Перейти к:
Метаболически ассоциированная жировая болезнь печени при метаболическом синдроме
https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6541
Аннотация
В статье проанализированы современные представления о патогенезе, диагностике и влиянии на прогноз метаболически ассоциированной жировой болезни печени при метаболическом синдроме. Приведен обзор современных возможностей диагностики, немедикаментозной и медикаментозной терапии метаболически ассоциированной жировой болезни печени, а также проведен обзор влияния терапии коморбидной патологии на ее течение.
Ключевые слова
Для цитирования:
Драпкина О.М., Недогода С.В. Метаболически ассоциированная жировая болезнь печени при метаболическом синдроме. Российский кардиологический журнал. 2025;30(1S):6541. https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6541
For citation:
Drapkina O.M., Nedogoda S.V. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in metabolic syndrome. Russian Journal of Cardiology. 2025;30(1S):6541. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6541
Метаболически ассоциированная жировая болезнь печени (МАЖБП) рассматривается как ее поражение вследствие мультисистемной метаболической дисфункции с повышенным риском развития печеночных и сердечно-сосудистых осложнений [1-3].
Терминология
Попытки изменить привычные термины "неалкогольная жировая болезнь печени" (НАЖБП) и "неалкогольный стеатогепатит" (НАСГ) начались в начале 2000-х годов и общим подходом в них были предложения отразить связь с метаболическим синдромом (МС) [4-8]. В итоге ~5 лет назад появился термин МАЖБП [2][9][10]. Предпосылками к этому стали:
— неудовлетворённость используемыми критериями диагностики НАЖБП (их сложность для реальной клинической практики на фоне роста числа пациентов со стеатозом печени, использование метода "исключения" (злоупотребления алкоголем, лекарственного повреждения, вирусных гепатитов, аутоиммунных заболеваний [11]) при постановке диагноза;
— сложность выявления НАЖБП при наличии сопутствующих хронических неинфекционных заболеваний с метаболическими нарушениями [12-14].
Переход к термину "МАЖБП", который имеет понятные количественные критерии диагностики, позволяет выделить эту группу пациентов вне зависимости от коморбидной патологии [15] и вне зависимости от наличия избыточной массы тела/ожирения, сахарного диабета (СД) 2 типа и иных метаболических факторов риска [16][17]. Более того, использование термина "МАЖБП" и ее критериев диагностики позволяет выделить группу лиц с высоким риском метаболических нарушений [18] и рассматривать ее как с позиции повышенного риска сердечно-сосудистых осложнений, так и прогрессирования от стеатоза печени до стеатогепатита и фиброза [19].
Однако в настоящее время в нормативных документах, в т.ч. в клинических рекомендациях, утвержденных Минздравом России, используется термин НАЖБП1. Поэтому в настоящее время имеется параллелизм в использовании этих двух терминов при понимании того, что МАЖБП более современный и адекватный имеющимся представлениями о заболевании.
За последние 2 года определение МАЖБП стало все чаще использоваться в медицинской литературе, и недавние исследования показали, что глобальная распространенность МАЖБП выше, чем НАЖБП (39% vs 33% [20]). Кроме того, у пациентов с МАЖБП больше метаболических сопутствующих заболеваний по сравнению с пациентами с НАЖБП [20][21], а новые данные также свидетельствуют, что смертность от всех причин и сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний может быть выше при МАЖБП по сравнению с НАЖБП [22-25].
Эпидемиология
Принято считать, что частота НАЖБП в общей популяции составляет ~25% [26], а при МС — 43-67%, причем с увеличением числа симптомов МС частота фиброза печени возрастает, достигая максимального значения 30% [27]. При этом 42% лиц с НАЖБП имеют МС, 69% гиперлипидемию, 51-95% ожирение [28][29], 39% артериальную гипертензию и 22% СД 2 типа [26]. При СД 2 типа частота НАЖБП составляет 60-78% [30][31]. В Российской Федерации стандартизованные показатели распространенности индекса FLI (Fatty liver index) ≥60 по данным ЭССЕ-РФ3 составили 42,3% [32].
Особенности патогенеза
Можно считать доказанным, что повышение риска НАЖБП в 2,23 (95% доверительный интервал (ДИ): 1,28-3,89) раза напрямую ассоциировано с количеством висцерального жира по данным ультразвукового исследования и компьютерной томографии [33].
Наиболее распространенной теорией патогенеза НАЖБП до недавнего времени была концепция "двух-ударов" ("two-hit hypothesis"). "Первый удар" ("first hit") — накопление жира в печени (прежде всего триглицеридов (ТГ)), приводит к развитию инсулинорезистентности (ИР), а "второй удар" ("second hit") запускает процессы воспаления (повышение уровня провоспалительных цитокинов, прежде всего интерлейкина-6 и фактора некроза опухоли α-1, на фоне снижения уровня адипонектина) и фиброза. В последнее время появилась теория "множественных ударов" ("multi-hit hypothesis"), которая предполагает совокупное влияние факторов окружающей среды, генетических факторов, увеличение массы тела, повышение концентрации свободных жирных кислот в крови, появление эктопических жировых отложений и ИР [34]. Последняя является ведущим фактором в развитии НАЖБП [35, 36] поскольку усиливает липолиз, захват свободных жирных кислот печенью и активацию липогенеза в печени. Повышение уровня ТГ и липотоксичность вызывают развитие митохондриальной дисфункции и стресс эндоплазматического ретикулума, что приводит к повреждению гепатоцитов, апоптозу и фиброзу [34]. Схожую теорию предложили Virtue and Vidal-Puig [37]. Согласно этой теории, вследствие ограниченной способности жировой ткани к накоплению жира, образуются новые эктопические жировые депо в печени и мышцах, что способствует усилению ИР через липотоксичность. Образование адипоцитов из преадипоцитов из мезенхимальных стволовых клеток увеличивает возможность накопления ТГ в жировой ткани [38]. Известно, что ИР печени появляется, когда количество жировых отложений в ней достигает приблизительно 1,5%, а ИР мышц — при количестве жира в них 6,0%. Это позволяет рассматривать печень как "барометр" метаболического здоровья [39].
Особенности течения
Важно отметить, что чем большее количество симптомов МС имеется у пациента, тем выше у него вероятность наличия НАЖПБ. Традиционно можно выделить группу лиц с повышенным риском НАЖБП — пациенты старше 60 лет, с ожирением, повышением активности трансаминаз (в частности соотношением аланинаминотрансфераза/аспартатаминотрансфераза) [40].
При МАЖБП повышен риск развития сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний (отношение шансов (ОШ) 1,77; 95% ДИ: 1,26-2,48), ишемической болезни сердца (ОШ 2,26; 95% ДИ: 1,04-4,92; p<0,001), ишемического инсульта (ОШ 2,09; 95% ДИ: 1,46-2,98; p<0,001) [41], атеросклероза (ОШ 1,64; 95% ДИ: 1,42-1,89) [42] и патологии гепатобилиарной системы [43], а также гепатоцеллюлярного [44][45] и других видов рака [46].
Особенности диагностики
НАЖБП — хроническое заболевание печени, связанное с метаболической дисфункцией, при котором более чем в 5% гепатоцитов определяется макровезикулярный стеатоз1.
Диагноз НАЖБП устанавливается: 1) при подтверждении стеатоза печени (по данным визуализирующих исследований или гистологического исследования ткани печени); 2) наличии ≥1 факторов кардиометаболического риска; 3) исключении других ведущих причин развития жировой болезни печени1.
Критерии диагностики МАЖБП включают в себя накопление жира в печени, подтвержденное данными гистологического исследования, лучевой диагностики или биомаркерами крови, дополненное одним и более фактором кардиометаболического риска:
— индекс массы тела (ИМТ) >25 кг/м2 или окружность талии >94 см у мужчин, >80 см у женщин (либо выше верхней границы нормы, если пациент относится к этнической группе, для которой приняты другие нормы ИМТ и/или окружности талии);
— глюкоза натощак >5,6 ммоль/л или постпрандиальная глюкоза >7,8 ммоль/л или гликированный гемоглобин >5,7% или уже диагностированный СД 2 типа или проводится лечение СД 2 типа;
— артериальное давление ≥130/85 мм рт.ст. или фармакотерапия уже диагностированной артериальной гипертензии;
— ТГ в плазме ≥1,70 ммоль/л или липидоснижающее лечение;
— холестерин липопротеидов высокой плотности в плазме <1,0 ммоль/л у мужчин и <1,3 ммоль/л у женщин или липидоснижающее лечение.
"Золотым стандартом" диагностики стеатоза печени является ультразвуковое исследование. К ультразвуковым признакам стеатоза печени относят: 1) затухание ультразвукового сигнала по периферии органа; 2) обеднение сосудистого рисунка; 3) повышение эхогенности ткани печени в сравнении с корковым веществом почки. В качестве инструмента "второй линии" в специализированных лечебных учреждениях для количественной оценки стеатоза рекомендуется использование параметра контролируемого затухания (Controlled Attenuation Parameter — CAP) ультразвука, при доступности данного метода.
Магнитно-резонансная томография при диагностике стеатоза имеет чувствительность 92-100% и специфичность 92-97% и позволяет провести "картирование" печени, но является более дорогостоящим методом диагностики [47].
Ни один из методов визуализации не дает возможность дифференцировать НАЖБП от НАСГ.
Применение биопсии печени среди пациентов с НАЖБП в настоящее время ограничено следующими клиническими ситуациями: 1) диагностика НАСГ; 2) уточнение диагноза при наличии смешанной этиологии заболевания в диагностически неясных случаях; 3) клинические исследования (для подтверждения диагноза, оценки активности, выраженности фиброза, динамики на фоне терапии)1.
В настоящее время все более широкое применение для оценки степени фиброза печени находит эластография (чувствительность 78-84%, специфичность 89-94%) [48-50]. Процедура занимает ~15-20 мин, безболезненна и комфортна для пациента (ощущения аналогичны таковым при проведении ультразвукового исследования печени).
Для диагностики МАЖБП у пациентов из групп высокого риска (МС, ожирение, СД 2 типа) целесообразно использовать ступенчатый подход, в максимальной степени используя неинвазивные подходы. Для скрининга МАЖБП и исключения выраженного фиброза печени могут быть использованы различные индексы, которые основаны на рутинных клинико-лабораторных данных [51-54] (табл. 1).
Индексы FIB-4, APRI и NFS позволяют исключить выраженный фиброз [53][54][59][60], мониторировать динамику в процессе лечения [57]. Следующей диагностической ступенью является эластография печени [48][50][61]. Магнитно-резонансная томография является конечной диагностической ступенью [61].
Таблица 1
Системы оценки стеатоза или фиброза у пациентов с НАЖБП (адаптировано из [38])
Компоненты | Стеатоз | Фиброз | |||||
FLI [53] | Тест NLFS [54] | HSI [55] | Шкала BARD [56] | Индекс APRI [57] | Индекс фиброза-4 [57] | Шкала NFS [58] | |
Возраст | X | X | |||||
Пол | X | ||||||
ИМТ | X | X | X | X | X | ||
Дисгликемия (или диагноз СД 2 типа) | X | X | X | X | |||
Количество тромбоцитов | X | X | X | ||||
Альбумин | X | ||||||
АСТ | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
АЛТ | X | X | X | X | X | ||
ГГТ | X | ||||||
ТГ | X | ||||||
ОТ | X | ||||||
МС и инсулин | X | ||||||
Примечание: FLI — индекс стеатоза печени (Fatty liver index); индекс NLFS — NAFLD liver fat score; HSI — индекс стеатоза печени (The Hepatic Steatosis Index); шкала BARD — BMI, AST/ALT Ratio and Diabetes Score (ИМТ, отношение АСТ/АЛТ, СД); индекс APRI — Aspartate Aminotransferase to Platelet Ratio Index, индекс отношения АСТ к тромбоцитам; индекс фиброза-4 — FIB-4, Fibrosis-4 Index; шкала NFS — NAFLD Fibrosis Score.
Сокращения: АЛТ — аланинаминотрансфераза, АСТ — аспартатаминотрансфераза, ИМТ — индекс массы тела, ГГТ — гамма-глутамилтрансфераза, МС — метаболический синдром, НАЖБП — неалкогольная жировая болезнь печени, ОТ — окружность талии, СД — сахарный диабет, ТГ — триглицериды.
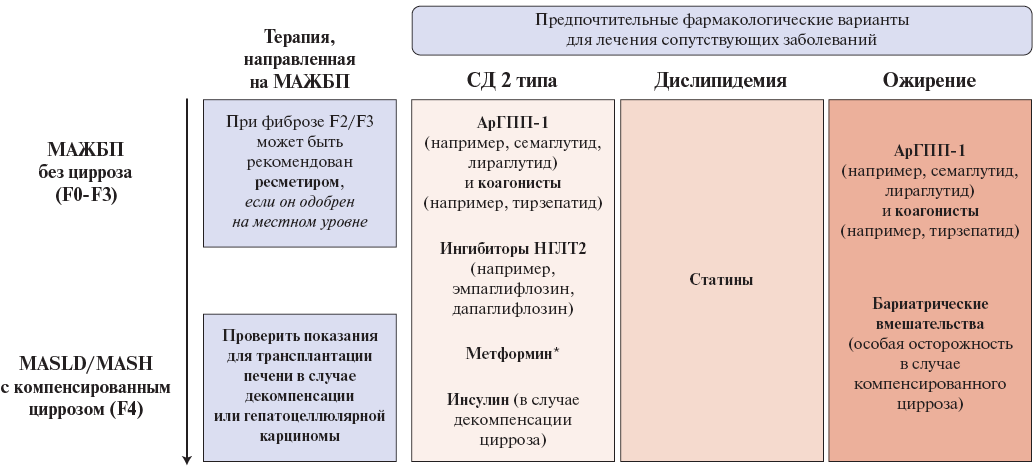
Рис. 1. Фармакологические возможности ведения пациентов с МАЖБП и МС (адаптировано из [52]).
Примечание: рекомендации по лечению, выходящие за рамки модификации образа жизни при МАЖБП. Выбор фармакологических вариантов лечения у пациентов с МАЖБП зависит от сопутствующих заболеваний и стадии болезни; * — при скорости клубочковой фильтрации >30 мл мин/1,73 м2.
Сокращения: арГПП-1 — агонисты рецепторов глюкагоноподобного пептида-1, НГЛТ2 — натрий-глюкозный котранспортер 2 типа, МАЖБП — метаболически ассоциированная жировая болезнь печени, СД — сахарный диабет.
Особенности лечения
Снижение избыточного веса является краеугольным камнем патогенетически обоснованной терапии МАЖБП, положительно влияющей на ее течение и исходы [62]. Снижение массы тела на ≥3% уменьшает выраженность стеатоза, на ≥5% — уменьшает воспаление [63] и замедляет прогрессирование фиброза [64-66], на ≥7% — способствует разрешению НАСТ у 65-90% пациентов [64-66], на ≥10% — уменьшает фиброз, а у 45% вызывает его регресс [63][65]. Поэтому снижение веса на 7-10% необходимо рассматривать как первичную цель при ведении пациентов с МАЖБП [51][52].
Рекомендуется низкокалорийная диета (50-60% калорий обеспечивается потреблением углеводов и 20-25% жиров, причем доля насыщенных жиров должна быть <10% [67][68], снеки и частые перекусы должны быть исключены [68]). Очень низкокалорийная диета (500-800 ккал/день) не рекомендуется [67][68]. Одним из предпочтительных является средиземноморский тип питания, который отличается высоким содержанием полиненасыщенных жирных кислот и полифенолов, что уменьшает ИР и стеатоз печени [52][69][70]. Низкокалорийные диеты с повышенным содержанием белка и клетчатки благоприятно влияют на маркеры фиброза печени [67][69][71-73].
Для лечения пациентов с МАЖБП и МС применяются различные лекарственные средства, которые можно условно разделить на 2 группы1 [52] (рис. 1):
1) препараты с гепатотропным эффектом, в т.ч. с зарегистрированным показанием НАЖБП; некоторые из них обладают полипотентным действием и одновременно влияют на сердечно-сосудистую систему, липидный и углеводный обмен;
2) препараты, зарегистрированные для лечения типичных для МАЖБП коморбидных состояний с дополнительным гепатотропным эффектом.
Препараты с гепатотропным эффектом, включенные в клинические рекомендации НАЖБП Минздрава России, включают в себя урсодезоксихолевую кислоту (УДХК), альфа-токоферола ацетат (витамин Е), адеметионин, бициклол, орнитин и фиксированную комбинацию инозин + меглюмин + метионин + никотинамид + янтарная кислота1. В клинических рекомендациях EASL-EASD-EASO по лечению МАЖБП 2024г включен ресметиром в качестве таргетного препарата для лечения МАЖБП, гепатотропные препараты представлены витамином Е, УДХК, обетихолевой кислотой [52].
Агонист рецепторов тиреоидных гормонов, действующий на печень (ресметиром), является единственным таргетным препаратом для лечения НАЖБП, влияющим как на активность заболевания (разрешение стеатогепатита), так и на выраженность фиброза печени по данным исследования MAESTRO-NASH [74]. В данное исследование включали пациентов с МС (≥3 из 5 метаболических факторов риска), фиброзом печени 1b, 2 или 3 стадии и подтвержденным биопсией метаболическим стеатозом печени, и после публикации его результатов препарат был одобрен в США по процедуре ускоренного одобрения в марте 2024г. В США биопсия печени не требуется согласно инструкции по применению препарата, достаточно использование тестов NILDA для подтверждения выраженности стеатоза и фиброза 1b, 2 или 3 стадии [75]. Прогностические критерии ответа и оптимальная продолжительность терапии в настоящее время неизвестны. Препарат на текущий момент не зарегистрирован в Российской Федерации, кроме того, отсутствуют данные о его долгосрочной эффективности [75]. Исследование MAESTRO-NASH продолжается, и его результаты позволят узнать, приводит ли более длительное лечение к улучшению клинических результатов, включая предотвращение прогрессирования цирроза.
УДХК по сравнению с другими "гепатопротекторами" имеет наибольшую доказательную базу. Отдельные исследования и метаанализы продемонстрировали, что она уменьшает стеатоз, воспаление, фиброз и улучшает функциональные показатели печени [76][77], а также снижает уровень глюкозы, гликированного гемоглобина, инсулина, общего холестерина [78][79]. Назначение УДХК рекомендуется пациентам с НАЖБП с целью уменьшения содержания липидов в гепатоцитах, уменьшения воспаления и профилактики прогрессирования фиброза1.
Витамин Е используется для лечения НАЖБП у пациентов с гистологически подтвержденным прогрессирующим НАСГ и входит в ряд КР ведения пациентов с НАЖБП, которые основаны на результатах рандомизированного исследования PIVENS [80], в котором добавление витамина E (800 МЕ ежедневно в течение 2 лет) у лиц с МС и НАСГ без СД 2 типа привело к улучшению как стеатоза, так и активности заболевания, что подтверждалось снижением активности печеночных ферментов. Витамин Е при добавлении к диете снижает риск развития МАЖБП, как клинически, так и рентгенологически определяемого, особенно у лиц с СД 2 типа [81]. У лиц с МС и НАСГ исследования случай-контроль показали, что длительный прием витамина E связан со снижением риска смерти, трансплантации и печеночной декомпенсации [82]. Тем не менее влияние добавок витамина E на сердечно-сосудистую смертность или рак предстательной железы до сих пор не установлено, и клинические интервенционные исследования не показали никакой пользы [83-85]. В менее масштабных исследованиях показано снижение активности печеночных ферментов, но в настоящее время нет четких данных об улучшении степени выраженности фиброза печени, и не проводилось крупных исследований III фазы.
Обетихоевая кислота в дозе 25 мг в сутки обеспечивала как более высокую вероятность улучшения степени выраженности фиброза, так и более низкую вероятность ухудшения, чем плацебо [86]. Однако, несмотря на снижение активности заболевания (гепатоцеллюлярное баллонирование и дольковое воспаление), существенной разницы в разрешении стеатогепатита не наблюдалось. В настоящее время применение обетихоевой кислоты для лечения НАЖБП ограничено в связи с опасениями по поводу соотношения риска и пользы (включая гепатотоксичность), что привело к прекращению фазы клинических исходов регистрационного исследования.
Препараты, зарегистрированные для лечения типичных для МАЖБП коморбидных состояний с дополнительным гепатотропным эффектом
Применение метформина по данным метаанализа (>90% пациентов не имели СД 2 типа, средний ИМТ составлял 30±2,5 кг/м2, средняя длительность лечения 9 мес.) сопровождалось незначительным уменьшением явлений стеатоза и воспаления в ткани печени, но не влияло на фиброз [87]. У пациентов с СД 2 типа применение метформина в сравнении с плацебо не различалось с точки зрения влияния на выраженность стеатоза и активность трансаминаз [88][89]. При этом необходимо отметить снижение риска (в среднем на 7% за 12-16 лет применения) развития гепатоцеллюлярного рака при длительном приеме метформина [90].
В настоящее время стали широко использоваться агонисты рецепторов глюкагоноподобного пептида-1 (ГПП-1) (лираглутид и семаглутид [91-95], которые благодаря снижению веса улучшают течение МАЖБП (уменьшение стеатоза, активности трансаминаз, образования провоспалительных цитокинов, выраженности ИР, липогенеза, липолиза, оксидативного стресса [95-98]). Часть этих положительных эффектов не связана со снижением массы тела [98-100]. Агонист рецепторов глюкозозависимого инсулинотропного полипептида (ГИП) и ГПП-1 (арГПП-1/ГИП) тирзепатид в исследовании 2 фазы SYNERGY-NASH у пациентов с НАЖБП и умеренным или тяжёлым фиброзом оказался эффективнее плацебо в отношении разрешения НАЖБП без усугубления фиброза [101]. Однако в отсутствие демонстрации гистологического улучшения в крупных исследованиях фазы III агонисты арГПП-1 и арГПП-1/ГИП в настоящее время не могут быть рекомендованы в качестве терапии МАЖБП вне терапии коморбидной патологии.
Ингибиторы натрий-глюкозного котранспортера 2 типа по результатам отдельных исследований (E-LIFT trial [102], EFFECT-II trial [103]) и данным метаанализа благоприятно влияют на активность трансаминаз, выраженность стеатоза и фиброза печени у пациентов с СД 2 типа и МАЖБП [104][105], причем эти эффекты не зависят от динамики веса и гликированного гемоглобина у пациентов [104].
Согласно результатам исследования PIVENS [80] и метаанализа (>85% пациентов без СД 2 типа, средняя длительность лечения 12 мес.) [87], тиазолидиндионы (пиоглитазон) эффективны в уменьшении выраженности стеатоза, воспаления [106] и фиброза печени [106-109], а также активности трансаминаз [87] при МАЖБП. Применение тиазолидиндионов у пациентов с СД 2 типа ассоциировано с уменьшением выраженности стеатоза печени на 6,6% [110] — 54% [106].
Данные о влиянии ингибиторов дипептидилпептидазы 4 на течение МАЖБП противоречивы. Так, применение вилдаглиптина сопровождалось уменьшением активности аланинаминотрансферазы, а также выраженности стеатоза печени у пациентов с СД 2 типа на 27% [111], в то время как применение ситаглиптина не приводило к подобными изменениям [112].
Бариатрическая хирургия может быть показана пациентам с ИМТ ≥35 кг/м2 при наличии коморбидной патологии, включая НАЖБП1. В соответствии с результатами метаанализа, бариатрическое вмешательство способствовало уменьшению выраженности стеатоза и стеатогепатита у 88% пациентов, а также уменьшению выраженности фиброза печени у 30% пациентов1.
Отношения и деятельность: все авторы заявляют об отсутствии потенциального конфликта интересов, требующего раскрытия в данной статье.
1 Клинические рекомендации Неалкогольная жировая болезнь печени. ID:748_2. URL: https://cr.minzdrav.gov.ru/view-cr/748_2.
Список литературы
1. Маев И. В., Андреев Д. Н., Кучерявый Ю. А., Умярова Р. М. Метаболически ассоциированная жировая болезнь печени. М.: Прима Принт, 2021. 72 с.: ил. (Клиническая гепатология).
2. Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. 2020;73(1):202-9. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039.
3. Zhang H-J, Wang Y-Y, Chen C, et al. Cardiovascular and renal burdens of metabolic associated fatty liver disease from serial US national surveys, 1999-2016. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(13):1593-601. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000001.
4. Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Caldwell SH. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: summary of an AASLD Single Topic Conference. Hepatology. 2003;37(5):1202-19. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50193.
5. Loria P, Lonardo A, Carulli N. Should nonalcoholic fatty liver disease be renamed? Dig Dis. 2005;23(1):72-82. doi:10.1159/000084728.
6. Корнеева О. Н., Драпкина О. М., Буеверов А. О., Ивашкин В. Т. Неалкогольная жировая болезнь печени как проявление метаболического синдрома. Клин. персп. гастроэнтерол. гепатол. 2005;4:21-4.
7. Ratziu V, Bellentani S, Cortez-Pinto H, et al. A position statement on NAFLD/NASH based on the EASL 2009 special conference. J Hepatol. 2010;53(2):372-84. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.04.008.
8. Bellentani S, Tiribelli C. Is it time to change NAFLD and NASH nomenclature? Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2(8):547-8. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30146-2.
9. Eslam M, Sanyal AJ, George J. International Consensus Panel. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(7):1999-2014.e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.312.
10. Eslam M, Sarin SK, Wong VW, et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol Int. 2020;14(6):889-19. doi:10.1007/s12072-020-10094-2.
11. Ludwig J, Viggiano TR, McGill DB, Oh BJ. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980;55(7):434-8.
12. Burt AD, Lackner C, Tiniakos DG. Diagnosis and Assessment of NAFLD: Definitions and Histopathological Classification. Semin Liver Dis. 2015;35(3):207-20. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1562942.
13. Mendez-Sanchez N, Bugianesi E, Gish RG, et al. Global multi-stakeholder endorsement of the MAFLD definition. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7(5):388-90. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00062-0.
14. Alharthi J, Gastaldelli A, Cua IH, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a year in review. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2022;38(3):251-60. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000823.
15. Eslam M, Ahmed A, Despres JP, et al. Incorporating fatty liver disease in multidisciplinary care and novel clinical trial designs for patients with metabolic diseases. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6(9):743-53. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00132-1.
16. Liu Q, Zhao G, Li Q, et al. A comparison of NAFLD and MAFLD diagnostic criteria in contemporary urban healthy adults in China: a cross-sectional study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22(1):471. doi:10.1186/s12876-022-02576-4.
17. Grabherr F, Grander C, Effenberger M, et al. MAFLD: what 2 years of the redefinition of fatty liver disease has taught us. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2022;13:20420188221139101. doi:10.1177/20420188221139101.
18. Sarin SK, Eslam M, Fan JG, et al. MAFLD, patient-centred care, and APASL. Hepatol Int. 2022;16(5):1032-34. doi:10.1007/s12072-022-10408-6.
19. Yamamura S, Eslam M, Kawaguchi T, et al. MAFLD identifies patients with significant hepatic fibrosis better than NAFLD. Liver Int. 2020;40(12):3018-30. doi:10.1111/liv.14675.
20. Lim GEH, Tang A, Ng CH, et al. An Observational Data Meta-analysis on the Differences in Prevalence and Risk Factors Between MAFLD vs NAFLD. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021; S1542-3565(21)01276-73. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.11.038.
21. Nguyen VH, Le MH, Cheung RC, Nguyen MH. Differential Clinical Characteristics and Mortality Outcomes in Persons With NAFLD and/or MAFLD. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(10):2172-81.e6. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.029.
22. Kim D, Konyn P, Sandhu KK, et al. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is associated with increased all-cause mortality in the United States. J Hepatol. 2021;75(6):1284-91. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.07.035.
23. Lee H, Lee YH, Kim SU, Kim HC. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Incident Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(10):2138-47.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2020.12.022.
24. Liang Y, Chen H, Liu Y, et al. Association of MAFLD With Diabetes, Chronic Kidney Disease, and Cardiovascular Disease: A 4.6-Year Cohort Study in China. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107(1):88-97. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab641.
25. Yoneda M, Yamamoto T, Honda Y, et al. Risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with fatty liver disease as defined from the metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease point of view: a retrospective nationwide claims database study in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2021;56(11):1022-32. doi:10.1007/s00535-021-01828-6.
26. Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64(1):73-84. doi:10.1002/hep.28431.
27. Jinjuvadia R, Antaki F, Lohia P, Liangpunsakul S. The Association Between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Metabolic Abnormalities in The United States Population. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;51(2):160-6. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000666.
28. Pallayova M, Taheri S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese adults: clinical aspects and current management strategies. Clin Obes. 2014;4(5):243-53. doi:10.1111/cob.12068.
29. Perumpail BJ, Khan MA, Yoo ER, et al. Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(47):8263-76. doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8263.
30. Dai W, Ye L, Liu A, et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(39):e8179. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000008179.
31. Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2019;71(4):793-801. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021.
32. Драпкина О. М., Евстифеева С. Е., Шальнова С. А. и др. Распространенность неалкогольной жировой болезни печени и ее ассоциации с сердечно-сосудистыми факторами риска (данные российских эпидемиологических исследований). Кардиоваскулярная терапия и профилактика. 2025;24(2):4316. doi:10.15829/1728-8800-2025-4316.
33. Kim D, Chung GE, Kwak MS, et al. Body Fat Distribution and Risk of Incident and Regressed Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(1):132-8.e4. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.024.
34. Buzzetti E, Pinzani M, Tsochatzis EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism. 2016;65(8):1038-48. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.012.
35. Bril F, Barb D, Portillo-Sanchez P, et al. Metabolic and histological implications of intrahepatic triglyceride content in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2017;65(4):1132-44. doi:10.1002/hep.28985.
36. Kitade H, Chen G, Ni Y, Ota T. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance: New Insights and Potential New Treatments. Nutrients. 2017;9(4):387. doi:10.3390/nu9040387.
37. Virtue S, Vidal-Puig A. It’s not how fat you are, it’s what you do with it that counts. PLoS Biol. 2008;6(9):e237. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060237.
38. Godoy-Matos AF, Silva Júnior WS, Valerio CM. NAFLD as a continuum: from obesity to metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2020;12:60. doi:10.1186/s13098-020-00570-y.
39. Rotman Y, Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Liver fat accumulation as a barometer of insulin responsiveness again points to adipose tissue as the culprit. Hepatology. 2017;65(4):1088-90. doi:10.1002/hep.29094.
40. Sheka AC, Adeyi O, Thompson J, et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Review. JAMA. 2020;323(12):1175-83. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2298. Erratum in: JAMA. 2020;323(16): 1619. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.5249.
41. Mahfood Haddad T, Hamdeh S, Kanmanthareddy A, Alla VM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the risk of clinical cardiovascular events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2017;11(S1):S209-16. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2016.12.033.
42. Kapuria D, Takyar VK, Etzion O, et al. Association of Hepatic Steatosis With Subclinical Atherosclerosis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hepatol Commun. 2018;2(8):873-83. doi:10.1002/hep4.1199.
43. Jaruvongvanich V, Sanguankeo A, Upala S. Significant Association Between Gallstone Disease and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2016;61(8):2389-96. doi:10.1007/s10620-016-4125-2.
44. Stine JG, Wentworth BJ, Zimmet A, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis without cirrhosis compared to other liver diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;48(7):696-703. doi:10.1111/apt.14937.
45. Orci LA, Sanduzzi-Zamparelli M, Caballol B, et al. Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Meta-regression. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20(2):283-92.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.002.
46. Liu SS, Ma XF, Zhao J, et al. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and extrahepatic cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2020;19(1):118. doi:10.1186/s12944-020-01288-6.
47. Siddiqui MS, Harrison SA, Abdelmalek MF, et al.; Liver Forum Case Definitions Working Group. Case definitions for inclusion and analysis of endpoints in clinical trials for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through the lens of regulatory science. Hepatology. 2018;67(5):2001-12. doi:10.1002/hep.29607.
48. Shi KQ, Tang JZ, Zhu XL, et al. Controlled attenuation parameter for the detection of steatosis severity in chronic liver disease: a meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29(6):1149-58. doi:10.1111/jgh.12519.
49. Park CC, Nguyen P, Hernandez C, et al. Magnetic Resonance Elastography vs Transient Elastography in Detection of Fibrosis and Noninvasive Measurement of Steatosis in Patients With Biopsy-Proven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(3):598-607. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.10.026.
50. Petta S, Wong VW, Cammà C, et al. Serial combination of non-invasive tools improves the diagnostic accuracy of severe liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46(6):617-27. doi:10.1111/apt.14219.
51. Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328-57. doi:10.1002/hep.29367.
52. European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines, on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J Hepatol. 2024;81(3):492-542. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2024.04.031.
53. Bedogni G, Bellentani S, Miglioli L, et al. The Fatty Liver Index: a simple and accurate predictor of hepatic steatosis in the general population. BMC Gastroenterol. 2006;6:33. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-6-33.
54. Kotronen A, Peltonen M, Hakkarainen A, et al. Prediction of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fat using metabolic and genetic factors. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(3):865-72. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2009.06.005.
55. Lee JH, Kim D, Kim HJ, et al. Hepatic steatosis index: a simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2010;42(7):503-8. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2009.08.002.
56. Harrison SA, Oliver D, Arnold HL, et al. Development and validation of a simple NALFD clinical scoring system for identifying patient without advanced disease. Gut. 2008;57:1441-7. doi:10.1136/gut.2007.146019.
57. Wai CT, Greenson JK, Fontana RJ, et al. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003;38:518-26.
58. Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007;45(4):846-54. doi:10.1002/hep.21496.
59. Xiao G, Zhu S, Xiao X, et al. Comparison of laboratory tests, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance elastography to detect fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2017;66(5):1486-501. doi:10.1002/hep.29302.
60. Siddiqui MS, Yamada G, Vuppalanchi R, et al.; NASH Clinical Research Network. Diagnostic Accuracy of Noninvasive Fibrosis Models to Detect Change in Fibrosis Stage. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(9):1877-85. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2018.12.031.
61. Altamirano J, Qi Q, Choudhry S, et al. Non-invasive diagnosis: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic liver disease. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5:31. doi:10.21037/tgh.2019.11.14.
62. Polyzos SA, Kountouras J, Mantzoros CS. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Metabolism. 2019;92:82-97. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2018.11.014.
63. Hannah WN Jr, Harrison SA. Effect of Weight Loss, Diet, Exercise, and Bariatric Surgery on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2016;20(2):339-50. doi:10.1016/j.cld.2015.10.008.
64. Patel NS, Doycheva I, Peterson MR, et al. Effect of weight loss on magnetic resonance imaging estimation of liver fat and volume in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13(3):561-8. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2014.08.039.
65. Musso G, Cassader M, Rosina F, Gambino R. Impact of current treatments on liver disease, glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Diabetologia. 2012;55(4):885-904. doi:10.1007/s00125-011-2446-4.
66. Vilar-Gomez E, Martinez-Perez Y, Calzadilla-Bertot L, et al. Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(2):367-78.e5; quiz e14-5. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.005.
67. Brunner KT, Henneberg CJ, Wilechansky RM, Long MT. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Obesity Treatment. Curr Obes Rep. 2019;8(3):220-8. doi:10.1007/s13679-019-00345-1.
68. Ratziu V, Ghabril M, Romero-Gomez M, Svegliati-Baroni G. Recommendations for Management and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Transplantation. 2019;103(1): 28-38. doi:10.1097/TP.0000000000002483.
69. Misciagna G, Del Pilar Díaz M, Caramia DV, et al. Effect of a Low Glycemic Index Mediterranean Diet on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. A Randomized Controlled Clinici Trial. J Nutr Health Aging. 2017;21(4):404-12. doi:10.1007/s12603-016-0809-8.
70. Aller R, Izaola O, de la Fuente B, De Luis Román DA. Mediterranean diet is associated with liver histology in patients with non alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr Hosp. 2015;32(6):2518-24. doi:10.3305/nh.2015.32.6.10074.
71. Markova M, Pivovarova O, Hornemann S, et al. Isocaloric Diets High in Animal or Plant Protein Reduce Liver Fat and Inflammation in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(3):571-85. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.10.007.
72. Arslanow A, Teutsch M, Walle H, et al. Short-Term Hypocaloric High-Fiber and High-Protein Diet Improves Hepatic Steatosis Assessed by Controlled Attenuation Parameter. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2016;7(6):e176. doi:10.1038/ctg.2016.28.
73. Larsen TM, Dalskov SM, van Baak M, et al.; Diet, Obesity, and Genes (Diogenes) Project. Diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index for weight-loss maintenance. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(22):2102-13. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1007137.
74. Harrison SA, Taub R, Neff GW, et al. Resmetirom for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Nat Med. 2023;29(11):2919-28. doi:10.1038/s41591-023-02603-1.
75. Chen VL, Morgan TR, Rotman Y, et al. Resmetirom therapy for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: October 2024 updates to AASLD Practice Guidance. Hepatology. 2025;81(1):312-20. doi:10.1097/HEP.0000000000001112.
76. Xiang Z, Chen YP, Ma KF, et al. The role of ursodeoxycholic acid in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a systematic review. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013;13:140. doi:10.1186/1471-230X-13-140.
77. Ratziu V, de Ledinghen V, Oberti F, et al. A randomized controlled trial of high-dose ursodesoxycholic acid for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2011;54(5):1011-9. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.08.030.
78. Sánchez-García A, Sahebkar A, Simental-Mendía M, Simental-Mendía LE. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on glycemic markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Pharmacol Res. 2018;135:144-9. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.008.
79. Simental-Mendía LE, Simental-Mendía M, Sánchez-García A, et al. Impact of ursodeoxycholic acid on circulating lipid concentrations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Lipids Health Dis. 2019;18(1):88. doi:10.1186/s12944-019-1041-4.
80. Sanyal AJ, Chalasani N, Kowdley KV, et al.; NASH CRN. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(18):1675-85. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0907929.
81. Scorletti E, Creasy KT, Vujkovic M, et al. Dietary Vitamin E Intake Is Associated With a Reduced Risk of Developing Digestive Diseases and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117(6):927-30. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000001726.
82. Vilar-Gomez E, Vuppalanchi R, Gawrieh S, et al. Vitamin E Improves Transplant-Free Survival and Hepatic Decompensation Among Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Advanced Fibrosis. Hepatology. 2020;71(2):495-509. doi:10.1002/hep.30368.
83. Fortmann SP, Burda BU, Senger CA, et al. Vitamin and mineral supplements in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer: An updated systematic evidence review for the U. S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(12):824-34. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-159-12-201312170-00729.
84. Myung SK, Ju W, Cho B, et al.; Korean Meta-Analysis Study Group. Efficacy of vitamin and antioxidant supplements in prevention of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2013;346:f10. doi:10.1136/bmj.f10.
85. Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Gluud C. Meta-regression analyses, meta-analyses, and trial sequential analyses of the effects of supplementation with beta-carotene, vitamin A, and vitamin E singly or in different combinations on all-cause mortality: do we have evidence for lack of harm? PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74558. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074558.
86. Younossi ZM, Ratziu V, Loomba R, et al.; REGENERATE Study Investigators. Obeticholic acid for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: interim analysis from a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;394(10215):2184-96. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)33041-7.
87. Mantovani A, Byrne CD, Scorletti E, et al. Efficacy and safety of anti-hyperglycaemic drugs in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with or without diabetes: An updated systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Metab. 2020;46(6):427-41. doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2019.12.007.
88. Haukeland JW, Konopski Z, Eggesbø HB, et al. Metformin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, controlled trial. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2009;44(7):853-60. doi:10.1080/00365520902845268.
89. Blazina I, Selph S. Diabetes drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review. Syst Rev. 2019;8(1):295. doi:10.1186/s13643-019-1200-8.
90. Chen HP, Shieh JJ, Chang CC, et al. Metformin decreases hepatocellular carcinoma risk in a dose-dependent manner: population-based and in vitro studies. Gut. 2013;62(4):606-15. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301708.
91. Khoo J, Hsiang J, Taneja R, et al. Comparative effects of liraglutide 3 mg vs structured lifestyle modification on body weight, liver fat and liver function in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19(12):1814-7. doi:10.1111/dom.13007.
92. Bandyopadhyay S, Das S, Samajdar SS, Joshi SR. Role of semaglutide in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2023;17(10):102849. doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2023.102849.
93. Song T, Jia Y, Li Z, et al. Effects of Liraglutide on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2021;12(6):1735-49. doi:10.1007/s13300-021-01072-4.
94. Kalogirou MS, Patoulias D, Haidich AB, et al. Liraglutide in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2021;45(3):101568. doi:10.1016/j.clinre.2020.10.012.
95. Mantovani A, Petracca G, Beatrice G, et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Metabolites. 2021;11(2):73. doi:10.3390/metabo11020073.
96. Gupta NA, Mells J, Dunham RM, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is present on human hepatocytes and has a direct role in decreasing hepatic steatosis in vitro by modulating elements of the insulin signaling pathway. Hepatology. 2010;51(5):1584-92. doi:10.1002/hep.23569.
97. Armstrong MJ, Hull D, Guo K, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 decreases lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2016;64(2):399-408. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.038.
98. Liu Y, Wei R, Hong TP. Potential roles of glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(27):9090-7. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9090.
99. Wang Y, Parlevliet ET, Geerling JJ, et al. Exendin-4 decreases liver inflammation and atherosclerosis development simultaneously by reducing macrophage infiltration. Br J Pharmacol. 2014;171(3):723-34. doi:10.1111/bph.12490.
100. Xu F, Li Z, Zheng X, et al. SIRT1 mediates the effect of GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide on ameliorating hepatic steatosis. Diabetes. 2014;63(11):3637-46. doi:10.2337/db14-0263.
101. Loomba R, Hartman ML, Lawitz EJ, et al.; SYNERGY-NASH Investigators. Tirzepatide for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis with Liver Fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2024;391(4):299-310. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2401943.
102. Kuchay MS, Krishan S, Mishra SK, et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Liver Fat in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial (E-LIFT Trial). Diabetes Care. 2018;41(8):1801-8. doi:10.2337/dc18-0165.
103. Eriksson JW, Lundkvist P, Jansson PA, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin and n-3 carboxylic acids on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in people with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia. 2018;61(9):1923-34. doi:10.1007/s00125-018-4675-2.
104. Sattar N, Fitchett D, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin is associated with improvements in liver enzymes potentially consistent with reductions in liver fat: results from randomised trials including the EMPA-REG OUTCOME® trial. Diabetologia. 2018;61(10):2155-63. doi:10.1007/s00125-018-4702-3.
105. Xu R, Lian D, Xie Y, et al. SGLT-2 Inhibitors for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023;28(7):134. doi:10.31083/j.fbl2807134.
106. Belfort R, Harrison SA, Brown K, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(22):2297-307. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa060326.
107. Aithal GP, Thomas JA, Kaye PV, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2008;135(4):1176-84. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.06.047.
108. Musso G, Cassader M, Paschetta E, Gambino R. Thiazolidinediones and Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(5):633-40. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.9607.
109. Cusi K, Orsak B, Bril F, et al. Long-Term Pioglitazone Treatment for Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Trial. Ann Intern Med. 2016;165(5):305-15. doi:10.7326/M15-1774.
110. Tang W, Xu Q, Hong T, et al. Comparative efficacy of anti-diabetic agents on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and non-randomized studies. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32(2):200-16. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2713.
111. Macauley M, Hollingsworth KG, Smith FE, et al. Effect of vildagliptin on hepatic steatosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(4):1578-85. doi:10.1210/jc.2014-3794.
112. Deng XL, Ma R, Zhu HX, Zhu J. Short article: A randomized-controlled study of sitagliptin for treating diabetes mellitus complicated by nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;29(3):297-301. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000000780.
Об авторах
О. М. ДрапкинаРоссия
Д.м.н., профессор, академик РАН, директор, главный внештатный специалист по терапии и общей врачебной практике Минздрава России.
Москва
Конфликт интересов:
Нет
С. В. Недогода
Россия
Д.м.н., профессор, зав. кафедрой внутренних болезней Института непрерывного медицинского и фармацевтического образования.
Волгоград
Конфликт интересов:
Нет
Дополнительные файлы
Рецензия
Для цитирования:
Драпкина О.М., Недогода С.В. Метаболически ассоциированная жировая болезнь печени при метаболическом синдроме. Российский кардиологический журнал. 2025;30(1S):6541. https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6541
For citation:
Drapkina O.M., Nedogoda S.V. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease in metabolic syndrome. Russian Journal of Cardiology. 2025;30(1S):6541. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.15829/1560-4071-2025-6541
JATS XML

















































