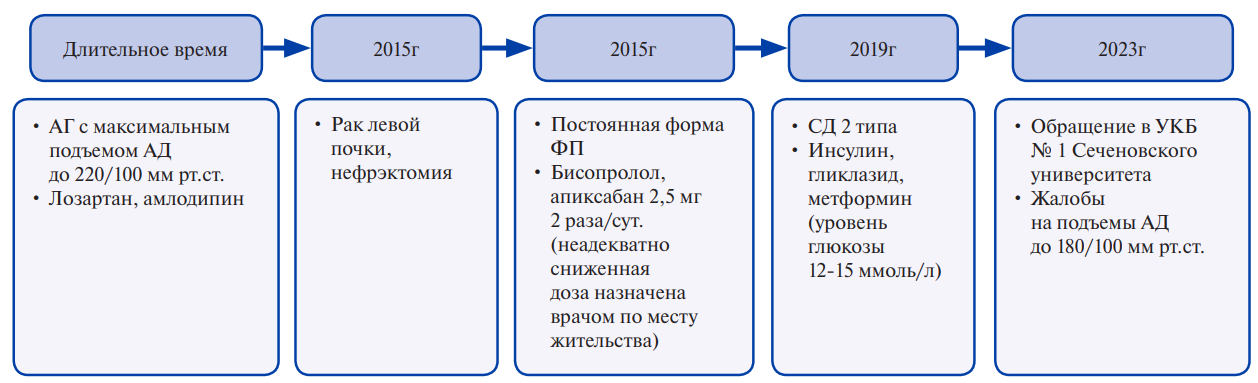
Brief description. The presented case describes a female patient with a longterm uncontrolled hypertension, whose examination revealed bilateral renal artery stenosis. Considering the debatable clinical effectiveness of revascularization of renal artery stenosis, the patient underwent distal renal artery denervation using multielectrode catheters. A decrease in blood pressure was shown. Follow-up of the patient demonstrated stable antihypertensive effect of the procedure, as well as its safety in case of impaired renal function.
Discussion. This clinical demonstrates the third way in the treatment of patients with renal arteries stenosis and resistant hypertension — renal sympathetic denervation. This method requires a separate controlled study with individuals with renal dysfunction, including renovascular origin.
- Post-implantation syndrome (PIS) is a systemic inflammatory reaction occurring early after endovascular aortic valve implantation.
- The pathophysiology underlying PIS is still not fully understood.
- Type of valve implanted may play a role in determining this inflammatory response. Current literature provides low evidence and no established algorithm regarding the type and duration of treatment for PIS.
- High glucocorticoid doses for PIS in some cases leads to a reduction of the inflammatory response with faster recovery of patients.
Introduction. The growing prevalence of transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) over the past few years has revealed a unique set of events and complications that require rapid identification and treatment to improve outcomes, often involving a multidisciplinary team.
Brief description. We present the case of a 79-year-old woman with severe aortic stenosis who underwent a TAVI procedure that was complicated postoperatively by hectic fever without an identified source of infection. After excluding all possible causes of fever, a diagnosis of post-implantation syndrome was made, and glucocorticosteroid therapy led to the patient's recovery.
Discussion. A systemic inflammatory response may occur after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair in some patients. This inflammatory response is called postimplantation syndrome and includes fatigue or other flu-like symptoms, fever, and laboratory signs of inflammation. Our case describes the difficulties in differential diagnosis of post-implantation syndrome as a possible complication of TAVI, and also demonstrates the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to such patients.
- A case of non-invasive and invasive diagnostics of transplant coronary artery disease in the post-transplant period and successful transluminal balloon angioplasty and stenting of the anterior descending artery, further patient management tactics are presented.
- The purpose of this report is to draw the attention to the early diagnosis of one of the complications after orthotopic heart transplantation — cardiac transplant vasculopathy.
Introduction. Today, heart failure (HF) is the most common natural outcome of diseases that are not diagnosed and treated in time. Despite the advances in cardiovascular pharmacotherapy, orthotopic heart transplantation is a generally recognized gold standard for the treatment of end-stage heart failure.
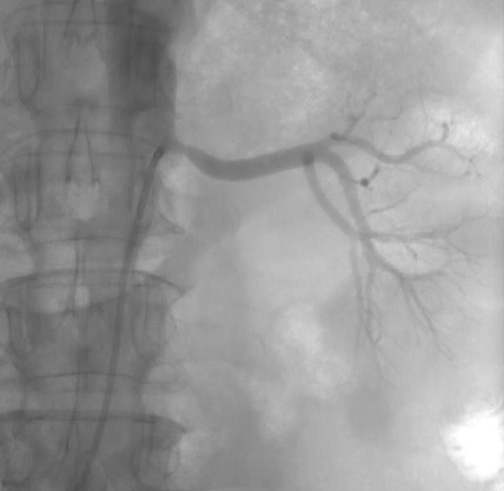
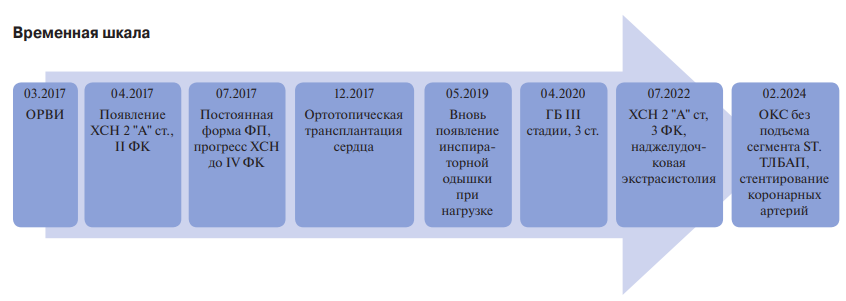
Brief description. The article describes a 55-year-old male patient admitted to the Cardiology Dispensary (Kabardino-Balkarian Republic) with a clinical picture of non-ST segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (ACS). Earlier in 2017, the patient underwent orthotopic heart transplantation (OHT) for end-stage HF due to dilated cardiomyopathy. Hypertension was registered 2,5 years after surgery, and clinical manifestations of HF were registered for 5 years. In 2024, coronary angiography revealed subtotal stenosis of 95% in the middle segment of the anterior descending artery. Intraoperatively, the consensus assessed the risk and made a decision on surgical endovascular treatment of the stenosis. The postoperative period was uneventful.
Discussion. The presented case is an example of timely diagnosis of coronary artery disease in a transplanted heart and successful transluminal balloon angioplasty and stenting of the anterior descending artery.
- Heart transplant patients are at high risk of complications during non-cardiac surgery.
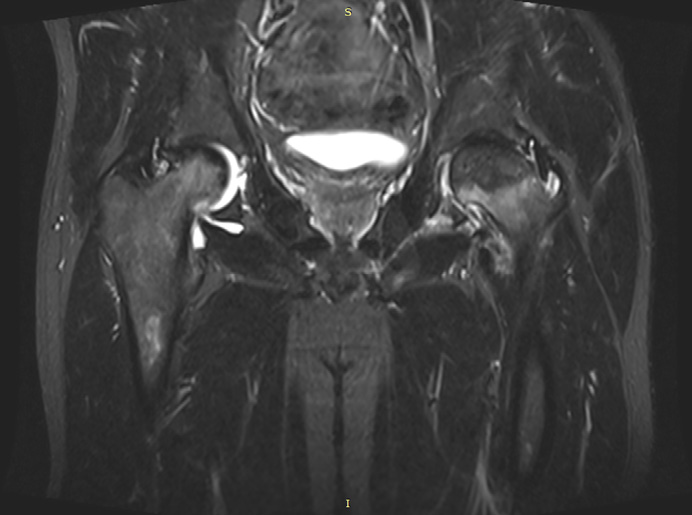
- Immunosuppressive therapy is a risk factor for osteonecrosis.
- A case report demonstrates successful hip replacement in a heart transplant patient on immunosuppression.
Solid organ transplantation is considered the most effective treatment for endstage heart, lung, pancreatic, liver, and kidney diseases. The increasing number of transplants performed, and long-term survival of recipients have contributed to an increase in the diagnostic rate of non-transplant-related diseases.
Heart transplant patients are at increased risk of complications when undergoing elective or emergency surgery. We report a case of hip replacement in a young man after orthotopic heart transplantation.
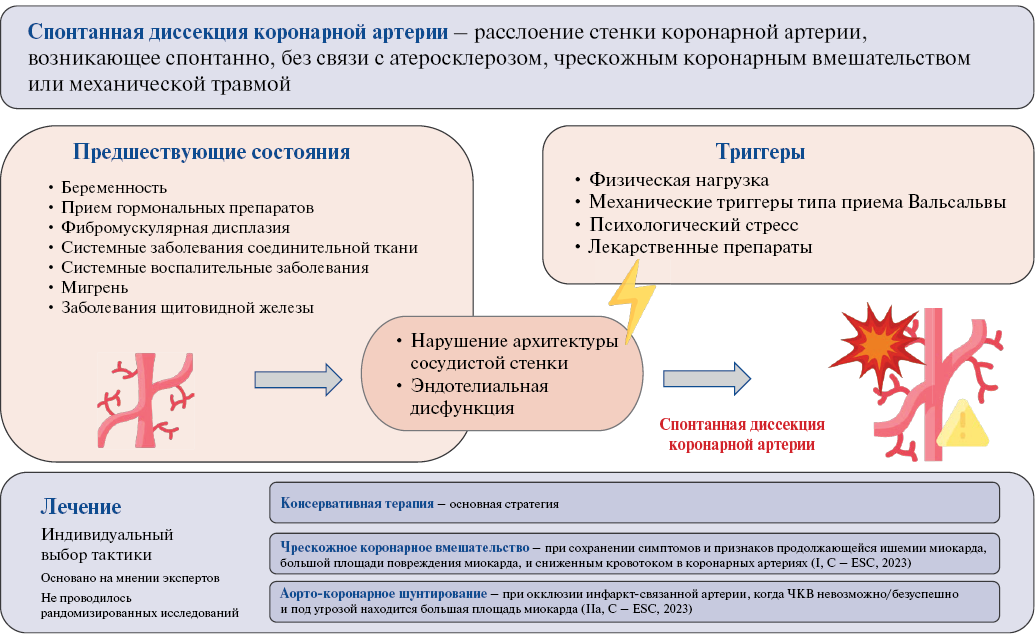
- Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) represents a rare cause of acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
- SCAD should be considered in the differential diagnosis of ACS, particularly in young women without risk factors for atherosclerosis.
- The management of patients with SCAD has not been studied in randomized trials, and recommendations are based primarily on expert consensus.
- The variety of SCAD clinical variants requires an individual approach to patient management, taking into account the characteristics of the disease course.
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) is defined as a spontaneous dissection of the coronary artery wall that occurs independently of atherosclerosis, percutaneous coronary intervention, or mechanical trauma. Its distinctive feature is high prevalence in young women. This condition is associated with pregnancy and hormonal changes. A number of risk factors have been identified, including vascular pathology (most commonly fibromuscular dysplasia), other hereditary connective tissue disorders, systemic inflammatory diseases, migraine, and thyroid diseases. Nevertheless, the precise mechanisms of the pathophysiological relationship remain to be elucidated, and risk factors cannot be identified in all patients, indicating the complex and incompletely understood nature of the disease. The present article presents a case series on the development of SCAD in women and a review of the predisposing factors for the disease.
- Patients with moderate COVID-19 are at increased risk of pulmonary embolism.
- Severe course of H1N1 influenza is also associated with an increased thromboembolism risk.
- There are features in risk factors, clinical performance of pulmonary embolism and prognosis in patients with viral pneumonia of various origins.
- We have summarized the analyzed literature data; this will be useful in practice for doctors of all specialties, especially cardiologists.
The article presents two case reports of pulmonary embolism in patients with viral pneumonia. In one case, in a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) survivor, while in the second case — in a patient with influenza. A comparative analysis of thromboembolism characteristics in two patients is consistent with the literature data and confirms the differences in its predictors and the different clinical picture. Pulmonary embolism is becoming an increasingly relevant disease for cardiologists. The importance of understanding the risk factors for pulmonary embolism and clinical picture aspects in patients with viral pneumonia in the current epidemiological situation with both a COVID-19 and seasonal pathogens, including the influenza virus, is emphasized.
REVIEW
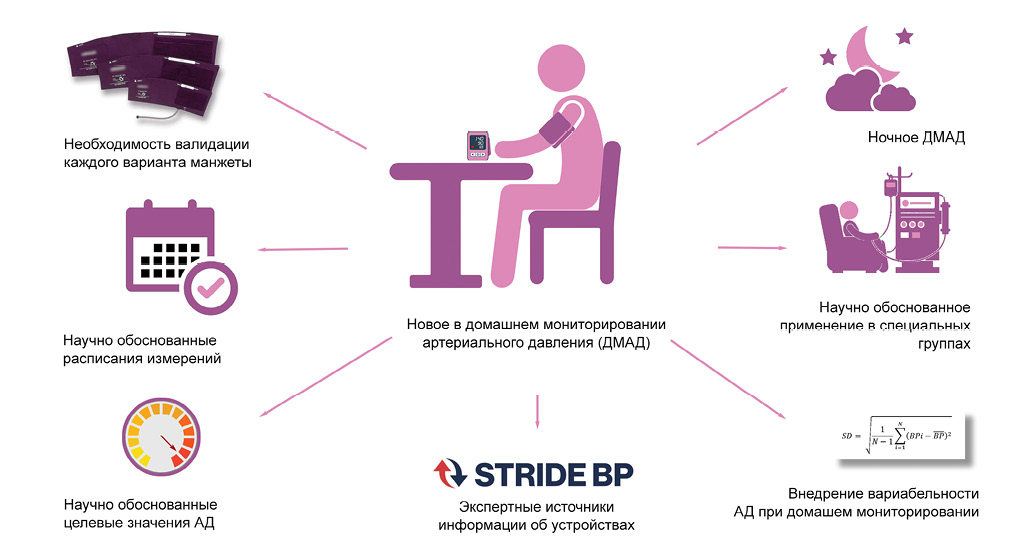
What might this study add regarding home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM)?
- The need for validation of each cuff type has been substantiated.
- Optimal measurement schedules and HBPM features in special groups have now been determined by studies.
- Target values have appeared in HBPM.
- Night-time HBPM has appeared.
- Calculation of home blood pressure variability is being introduced.
Over the past decade, methodological and clinical approaches to home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) have changed. The changes are so significant that they have led to differences between modern and traditional concepts of HBPM. The aim of this review was to briefly describe these differences.
- After diagnosis verification, there is a significant increase in the PH costs, with the main cost driver of PH-specific therapy.
- However, after verification of PH, a number of studies observed a decrease in costs not associated with therapy.
Aim. A systematic review of studies on pulmonary hypertension (PH) cost estimates.
Material and methods. A systematic literature search was performed for studies assessing the cost of PH published up to November 30, 2023. The search was carried out in the PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBACE databases for publications in English and in the RSCI database for articles in Russian according to inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Results. The systematic review included 13 studies. The mean direct costs per patient with PH after verification of the diagnosis per month ranged from 2023 to 9915 USD, while the median from 1141,5 to 8144 USD. Indirect costs were assessed in only 3 following studies: in Spain and USA, the mean indirect costs were 214 and 1226 USD per patient per month, respectively, while in Russia the median was 65 USD. The mean direct costs per patient with PH per month before diagnosis verification ranged from 1017 to 9723 USD. Indirect costs before diagnosis verification were assessed in only 1 study (median $102 per patient per month). After PH verification, in general, there was an increase in treatment costs with a decrease in other direct costs.
Conclusion. PH causes great socio-economic damage to society and healthcare system. A decrease in non-drug therapy costs after PH verification may indicate not only the clinical effectiveness of PH-specific therapy, but also its potential costeffectiveness with reduced costs.
- The substrate for reperfusion arrhythmias is a complex electrically inhomogeneous substrate, which specifies multiple reentry circuits.
- The incidence of life-threatening reperfusion arrhythmias ranges from 2,8% to 4,7%.
- Early reperfusion will save a larger number of cardiomyocytes from ischemic injury and helps reduce myocardial electrical instability.
The problem of ischemia-reperfusion injury, in particular, reperfusion arrhythmias, has remained controversial for many years. To date, there are no one frame of mind on the clinical and prognostic significance of tachyarrhythmias in the acute period of myocardial infarction. In addition, data on the incidence of reperfusion arrhythmias and related mortality are very contradictory. The review summarizes current concepts and results of studies devoted to the study of the clinical role of reperfusion arrhythmias. Their pathogenesis, structure, and impact on the long-term prognosis of patients are discussed. The need to study ischemia-reperfusion injury within the pharmacoinvasive strategy using modern thrombolytic agents is emphasized, which seems especially relevant given the Russian geographical features.
- With the increasing number of cardiac surgeries, there is interest in identifying the characteristics of the systemic inflammatory response.
- The prognostic value of normal preoperative white blood cell counts among cardiac surgery patients continues to be studied.
The high prevalence of cardiovascular diseases inevitably entails an increase in the number of annual surgical myocardial revascularization procedures. In this regard, the increasing risk of postoperative complications is obvious. The aim of this work was to analyze the available literature on the study of the systemic inflammatory response (SIR) in cardiovascular diseases with an emphasis on coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). The study of the mechanisms of SIR after cardiac surgery allowed attempts to suppress the activity of the cytokinin storm. The main significance of leukocytes in the initiation of SIR served as the reason for studying the prognostic value of the leukocyte level, both in the postoperative and preoperative periods. The article reflects data on the role of hematological markers and indices. In addition, the results of studies on the significance of a normal high level of leukocytes in the preoperative period are presented, since a negative prognosis was noted in such a group of people who underwent CABG. While remaining a widely accessible and inexpensive method, the assessment of the leukocyte formula, as well as the calculated hematological indices, acquire predictive value for postoperative complications and outcomes.
ISSN 2618-7620 (Online)